Both armodafinil and modafinil are prescription medications approved by the FDA. These drugs are classified as eugeroics or wakefulness-promoting agents. They are commonly prescribed for conditions that cause excessive daytime sleepiness. These include narcolepsy, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), and shift work sleep disorder (SWSD). Modafinil is sold under the brand name Provigil. Armodafinil is available as Nuvigil. Generic versions of both drugs are also widely available. These medications work on the brain to promote alertness and reduce fatigue.
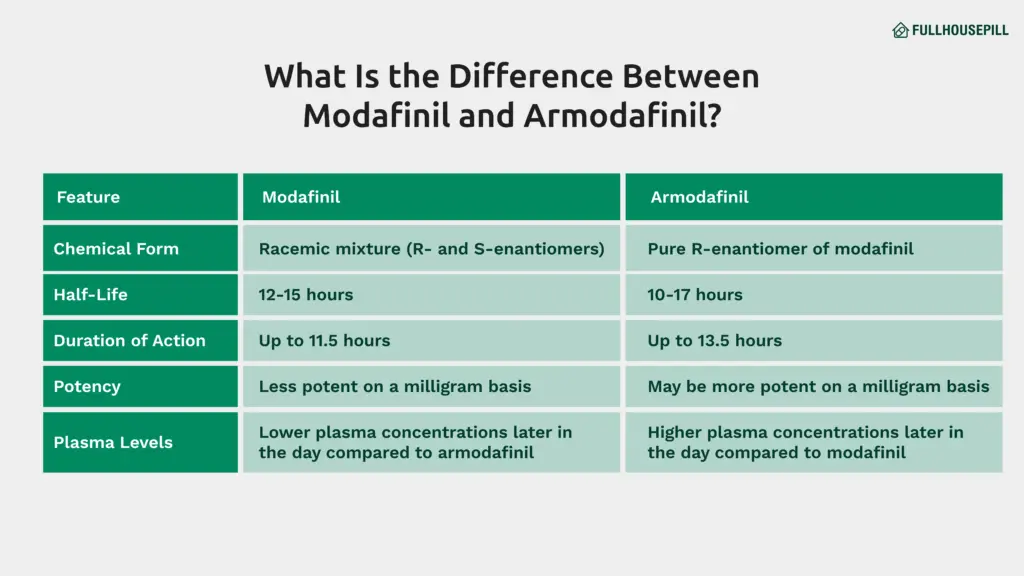
Armodafinil is the R-enantiomer of modafinil. Modafinil contains both R- and S-enantiomers. This racemic structure makes modafinil chemically different from armodafinil. Armodafinil contains only the R-enantiomer, which is considered the more active form. This chemical difference affects how long each drug works in the body. Armodafinil usually lasts longer and maintains higher blood levels later in the day. These prolonged effects may improve wakefulness for a longer duration. Studies have shown that armodafinil reaches higher plasma concentrations than modafinil over time.
| Feature | Modafinil | Armodafinil |
| Chemical Form | Racemic mixture (R- and S-enantiomers) | Pure R-enantiomer of modafinil |
| Half-Life | 12-15 hours | 10-17 hours |
| Duration of Action | Up to 11.5 hours | Up to 13.5 hours |
| Potency | Less potent on a milligram basis | May be more potent on a milligram basis |
| Plasma Levels | Lower plasma concentrations later in the day compared to armodafinil | Higher plasma concentrations later in the day compared to modafinil |
What Is the Difference Between Modafinil and Armodafinil?
Modafinil and armodafinil differ primarily in chemical composition. Modafinil is a racemic compound, while armodafinil is a purified version containing only one active isomer. This results in different pharmacokinetics between the two drugs.
Armodafinil typically stays longer in the bloodstream. Modafinil, due to its racemic nature, shows a shorter duration of plasma activity. Both medications produce wakefulness, but armodafinil may offer longer-lasting results.
Pharmacokinetic studies confirm these distinctions. On a milligram-to-milligram basis, armodafinil delivers more stable plasma levels later in the day. These differences affect how long patients feel alert after taking the medication.
What Are the Uses of Armodafinil and Modafinil?
Doctors prescribe both armodafinil and modafinil to treat excessive daytime sleepiness. These drugs improve alertness in various medical conditions.
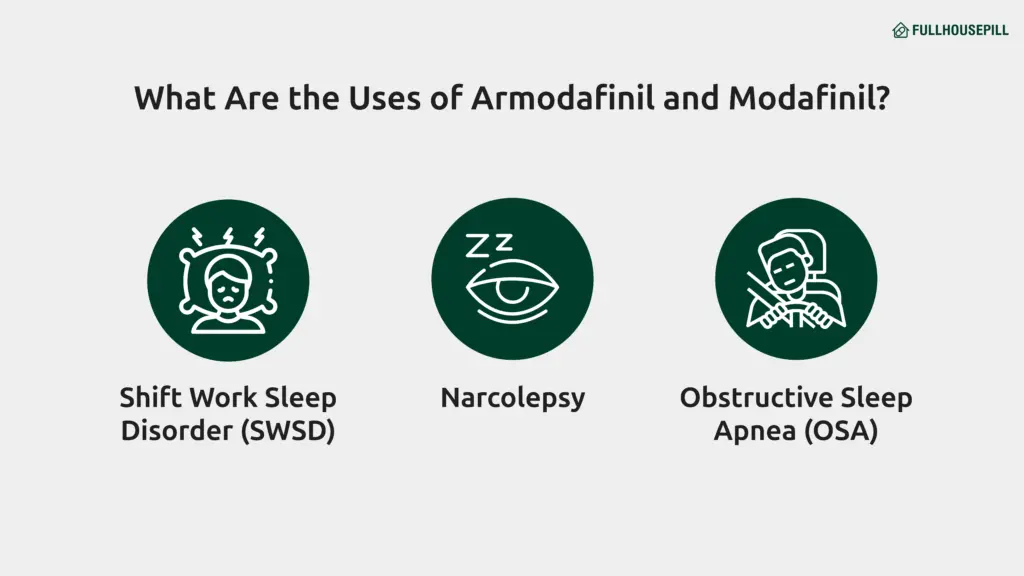
- Narcolepsy causes overwhelming drowsiness. Both medications help improve sustained wakefulness in narcoleptic patients. Armodafinil has shown consistent improvement in daytime alertness during clinical trials.
- Shift Work Sleep Disorder (SWSD) disrupts sleep-wake cycles in people who work night shifts. A 12-week clinical trial conducted by Tembe et al. (2011) showed that both modafinil and armodafinil significantly improved alertness in Indian patients with SWSD.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) leads to fragmented sleep and daytime fatigue. Even when the underlying condition is treated, many patients remain sleepy during the day. Both drugs help manage residual sleepiness. Armodafinil has been shown to increase mean sleep latency in these patients.
Doctors sometimes explore off-label uses for armodafinil and modafinil.
- ADHD in adults may benefit from armodafinil. A review by Lamas-Aguilar et al. (2024) explored armodafinil’s potential in ADHD treatment, though more evidence is needed.
- Bipolar depression has been a target for adjunctive armodafinil therapy. However, a meta-review by Bartoli et al. (2021) reported limited evidence for armodafinil or modafinil in treating bipolar symptoms.
- Cognitive deficits in schizophrenia have also been evaluated. Kane et al. (2010) conducted a placebo-controlled trial on armodafinil, showing modest improvement in wakefulness and cognition.
- Fatigue in multiple sclerosis has been addressed using modafinil in some small-scale studies.
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI) has been studied in relation to armodafinil. A trial by Menn et al. (2014) found that armodafinil improved alertness in patients with mild to moderate TBI.
What Is the Mechanism of Action of Armodafinil and Modafinil?
Armodafinil and modafinil influence brain regions that control wakefulness and alertness. These drugs promote alertness by increasing extracellular dopamine. Dopamine levels rise when these medications block dopamine transporters. This mechanism enhances wakefulness without causing the intense stimulation linked to traditional stimulants. Neither drug functions like amphetamines or methylphenidate. Both target specific pathways in the central nervous system involved in sleep-wake regulation.
Armodafinil acts as a unique dopamine uptake inhibitor. Studies like Loland et al. (2012) describe this mechanism in detail. Modafinil follows a similar path but may differ slightly in its onset of action and duration of effect. Both medications belong to a class called eugeroics, which are wakefulness-promoting agents. These agents help reduce excessive daytime sleepiness without causing jitteriness or dependence when used properly.
Both armodafinil and modafinil undergo hepatic metabolism. The liver processes these medications through cytochrome P450 enzymes, especially CYP3A4. These pathways determine how long the drugs stay active and how they interact with other substances. Armodafinil has a reported half-life ranging from 10 to 17 hours. Most medications require around five half-lives to be fully eliminated from the body. Armodafinil may remain in the system for approximately 40 to 85 hours.
Modafinil, with a slightly shorter half-life, clears the system a bit faster. Drug elimination rates depend on factors like age, liver health, metabolic speed, and concurrent drug use. These pharmacokinetic differences help explain why armodafinil may feel longer-lasting for some users. The sustained dopamine activity throughout the day helps maintain consistent wakefulness with fewer midday crashes.
| Property | Modafinil | Armodafinil |
| Half-Life | 12–15 hours | 10–17 hours |
| Time to Peak Concentration | 2–4 hours | 1.5–6.5 hours (range 0.5–11 h) |
| Elimination | Urine (80%), Feces (1%) | Presumed similar to modafinil |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP enzymes) | Liver (CYP3A4 and others) |
Is Armodafinil Stronger Than Modafinil?
Armodafinil is considered more potent on a milligram-to-milligram basis. Lower doses of armodafinil often produce effects similar to higher doses of modafinil. A study by Tembe et al. (2011) compared armodafinil 150 mg with modafinil 200 mg. Both showed similar effects in SWSD patients. Pharmacokinetic profiles show that armodafinil maintains higher blood levels later in the day. This suggests longer-lasting wakefulness.
Is Armodafinil Or Modafinil Safer?
Both drugs share similar safety profiles. These medications are generally well-tolerated when taken as prescribed. Both armodafinil and modafinil are considered well-tolerated when used at recommended doses. These medications are not traditional stimulants but still influence brain chemistry, which can lead to side effects. Most reported side effects are mild to moderate and tend to resolve as the body adjusts to the medication. Common side effects reported by users of both drugs include:
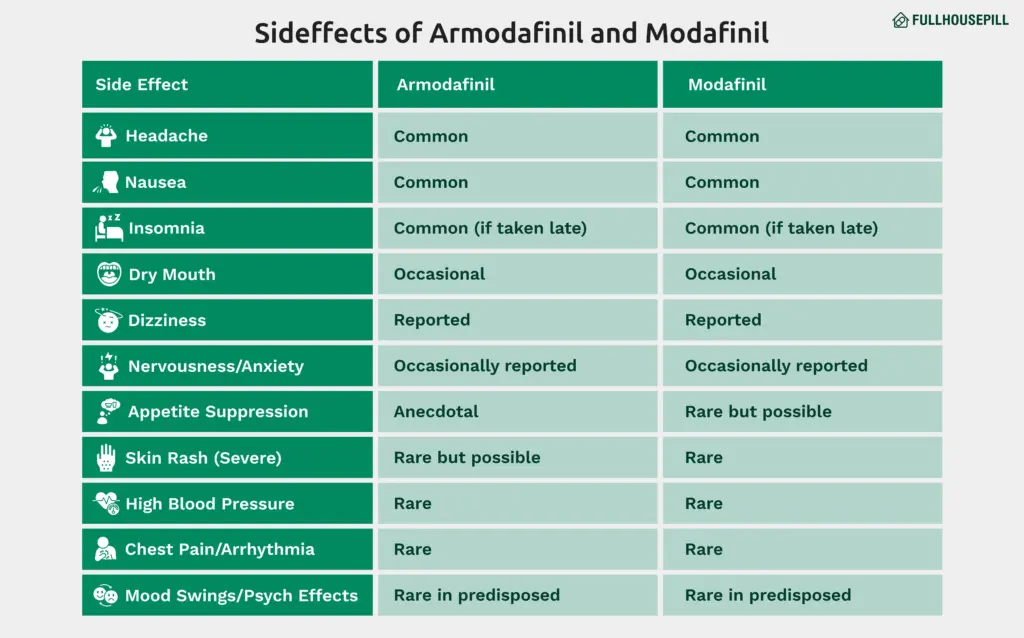
- Headache
- Nausea
- Insomnia
- Dry mouth
- Anxiety or nervousness
- Dizziness
Headaches remain the most frequently reported side effect. These typically occur within the first few days of use. Nausea and digestive discomfort may also be experienced, especially if the medication is taken on an empty stomach. Insomnia may occur if taken too late in the day, due to the extended half-life and stimulating effects. Mood changes, including irritability or mild anxiety, have been noted in some users. These effects are usually dose-dependent and may lessen over time or with a reduced dose. Appetite suppression has been anecdotally reported but is not a consistently documented effect in clinical trials. Serious side effects are rare but can occur. These may include:
- Severe rash or allergic reaction (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome)
- Chest pain or irregular heartbeat
- High blood pressure
- Mental health disturbances, such as mania, aggression, or hallucinations
Psychiatric side effects are more likely in individuals with a history of mood disorders. Skin rashes, while uncommon, should be treated seriously, and the medication should be stopped immediately if one occurs.
Armodafinil and modafinil have similar safety profiles. Multiple studies comparing both drugs found no statistically significant difference in side effect incidence between the two. However, individual reactions may vary based on personal sensitivity, underlying health conditions, or concurrent medication use. Weight loss is not a primary side effect. However, some users have reported reduced appetite, especially during long-term use. These effects should be monitored if significant appetite changes occur.
Clinical studies report no major differences in side effect frequency or severity. Individual responses can vary. Some people may tolerate one drug better than the other. Neither drug commonly causes weight loss, although appetite changes are possible. Patients should consult a healthcare provider for monitoring and adjustments. Patients should not self-diagnose or self-medicate. All side effects, whether mild or severe, should be reported to a healthcare professional. Adjustments in dosage or a switch between armodafinil and modafinil may help reduce unwanted symptoms.
| Side Effect | Armodafinil | Modafinil |
| Headache | Common | Common |
| Nausea | Common | Common |
| Insomnia | Common (if taken late) | Common (if taken late) |
| Dry Mouth | Occasional | Occasional |
| Dizziness | Reported | Reported |
| Nervousness/Anxiety | Occasionally reported | Occasionally reported |
| Appetite Suppression | Anecdotal | Anecdotal |
| Skin Rash (Severe) | Rare but possible | Rare but possible |
| High Blood Pressure | Rare | Rare |
| Chest Pain/Arrhythmia | Rare | Rare |
| Mood Swings/Psych Effects | Rare in predisposed | Rare in predisposed |
What Is the Recommended Dosage of Armodafinil vs. Modafinil?
Both armodafinil and modafinil have specific dosage guidelines based on the condition being treated. These wakefulness-promoting agents are typically taken once daily. Dosage timing and strength depend on the diagnosis and the patient’s response to treatment.
Armodafinil (Nuvigil) is generally prescribed at 150 mg to 250 mg per day. Most patients start with 150 mg once daily in the morning for narcolepsy or obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). This dose helps maintain wakefulness throughout the day without affecting nighttime sleep. For those with shift work sleep disorder (SWSD), the recommended dose is 150 mg taken approximately one hour before the start of the work shift. This schedule supports alertness during night shifts and helps reduce sleep-related performance issues.
Modafinil (Provigil) is usually prescribed at a standard dose of 200 mg once daily. For narcolepsy and OSA, patients take 200 mg in the morning to improve daytime wakefulness. Those with SWSD are advised to take 200 mg about one hour before the work shift begins. Some practitioners may adjust the dose based on tolerability or treatment response, but exceeding 400 mg per day is not typically recommended.
Both medications are available in tablet form and are not intended to replace sleep. They are meant to reduce excessive daytime sleepiness and improve wakefulness during active hours. Patients should follow their prescribed dose strictly. Dosage adjustments should only be made under medical supervision. Self-adjusting the dose may lead to increased side effects or reduced efficacy.
(Image copy)
For Armodafinil (Nuvigil):
- Narcolepsy or OSA: 150 mg to 250 mg once daily in the morning.
- SWSD: 150 mg about one hour before the work shift.
For Modafinil (Provigil):
- Narcolepsy or OSA: 200 mg once daily in the morning.
- SWSD: 200 mg about one hour before the work shift.
What Are the Drug Interactions of Armodafinil vs. Modafinil?
Both armodafinil and modafinil are metabolised by the liver. These medications interact with a wide range of drugs through the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme system. This interaction can alter how other drugs behave in the body and may change their effectiveness or toxicity.
Modafinil inhibits the CYP2C19 enzyme and induces the CYP3A4 enzyme. These actions can either increase or decrease the blood levels of co-administered medications. For example, warfarin, hormonal contraceptives, and certain antidepressants like SSRIs may show altered activity or plasma levels. A reduced effect of birth control pills is a known risk, and additional contraceptive measures are recommended during and after modafinil use.
Armodafinil, as the R-enantiomer of modafinil, shares a similar metabolic profile. It also affects CYP3A4 and CYP2C19. The interaction risks are nearly identical, and careful monitoring is advised when combining it with medications like antiepileptics, antifungals, benzodiazepines, or immunosuppressants.
Both medications should not be combined with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Cases of hypertensive crisis have been documented with the concurrent use of armodafinil and tranylcypromine (Kinslow et al., 2018). This reaction may result in dangerously high blood pressure and requires emergency medical attention.
CNS stimulants, blood thinners, and psychiatric medications may also be affected by either drug. Patients taking warfarin may require more frequent INR checks. Those on SSRIs or tricyclic antidepressants should be watched for enhanced effects or increased side effects.
Patients should always inform their healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and herbal products they are using. This step is essential to prevent unpredictable interactions and ensure safe and effective treatment.
| Feature | Modafinil | Armodafinil |
| Metabolism Pathway | Liver (via CYP enzymes) | Liver (via CYP enzymes) |
| CYP Enzyme Involvement | Inhibits CYP2C19, induces CYP3A4 | Inhibits CYP2C19, induces CYP3A4 |
| Hormonal Contraceptive Impact | Reduces effectiveness | Reduces effectiveness |
| SSRI Interaction (e.g. escitalopram) | Increases plasma levels | Increases plasma levels |
| Warfarin Interaction | Alters INR levels | Alters INR levels |
| MAOI Interaction | Risk of hypertensive crisis | Risk of hypertensive crisis |
| Antifungal Interaction | Reduces levels of ketoconazole, etc. | Reduces levels of ketoconazole, etc. |
| CNS Stimulant Interaction | Enhances stimulant effects | Enhances stimulant effects |
| Overall Drug Interaction Risk | Moderate to high | Moderate to high |
How Does the Cost of Armodafinil Compare to Modafinil?
Generic versions of armodafinil and modafinil are widely available and significantly more affordable than their brand-name counterparts. Modafinil generics entered the market after 2012, opening the door for cheaper alternatives to Provigil. Armodafinil followed shortly after, with Mylan and other pharmaceutical companies launching generic versions of Nuvigil. These generics offer identical active ingredients and clinical effects at a fraction of the cost.
Prices for both medications can vary depending on the pharmacy, country, and whether a customer uses insurance. Many people without insurance or with limited coverage prefer to buy these medications online. Online platforms like FullhousePill offer competitive pricing, flexible quantities, and discreet delivery, making them a go-to source for many buyers.
Modafinil generics such as Modvigil and Modalert are available in different strengths and price ranges. Armodafinil generics, such as Waklert, also come with bulk purchase discounts. Though per-pill prices may seem high for small packs, ordering larger quantities typically brings down the cost per dose.
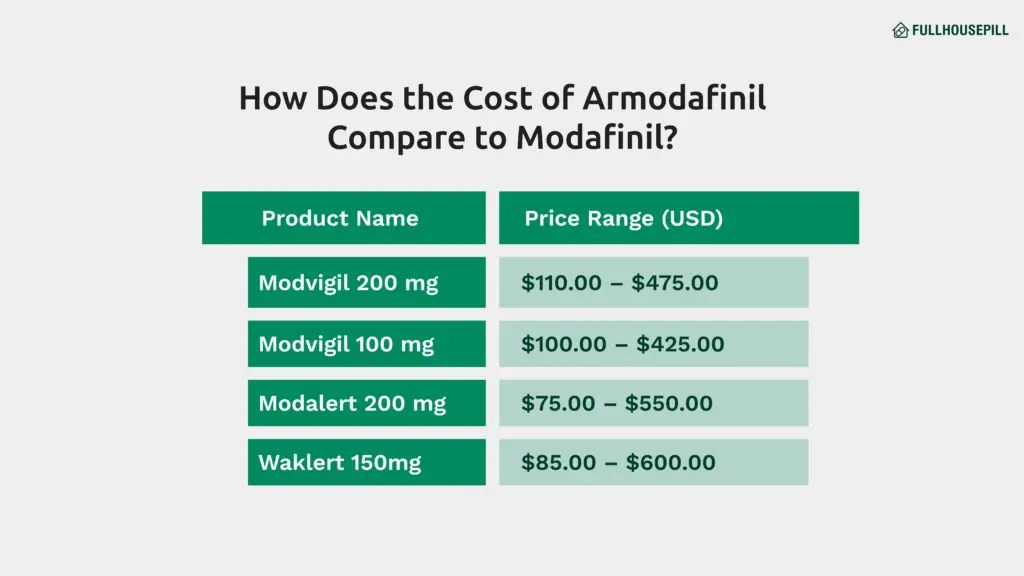
Below is a table showing the price range of popular modafinil and armodafinil products currently offered at FullhousePill:
| Product Name | Strength | Price Range (USD) |
| Modvigil | 200 mg | $110.00 – $475.00 |
| Modvigil | 100 mg | $100.00 – $425.00 |
| Modalert | 200 mg | $75.00 – $550.00 |
| Waklert | 150 mg | $85.00 – $600.00 |
What Are the Generic Versions of Modafinil and Armodafinil?
Generic modafinil is produced by several pharmaceutical manufacturers. Popular brands Generic modafinil and armodafinil are widely available and clinically equivalent to their brand-name counterparts, Provigil and Nuvigil. These generics are manufactured by trusted pharmaceutical companies and offer a cost-effective alternative without compromising efficacy. For modafinil, popular generics include Modalert by Sun Pharma and Modvigil by HAB Pharma. For armodafinil, Waklert by Sun Pharma is the most well-known and widely used generic on the market. These generics are FDA-approved in many countries and are frequently used by patients with sleep disorders as well as by off-label users seeking improved cognitive performance. Below are short breakdowns of the most trusted options:
- Waklert
Waklert is a generic form of armodafinil that helps treat excessive sleepiness linked to narcolepsy, obstructive sleep apnea, and shift work disorder. Known for its long-lasting effects and clean finish, Waklert often delivers more sustained alertness and fewer crashes than modafinil. It’s commonly used for sharper focus and cognitive endurance. - Modalert
Modalert is a widely used generic modafinil tablet made by Sun Pharma. It enhances mental energy, concentration, and mood—especially in those dealing with excessive daytime sleepiness. Its effects typically last up to 12 hours, making it ideal for long study sessions or demanding work shifts. It’s the go-to choice for many experienced users. - Modvigil
Modvigil is another modafinil generic, manufactured by HAB Pharma. It offers similar wakefulness-promoting effects as Modalert but with slightly milder stimulation. Because of its gentler impact, Modvigil is often recommended for first-time users or those who are sensitive to stimulants. It provides mental clarity and focus at a budget-friendly price.
Can You Take Modafinil And Armodafinil Together?
Taking both modafinil and armodafinil at the same time is not recommended. Armodafinil is already the active R-enantiomer found in modafinil. Combining both drugs could increase side effects without providing additional benefits. Doctors typically choose one based on patient response, condition, and tolerance.
mlnk9c
Here, you can access a great variety of casino slots from leading developers.
Users can enjoy traditional machines as well as feature-packed games with high-quality visuals and interactive gameplay.
Even if you’re new or a casino enthusiast, there’s something for everyone.
play casino
Each title are instantly accessible anytime and optimized for laptops and tablets alike.
All games run in your browser, so you can jump into the action right away.
Platform layout is easy to use, making it simple to browse the collection.
Sign up today, and discover the excitement of spinning reels!
Онлайн-площадка — интернет-представительство профессионального сыскного бюро.
Мы организуем помощь в сфере сыскной деятельности.
Коллектив опытных специалистов работает с повышенной осторожностью.
Мы занимаемся сбор информации и выявление рисков.
Заказать детектива
Любая задача получает персональный подход.
Мы используем эффективные инструменты и ориентируемся на правовые стандарты.
Если вы ищете ответственное агентство — добро пожаловать.
Онлайн-площадка — официальная страница частного сыскного бюро.
Мы оказываем услуги в области розыска.
Команда профессионалов работает с максимальной этичностью.
Мы занимаемся сбор информации и разные виды расследований.
Услуги детектива
Каждое дело подходит с особым вниманием.
Задействуем новейшие технологии и действуем в правовом поле.
Если вы ищете настоящих профессионалов — вы по адресу.
Do you mind if I quote a few of your posts as long as I provide credit and sources back to your weblog? My website is in the very same niche as yours and my users would genuinely benefit from some of the information you provide here. Please let me know if this alright with you. Cheers!