Erectile dysfunction (ED) refers to a consistent difficulty in attaining or sustaining an erection that is sufficient for sexual activity. ED is more common in men over 40, with prevalence increasing with age. Chronic medical conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hormonal imbalance and neurological disorders are major risk factors for erectile dysfunction. Psychological factors like depression and performance anxiety also contribute, though to a lesser extent, according to a study published by the National Library of Medicine. ED is also caused by medications such as antidepressants, antihypertensives, antipsychotics, opioids, and recreational drugs.
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in managing erectile dysfunction, and many foods to increase blood flow to the penis naturally can significantly support erectile function. These foods help in ED by improving cardiovascular health, enhancing nitric oxide production, and supporting healthy testosterone levels. The role of food and diet in erectile dysfunction is well-documented, with research showing that nutrient-rich, plant-based diets can lower the risk of ED by protecting blood vessels and reducing inflammation. Some of the best foods for erectile dysfunction and how they help in ED include leafy greens and beets (high in nitrates to boost nitric oxide), fatty fish (rich in omega-3s to support circulation), dark chocolate (contains flavonoids that improve blood flow), and watermelon (contains citrulline, which relaxes blood vessels). On the other hand, the worst foods for erectile dysfunction include processed meats, fried foods, refined sugars, and trans fats, all of which damage blood vessels and disrupt hormone levels, worsening ED symptoms.
With this comprehensive article, learn how making simple dietary changes helps with harder erections, improves sexual performance, and boosts overall male health.
How Food and Diet Affect Erectile Dysfunction?
Food influences erectile dysfunction by regulating blood flow, hormone levels, and overall vascular health. Unhealthy eating habits increase the risk of ED, while a balanced, nutrient-rich diet helps prevent or reverse symptoms of erectile dysfunction.
Foods high in antioxidants (like berries), healthy fats (like avocados), and vasodilatory compounds (such as nitric oxide precursors in beets and leafy greens) help improve erectile function. On the other hand, diets high in sugar, processed fats, and alcohol impair blood flow, damage vascular integrity, and suppress testosterone.
A cohort study involving 21,469 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study found a significant link between diet and erectile dysfunction. Men who followed a high-quality diet, such as the Mediterranean diet or the Alternative Healthy Eating Index 2010, had a lower risk of developing erectile dysfunction. These diets focus on eating more vegetables, fruits, nuts, legumes, and fish rich in omega-3 fats, while limiting red and processed meats.
The next sections outline foods that support or harm erectile performance based on their nutrient profile.
What Are the Best Foods for a Harder Erection?
The best foods for a harder erection are coffee, watermelon, fatty fish, dark chocolate, and leafy greens. These foods contain bioactive compounds like caffeine, L-citrulline, omega-3 fatty acids, nitrates, and flavonoids. These compounds improve erectile function by enhancing blood flow, stimulating nitric oxide production, and supporting testosterone levels.

Below are key foods that improve erectile function, backed by clinical and nutritional research.
Coffee
Coffee is a stimulant-rich beverage known for its vasodilatory and erectile benefits due to its caffeine content. Coffee helps with erectile dysfunction by increasing blood flow through vasodilation and enhancing smooth muscle relaxation in the penis. Coffee contains several bioactive compounds, most notably caffeine, which has direct effects on erectile physiology.
Its caffeine content boosts nitric oxide levels and inhibits phosphodiesterase enzymes, improving erectile response.
Caffeine is a natural stimulant. A 2015 study published in PLOS ONE analyzed data from 3,724 men in NHANES (2001–2004). Men who consumed 85–170 mg and 171–303 mg of caffeine daily had a 42% and 39% lower risk of ED, respectively, than those consuming 0–7 mg. This intake equals about 2 to 3 cups of coffee per day.
A systematic review using data from PubMed, Web of Science, and other databases concluded that caffeine enhances erectile function by promoting vasodilation via cAMP and cGMP pathways.
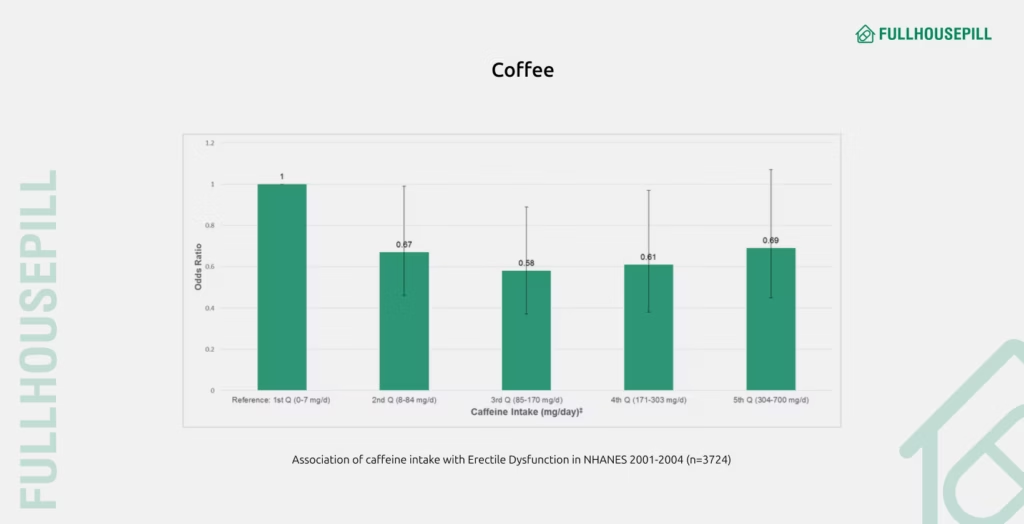
The graph above shows the risk of ED is lower in men with a daily intake of 85 – 303 mg of caffeine.
Watermelon
Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) is a hydrating fruit rich in nutrients, which helps boost erectile function by reducing arterial stiffness and enhancing nitric oxide production. It includes the amino acid L-citrulline. Watermelon contains L-citrulline, an amino acid that converts into L-arginine. L-arginine increases nitric oxide levels, which support smooth muscle relaxation and blood flow to the penile tissues.
A 2024 study in Current Research in Food Science found that watermelon improves semen quality, boosts gonadotropin secretion, and supports erectile function via its L-citrulline and antioxidant content.
A 2022 meta-analysis, in the British Journal of Nutrition (2022), of randomized controlled trials found that longer-term watermelon consumption improved arterial stiffness, as measured by pulse wave velocity, in adults. This shows that watermelon has beneficial effects on vascular function, which is closely linked to erectile health.
Fatty Fish (salmon, sardines, tuna)
Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and tuna are rich sources of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). They are especially high in eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These compounds are well known for their cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory benefits. Erectile dysfunction often results from endothelial damage, arterial stiffness, and systemic inflammation. Omega-3s reduce these risks by improving blood vessel function. Omega-3s in fatty fish contribute to improved endothelial function, reduced arterial plaque buildup, and decreased inflammation, all important factors for optimal penile blood flow.
Moreover, omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to reduce cardiovascular mortality and improve overall cardiovascular outcomes. Given that cardiovascular disease and ED share common pathophysiological mechanisms, these heart-healthy benefits of omega-3s translate to reduced risk of erectile dysfunction as well.
A cross-sectional study, published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Network (2020), involving 1,679 young Danish men found that those who consumed fish oil supplements had larger testicular size, higher semen volume, and improved sperm count compared to non-users. These findings suggest a positive association between omega-3 intake and male reproductive health.
Fruits (berries, apples, oranges, pomegranates, grape juice)
Fruits such as berries, apples, and oranges are rich in flavonoids, which are natural compounds with antioxidant properties that support vascular health. These flavonoids, including anthocyanins, flavanones, and flavones, are known to improve blood flow, both of which are crucial for erectile function.
A large 2016 study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition of 25,096 men found that consuming more flavonoid-rich foods significantly lowered the risk of erectile dysfunction. Especially, higher intake of anthocyanins, flavanones, and flavones (compounds commonly found in berries, citrus fruits, and apples) was associated with a 14% reduction in the likelihood of developing erectile dysfunction.
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study published in the International Journal of Impotence Research (2007) investigated the effects of pomegranate juice on erectile dysfunction in men with mild to moderate ED. The study found that pomegranate juice consumption led to significant improvements in erectile function, as assessed by the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) and Global Assessment Questionnaires (GAQ). These findings suggest that pomegranate juice serves as a beneficial adjunct in managing ED.
A study using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) found that men who consumed grape juice at least five times per week had a lower prevalence of erectile dysfunction, with the effect particularly pronounced in those over the age of 40.
Incorporating a wide variety of fruits into the diet has been shown to provide protective benefits against erectile dysfunction, primarily due to their rich content of flavonoids and other vital nutrients that support vascular function and overall health.
Olive Oil
Olive oil improves vascular health and may help prevent erectile dysfunction. Olive oil is a natural oil extracted from olives, the fruit of the olive tree (Olea europaea). It is a fundamental component of the Mediterranean diet and is widely recognized for its health benefits. Olive oil helps in combating erectile dysfunction by improving cardiovascular functions. It is rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA), mainly oleic acid. It is also rich in polyphenols, antioxidants, vitamin E, and other bioactive compounds. Oleic acid is known to improve cardiovascular health by reducing LDL cholesterol and increasing HDL cholesterol. Vitamin E protects the endothelial cells lining blood vessels, resulting in harder erections.
A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2018), investigated the effects of a Mediterranean diet enriched with extra-virgin olive oil on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. While the primary focus was on cardiovascular outcomes, the findings are important for erectile dysfunction, given the shared vascular mechanisms involved.
Garlic
Garlic (Allium sativum) is a widely used culinary and medicinal herb known for its distinctive flavor and health benefits. Garlic is recognized for its vasodilatory and antioxidant properties, which may contribute to improved blood flow and support sustained erectile function. It contains a variety of bioactive compounds, notably sulfur-containing compounds such as allicin, ajoene, and diallyl sulfides, which contribute to its therapeutic effects.
Garlic helps with erectile dysfunction by enhancing nitric oxide production in the blood vessels. Nitric oxide is essential for relaxing the smooth muscles of the penile arteries, allowing increased blood flow necessary for an erection. A study published in Phytotherapy Research (2005) demonstrated that garlic increases nitric oxide levels, which improves vascular dilation and erectile function. The study found that supplementation with aged garlic extract significantly improved endothelial function, as measured by flow-mediated dilation, compared to placebo. Since endothelial dysfunction is a key factor in erectile dysfunction, these findings suggest that aged garlic extract has potential benefits for improving erectile function.
Nuts and Legumes
Nuts like almonds and walnuts, and legumes like lentils and beans, are nutrient-rich and support erectile function. Both are staples in plant-based and Mediterranean-style diets and are known for their cardiometabolic benefits. They are rich in arginine (a precursor of nitric oxide), antioxidants, magnesium and folate, which have been linked to improving erectile health. Arginine boosts nitric oxide, which triggers penile artery dilation during arousal.
A randomized controlled trial published in Nutrients (2019), examined the effects of daily consumption of 60 grams of mixed nuts on erectile and sexual function in healthy men aged 18 – 35. Over a 14 – week period, participants who included nuts in their diet reported significant improvements in orgasmic function and sexual desire compared to those who did not consume nuts. These findings suggest that incorporating nuts into a regular diet enhances certain aspects of sexual health, potentially benefiting individuals experiencing erectile dysfunction.
Another study in The Journal of Food Biochemistry (2017) showed the positive effect of fermented legumes on key enzymes linked to erectile dysfunction. Extracts from Bambara groundnut (BGN) and other legumes block certain enzymes, like PDE-5, arginase, acetylcholinesterase, and ecto-5ʹ nucleotidase, that are known to interfere with normal erection. Including legumes in your diet helps you combat erectile dysfunction.
Oysters and Shellfish
Shellfish like oysters, clams, and mussels are rich in nutrients that support reproductive health. They are nutrient-dense, protein-rich foods known for their aphrodisiac effects, and thus support erection by improving hormone levels and circulation. These seafood sources are packed with essential nutrients that support reproductive, cardiovascular, and hormonal health.
The key nutrients in these are zinc, selenium, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin B12 and arginine. It is also a rich source of taurine, which is an important amino acid linked to healthy blood vessels and circulation. Taurine reduces oxidative stress in penile tissue and improves arterial elasticity.
Oysters are among the richest natural sources of zinc. Zinc increases testosterone production, which is necessary for libido and erectile firmness. Oysters contain D-aspartate, an amino acid which stimulates the release of sex hormones and enhances libido and sexual performance.
Shellfish contain arginine, which increases nitric oxide levels in the blood. Nitric oxide relaxes blood vessels and improves circulation to the penis. Selenium and B12 in shellfish act as antioxidants, protecting blood vessels and penile tissue from oxidative damage, which is often elevated in men with ED.
A prospective cohort study, published in Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (2018), involving 501 couples found that higher seafood consumption was associated with increased sexual activity and improved fertility. Men consuming seafood nine or more times per month had a 22.9% higher frequency of sexual intercourse compared to those consuming it two times or less. While this study didn’t focus solely on oysters, it suggests a positive link between seafood intake and sexual health.
Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate is made from cocoa solids, cocoa butter, and a small amount of sugar. It typically contains more than 50% of cocoa content, and less milk compounds than milk chocolate. Dark chocolate is rich in flavonoids, which are known to reduce the occurrence of erectile dysfunction. Flavonoids such as epicatechin and catechin provide antioxidant and vasodilatory effects, while phenylethylamine and theobromine stimulate endorphin and serotonin release, increasing sexual desire and performance.
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study published in the International Journal of Medicine (2022), assessed the effects of a composition containing Theobroma cacao (cocoa) seed extracts on aging male volunteers. The study found that supplementation improved sexual and erectile functions, suggesting benefits of cocoa-derived products like dark chocolate.
It also lowers the risk of high blood pressure which is a risk factor for erectile dysfunction. Moderate consumption of 1-2 squares a day is recommended to boost erectile health and sexual performance.

Spices
Spices are plant-derived substances primarily used to flavor food. Spices increase nitric oxide production, enhance insulin sensitivity, and act as natural antioxidants. Many spices also contain bioactive compounds with anti-inflammatory, vasodilatory, and aphrodisiac properties, mechanisms that are known to benefit erectile function. Common spices include – ginger (Zingiber officinale), turmeric (Curcuma longa), cinnamon (Cinnamomum spp.), saffron (Crocus sativus), chili pepper (Capsicum spp.)
According to a study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine, a combination of dark chocolate, chili, and spices work synergistically to improve erectile function in patients with erectile dysfunction. Another study in the same journal investigated the effects of a novel curcumin derivative (NCD) compared to sildenafil citrate on erectile function. It showed that curcumin containing compounds have the potential to replace traditional ED treatments such as sildenafil.
Diabetes is a major risk factor for erectile dysfunction. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial published in 2015 in the Journal of Evidence-Based Complementary & Alternative Medicine evaluated the effects of topical saffron gel on erectile function in diabetic men. Fifty participants applied either saffron gel or a placebo for one month. Results showed a significant improvement in erectile function in the saffron group compared to placebo, as measured by the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) questionnaire.
| Spice | Key Bioactive Compounds | Main Actions to Combat ED |
| Ginger | Gingerol, shogaol | Increases nitric oxide (NO), testosterone |
| Turmeric | Curcumin | Anti-inflammatory, boosts endothelial function by increasing NO |
| Cinnamon | Cinnamaldehyde | Improves insulin sensitivity, circulation |
| Saffron | Crocin | Aphrodisiac, antioxidant, improves erection |
| Chili Pepper | Capsaicin | Increases blood flow via vasodilation |
(can make this table into an image)
Avocados
Avocados (Persea americana) are nutrient-rich fruits known for their high content of monounsaturated fats, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Avocados provide antioxidants like vitamin E that protect blood vessel linings from oxidative stress, preserving nitric oxide levels essential for penile blood flow. The high content of oleic acid in avocados helps improve cholesterol levels by lowering LDL (bad cholesterol) and raising HDL (good cholesterol), which promotes cardiovascular health, which promotes sustained erections.
Vitamin D and potassium found in avocados further contribute to erectile health by supporting hormone balance and regulating blood pressure, respectively. Adequate vitamin D levels are linked with higher testosterone production and better endothelial function, both essential for sexual performance, while potassium helps lower blood pressure, reducing vascular strain and enhancing penile blood circulation. Folate in avocados also supports the production of nitric oxide, which relaxes penile muscles and facilitates erections.
Including avocados in your regular diet promotes better blood flow, hormone balance, and vascular health, which collectively helps improve erectile function and overall sexual wellness.
Leafy Greens (kale, spinach)
Leafy greens like kale and spinach are nutrient-dense vegetables rich in compounds like vitamin C, vitamin E, and polyphenols, which combat oxidative stress and protect endothelial function. These leafy vegetables are rich in dietary nitrates. The body converts these nitrates into nitric oxide, a molecule that promotes vasodilation and improves blood flow. This enhanced circulation helps the penile tissue maintain an erection for a longer duration.
A study published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2013) highlights that dietary nitrate from green leafy vegetables improve vascular function by enhancing nitric oxide availability, thereby enhancing erectile function. Another study from Shantou University in China found that men with higher antioxidant intake, including from spinach and kale, were 37% less likely to experience ED, showing that antioxidants in these vegetables improve blood flow and reduce vascular damage.
Root vegetables (beetroot, carrot)
Beetroot (Beta vulgaris) and carrots (Daucus carota) are nutrient-rich root vegetables that support erectile function through their effects on vascular health, hormone regulation, and oxidative stress reduction.
Beetroot juice (BRJ) is gaining widespread attention not only among athletes but also in the field of men’s health, particularly for its potential role in managing erectile dysfunction. Rich in dietary nitrates, beetroot helps boost nitric oxide levels in the body. In addition to cardiovascular benefits and enhanced muscle performance, the vasodilatory effects of beetroot juice directly influence erectile function, offering a holistic, non-pharmaceutical approach to improving male sexual health.
Carrots (Daucus carota) contain beta-carotene. The body converts beta-carotene into vitamin A, which reduces oxidative stress and supports endothelial health. Antioxidants help combat oxidative stress, a factor that impairs endothelial function and contributes to erectile dysfunction.
Oats
Oats (Avena sativa) are whole grains rich in nutrients that support cardiovascular health, hormonal balance, and endothelial function, which are key factors for good erectile health. Oats are a source of L-arginine, an amino acid that the body uses to produce nitric oxide, a molecule that facilitates vasodilation and enhances blood flow, including to the corpus cavernosum.
A study, in the Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy (2003), demonstrated that supplementation with L-arginine and Pycnogenol significantly improved erectile function in men with ED, highlighting the role of nitric oxide in sexual health. It involved 40 men aged 25 – 45 with mild ED, participants received 1.7 g/day of L-arginine for the first month, followed by the addition of 80 mg/day of Pycnogenol in the second month, and increased to 120 mg/day in the third month. Results showed that after three months, 92.5% of participants experienced a normal erection, suggesting that the combination significantly improved sexual function without side effects.
What Are the Worst Foods for Erectile Dysfunction?
The worst foods for erectile dysfunction are alcohol, foods high in trans and saturated fats, and added sugars. These factors adversely affect blood flow, hormone balance, and overall vascular health, thereby making it more difficult to achieve and maintain erections.

The comprehensive list for the worst foods for erectile dysfunction is listed below.
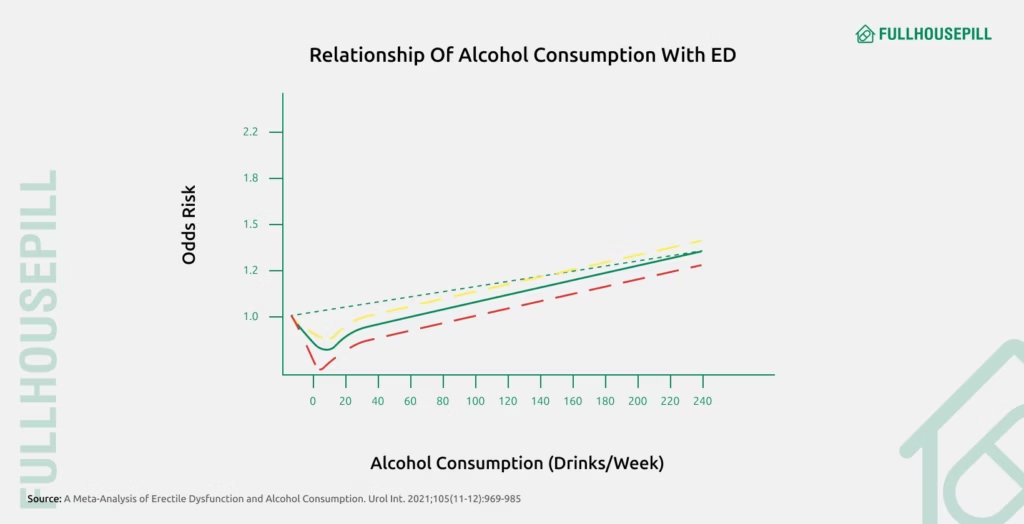
Alcohol (excessive)
Alcohol is a psychoactive ingredient found in beverages like beer, wine, and spirits. Ethanol, the active compound in alcohol, depresses the central nervous system.
Some individuals use alcohol to reduce sexual performance anxiety, but this often leads to worse outcomes over time. But, chronic heavy drinking impairs erectile function through several mechanisms. Firstly, it disrupts the hormonal balance by inhibiting testosterone production, a hormone crucial for sexual desire and performance. Secondly, excessive alcohol consumption leads to vascular damage, reducing blood flow to the penis, which interferes with achieving and maintaining an erection. Lastly, it suppresses key neurotransmitters involved in arousal and erection, further contributing to sexual dysfunction.
A meta-analysis, in the Urologia Internationalis (2021), encompassing 46 studies with over 216,461 participants found a J-shaped relationship between alcohol consumption and ED risk. Light to moderate drinking was associated with a reduced risk, whereas heavy consumption increased the likelihood of ED. The study concluded that while moderate alcohol intake might offer some protective effects, chronic heavy drinking can cause vascular damage that contributes to erectile dysfunction.
Food High in Saturated and Trans Fat
Foods high in saturated and trans fat include fried foods, processed meats, baked snacks, and full-fat dairy. Consuming such foods negatively impacts heart and sexual health. Saturated and trans fats increase low-density lipoprotein (LDL). They decrease high-density lipoprotein (HDL). They also trigger inflammation, which damages the vascular lining. Over time, this damages blood vessels and reduces blood flow, including to the penis. Reduced blood flow impairs erectile function, making these fats a dietary risk factor for ED. Limiting these fats is crucial for supporting both cardiovascular and erectile function.
Research indicates that high intake of saturated and trans fats is associated with endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis, conditions that restrict blood flow and are linked to ED. A study published in Nutrition, highlights the role of these fats in promoting plaque formation within arteries, thereby compromising vascular health. Poor vascular health leads to an increased risk of erectile dysfunction.
On the other hand, following a diet low in saturated and trans fats, like the Mediterranean diet, significantly supports erectile function and cardiovascular health. The Mediterranean diet emphasises healthy fats (olive oil, nuts), lean protein (fish, poultry), and antioxidant-rich produce.
These foods reduce inflammation, enhance vascular function, and improve erectile response. Adopting a Mediterranean-style diet is a natural, science-backed way to support better erections and overall vascular health.
Refined Carbohydrates
Refined carbohydrates are processed grains stripped of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They are found in foods like white bread, pastries, sugary cereals, and sweetened beverages. Refined carbs elevate blood sugar and insulin levels. Frequent spikes cause insulin resistance and inflammation. Both of which are linked to erectile dysfunction.
A review published in the Central European Journal of Urology (2011) discusses the potential role of sugar-sweetened beverages, particularly their high refined carbohydrate content, in the development of erectile dysfunction. The authors emphasized that regular intake of high-calorie, low-satiety sugar drinks can silently trigger metabolic disorders that gradually impair vascular function and erectile capacity. Furthermore, the review suggested that ED may represent an early clinical marker of deeper metabolic disease, particularly in men with diabetes.
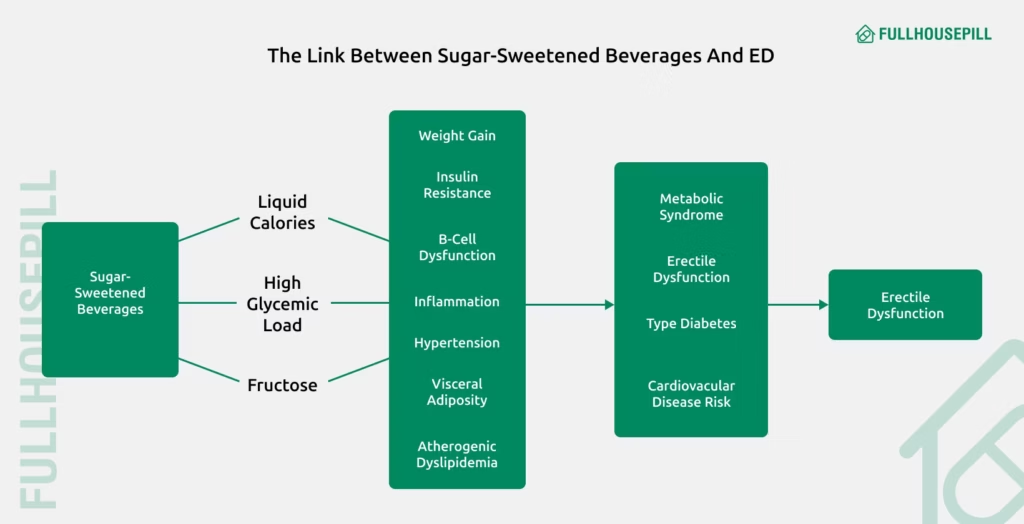
Sugar
Sugar, mainly found in added sugars and refined carbohydrates, is a basic carbohydrate source that delivers energy but is deficient in important nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals. While added sugars refer to sweeteners added during processing or preparation, refined carbohydrates include a broader category of processed foods like white bread, pastries, and many packaged snacks that also have reduced nutritional value, as discussed in the section above. Common sources include sugary beverages, candies, baked goods, and processed foods. Excessive consumption of sugar leads to metabolic disturbances, such as insulin resistance, obesity, and systemic inflammation, all of which are risk factors for erectile dysfunction.
A systematic review published in Journal of Royal Society of Medicine (2016), analyzed five cross-sectional studies involving 3,299 men aged between 27 – 85 years with type 2 diabetes to assess the impact of glycemic control on erectile dysfunction. The review found that poor glycemic control, indicated by higher HbA1c levels, was positively associated with an increased prevalence of ED. Higher HbA1c levels indicate poorer long-term blood sugar control. HbA1c, or glycated hemoglobin, reflects the average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. Elevated HbA1c means that glucose has been consistently high, which damages blood vessels and nerves, factors that contribute to erectile dysfunction, especially in people with diabetes. Specifically, three studies reported a significant positive correlation, while one showed a weak correlation and another had borderline significance. Factors such as age, diabetes duration, body mass index (BMI), and peripheral neuropathy were identified as risk factors for erectile dysfunction in this population.
Fried and Processed Foods
Fried and processed foods refer to items that have been cooked in oils at high temperatures or have undergone industrial processing to extend shelf life, enhance flavor, or improve texture. These foods often contain high levels of unhealthy fats (trans fats and saturated fats), refined carbohydrates, added sugars, sodium, and various preservatives. These ingredients contribute to vascular inflammation, poor circulation, and hormonal imbalance, key drivers of erectile dysfunction.
These diets promote endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress. They also accelerate atherosclerosis, narrowing arteries and reducing blood flow to the penis.
A study published in Urology (2020) examined 271 men at a men’s health clinic to assess the relationship between dietary habits and erectile dysfunction. The findings indicated that individuals who adhered to an organic diet or practiced intermittent fasting were less likely to experience erectile dysfunction, even after adjusting for factors like age, BMI, and comorbidities. To lessen the risk of erectile dysfunction, it is better to avoid fried and processed food, or control the consumption.
High-Sodium Foods
Most high-sodium foods contain sodium chloride, which raises blood pressure and impairs blood vessel function. Excessive sodium intake is known to elevate blood pressure and impair endothelial function, thus increasing the occurrence of erectile dysfunction.
A study published in the American Journal of Hypertension (2019) found that excessive salt intake impairs erectile function. Researchers observed that high-sodium diets reduced apomorphine-induced penile erections in rats. Apomorphine is a dopamine agonist, a drug that stimulates dopamine receptors in the brain. It is used clinically to treat conditions like Parkinson’s disease and erectile dysfunction (ED). The study highlights the potential link between high-salt diets and increased risk of erectile dysfunction.
Limiting intake of salt reduces the risk of hypertension, and in turn helps avoid the occurrence of erectile dysfunction.
What are the foods that promote stronger erections?
Certain foods support stronger erections by improving blood flow, hormone balance, and nitric oxide production. These include fatty fish, leafy greens, oysters, eggs, avocados, and dark chocolate, each providing nutrients that promote vascular and sexual health.
Ingredients like omega-3 fatty acids in salmon or magnesium in spinach can support vascular health, which helps blood flow to the penis during arousal. This means a consistent intake of testosterone-boosting foods can indirectly lead to a stronger erection, especially in men with low hormone levels.
Foods that may help increase testosterone levels include fatty fish, leafy greens, oysters, eggs, avocados, and cocoa products. These foods are rich in nutrients like vitamin D, zinc, magnesium, and healthy fats, which are essential for testosterone production. Higher testosterone levels are linked to better sexual function and may improve symptoms of erectile dysfunction.
Oysters provide zinc, a mineral critical for hormone synthesis, while eggs offer both cholesterol and vitamin D, needed for testosterone conversion. Avocados supply vitamin E and heart-healthy fats, and dark chocolate contains antioxidants that protect testosterone-producing cells. Fruits like berries and pomegranates, along with onions and garlic, also support hormone balance and nitric oxide activity, further promoting erectile health.
Which Foods Help You Last Longer In Bed?
Certain foods may help improve blood flow, energy levels, and hormone balance, which together support better sexual performance and may help you last longer in bed. While no food acts as an instant solution, options like fatty fish, beets, spinach, and dark chocolate are known for promoting circulation by delivering nitric oxide or essential minerals like magnesium and folate. Improved blood flow allows for firmer erections and sustained arousal, especially when combined with good hydration and regular physical activity.
Bananas, avocados, and oysters also play a role by boosting energy and supporting testosterone production, both of which are crucial for endurance. Foods rich in zinc, such as nuts and seeds, aid in hormone regulation, while vitamin C from fruits like strawberries may help reduce anxiety, a common cause of early ejaculation. Ginger, often used to increase circulation, may further enhance blood supply to pelvic muscles. Together, these dietary choices can support vascular health, hormonal balance, and energy metabolism, all of which help the body respond more effectively during sex and potentially help men last longer without relying on medication.
What Are The Treatment Options For Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be treated through a combination of lifestyle changes, medical therapies, and mechanical or surgical interventions, depending on the underlying cause and severity. Common first-line treatments include erectile dysfunction pills. These pills are PDE5 inhibitors like sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil, which improve blood flow to the penis and help facilitate an erection during sexual stimulation. For those who don’t respond to oral medications, options like vacuum constriction devices, penile injections, intraurethral suppositories, or penile implants may be considered. In addition, managing contributing factors such as obesity, smoking, alcohol use, and stress can improve outcomes significantly.
Psychological counseling and sex therapy may also play a role, particularly when emotional or relational issues are involved. Newer approaches, such as stem cell therapy or hormone replacement in cases of low testosterone, are still being studied but show some promise. The best treatment plan should always be individualized, with guidance from a healthcare provider who can assess both physical and psychological contributors to the condition.
Which Supplement Help Improve Erectile Dysfunction?
Several supplements may help improve erectile dysfunction by supporting blood flow, hormone balance, or nerve function. Nutrients like L-arginine, zinc, magnesium, and ginseng have been studied for their potential to improve erectile quality in men with mild to moderate ED. Among these, vitamin D has received particular attention, as deficiency in this nutrient has been linked to poor vascular health and reduced testosterone levels, two key contributors to erectile issues. Research suggests that restoring optimal levels of this vitamin that can help ED may improve endothelial function and overall sexual performance.
Other supplements like ginkgo biloba, maca root, and fenugreek are also believed to offer mild benefits, though evidence varies. It’s important to note that while supplements may offer support, they should not replace clinically approved treatments without medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement for erectile dysfunction.
What Are The Best Drink For Erectile Dysfunction?
Several nutrient-rich drinks may support stronger erections by boosting circulation, hormone levels, and overall vascular health. While not direct treatments for erectile dysfunction (ED), they can complement lifestyle changes and improve sexual function over time. Pomegranate juice is packed with antioxidants that enhance blood flow and may help elevate testosterone levels. Beetroot juice increases nitric oxide in the body, which relaxes blood vessels and supports erection quality. Adequate water intake also promotes healthy circulation and energy, two essentials for optimal sexual performance.
Adding smoothies for erectile dysfunction into your daily routine is an effective way to combine multiple benefits. A blend of watermelon, leafy greens, and berries offers citrulline, nitrates, and polyphenols that promote penile blood flow. Green tea and coffee may indirectly aid ED by reducing inflammation and supporting cardiovascular health. Milk fortified with vitamin D helps regulate hormone levels, while aloe vera juice may support testosterone production and reduce oxidative stress, though more studies are needed. Though these beverages don’t replace medications like sildenafil, they can contribute to better erectile function when paired with other healthy habits.
