A strong erection depends on the smooth coordination of the brain, hormones, nerves, blood vessels, and the muscles within the penis. When a man is sexually aroused, through physical touch, mental stimulation, or emotional intimacy, the body releases nitric oxide. This molecule dilates blood vessels, allowing increased blood flow into the corpora cavernosa, which is the spongy tissue inside the penis. This leads to firmness and rigidity, allowing for satisfying sexual activity. Achieving and maintaining an erection is not just about desire; it also reflects overall cardiovascular, hormonal, and neurological health.
However, many men experience weaker erections or difficulty staying hard due to a combination of factors. Common causes include poor blood circulation, low testosterone, chronic health conditions like diabetes or hypertension, stress, performance anxiety, and unhealthy lifestyle habits such as smoking or a sedentary routine. These physical or psychological barriers disrupt the erection process and lead to frustration or loss of sexual confidence.
Achieving stronger erections involves improving overall health and addressing underlying issues. Consistent exercise, nutritious diets, restful sleep, and effective stress control improves circulation and support healthy hormone production. Treating conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure is also key. When needed, medical options such as PDE5 inhibitors or testosterone therapy support erectile function effectively.
This article explores how erections occur, the common issues that affect them, and effective ways to address those problems.
What Is an Erection?
An erection is a complex neurovascular event involving the nervous system, vascular system, and endocrine regulation that results in the enlargement and stiffening of the penis. It occurs when spongy erectile tissues within the penis fill with blood, typically in response to sexual arousal or stimulation.
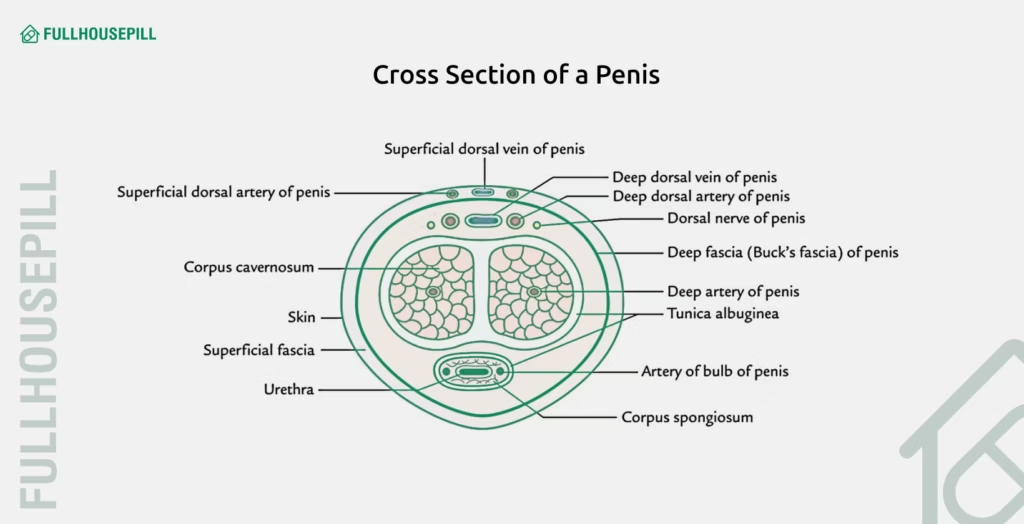
The penis is composed of three main cylindrical structures as listed below:
- Corpora cavernosa: They are aired erectile tissues that run along the top of the penis. These are primarily responsible for the rigidity during erection.
- Corpus spongiosum: It is located along the underside, surrounds the urethra and prevents compression of the urethra during erection.
- Tunica albuginea: It is a tough fibrous sheath surrounding the corpora cavernosa that traps blood in the penis, maintaining rigidity.
The other associated structures that support the erection function are the following:
- Penile arteries: They supply blood to erectile tissue.
- Penile veins: They drain blood from the penis (their compression maintains an erection).
- Pelvic nerves: They carry signals from the brain and spinal cord.
- Endothelial cells: They line the blood vessels and release nitric oxide (NO), a key chemical in erection.
Having established what an erection is, explore the physiological processes that govern how it occurs.
The penis functions through a complex interaction of the nervous, vascular, and hormonal systems. Sexual arousal triggers signals from the brain that coordinate blood flow and nerve responses. These processes work together to enable erection, intercourse, and ejaculation, while also supporting the elimination of urine from the body.
An erection occurs when sexual arousal activates the brain to send signals to the nerves in the pelvic region. These signals relax the blood vessels, increasing blood flow to the penis. At the same time, the outflow of blood is temporarily reduced, helping the penis stay firm until arousal subsides or ejaculation occurs.
How Does an Erection Work?
An erection is triggered by sexual arousal, which may be from physical, visual, or psychological cues. In response, the brain sends signals through the parasympathetic nervous system to the penis. The signal originates from the brain but travels via spinal cord centres before reaching the pelvic nerves. It prompts the release of nitric oxide (NO) within the penile tissue. Nitric oxide activates an enzyme that increases levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a key chemical that relaxes the smooth muscles in the corpora cavernosa. As the smooth muscle within the corpora cavernosa relaxes, blood flow to the penis increases, causing the spongy tissue to expand and initiate an erection.
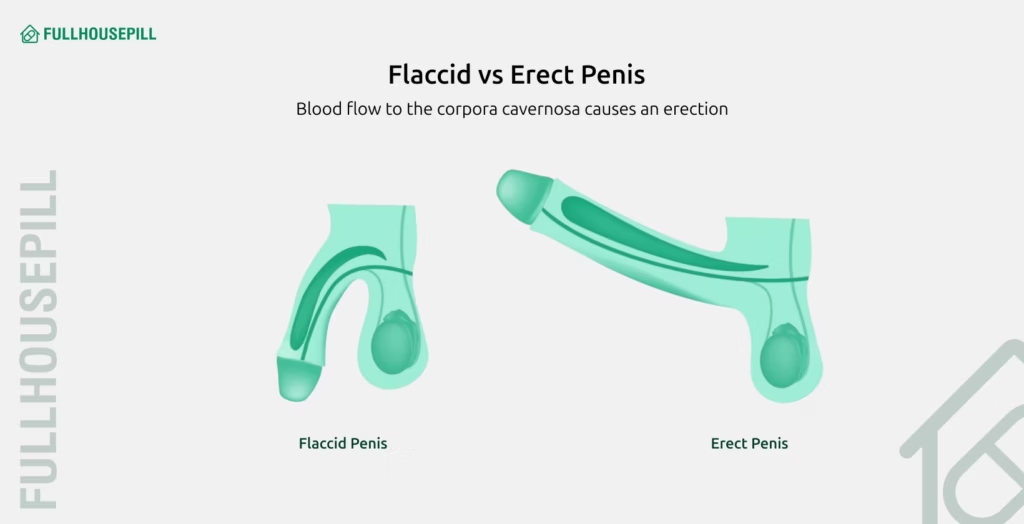
As the corpora cavernosa tissues fill with blood, they press against the surrounding veins, restricting blood from flowing out and maintaining penile rigidity. This process allows the penis to remain firm during sexual activity. After arousal or ejaculation, the enzyme PDE5 breaks down cGMP, causing smooth muscle contraction, reduced blood flow, and loss of erection. The entire erection process relies on healthy nerve signaling, proper blood circulation, and balanced hormone levels.
How Long Do Erections (Boners) Last?
On average, an erection lasts anywhere from 5 to around 30 minutes, depending on arousal, stimulation, and other individual factors. During sexual activity, most erections last between 5 to 15 minutes, though this varies widely from person to person.
However, some individuals may experience erections lasting longer, even up to a few hours. An erection lasting longer than four hours, known as priapism, requires immediate medical attention.
What Causes Erections or Boners?
Erections, or boners, are triggered by mental, emotional, and sensory stimulation. Sexual thoughts, visual cues, touch, or even dreams can activate the brain’s arousal centers, setting off a chain reaction that results in an erection. Emotional connection, mood, and confidence also play a role, as the mind and body work together to create a sexual response, even during sleep.
Common causes of weak or problematic erections include poor blood flow from conditions like heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes; nerve damage from neurological disorders; low testosterone levels; and psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, or depression. Lifestyle habits like smoking, excessive alcohol, obesity, lack of exercise, and certain medications (eg. antidepressants or blood pressure drugs) also interfere with normal erectile function.
Understanding these root causes explains why some men find it increasingly difficult to achieve or sustain an erection.
What Makes Getting Erections More Difficult?
Several factors make it harder for men to achieve or maintain an erection, especially as they age. Advancing age is one of the most well-documented risk factors. Studies show that men over 40 experience a gradual decline in erectile function, largely due to reduced testosterone levels, decreased endothelial function, and a natural decline in vascular elasticity. According to the Massachusetts Male Aging Study (1994), the prevalence of erectile dysfunction rises from about 40% in men aged 40 to nearly 70% in those over 70.
Chronic health conditions like diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and obesity significantly contribute to erectile difficulties. These conditions harm the blood vessels and nerves essential for achieving and maintaining erections. For example, men with diabetes are nearly three times more likely to develop erectile dysfunction due to poor glycemic control and resulting neuropathy. Similarly, high blood pressure and atherosclerosis reduce blood flow to the penis, weakening erectile response.
Lifestyle factors play a major role as well. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, sedentary behavior, and poor diet impair cardiovascular and hormonal health, both essential for strong erections. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (2004) found that lifestyle modifications such as exercise and healthy eating, like a Mediterranean diet, significantly improve erectile function in obese men.
Lastly, psychological factors like stress, performance anxiety, and depression disrupt the brain’s ability to send sexual arousal signals to the body. Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which interfere with testosterone production and nitric oxide release, two important elements in erectile function. As per a review in Sexual Medicine Reviews (2017), psychological causes are especially common in younger men experiencing ED.
How to Get an Erection (or Boner)?
Getting an erection involves a combination of mental arousal, healthy blood flow, and proper hormonal and nerve function. Getting an erection depends on more than just physical stimulation, it’s influenced by a range of mental, emotional, and physical factors. When these elements are in balance, the body is better able to respond to arousal.
To improve erectile function, focus on consistent exercise, reducing stress, getting restful sleep, and following a nutrient-rich diet that supports circulation and hormone balance. Limit alcohol intake, stop smoking, and address underlying health conditions through proper medical care and lifestyle adjustments. In some cases, medications or therapy may be needed for additional support.
Below are the key factors, explained in detail, that support a man’s ability to achieve and maintain a strong erection.
Diet for Blood Flow & Testosterone Boost
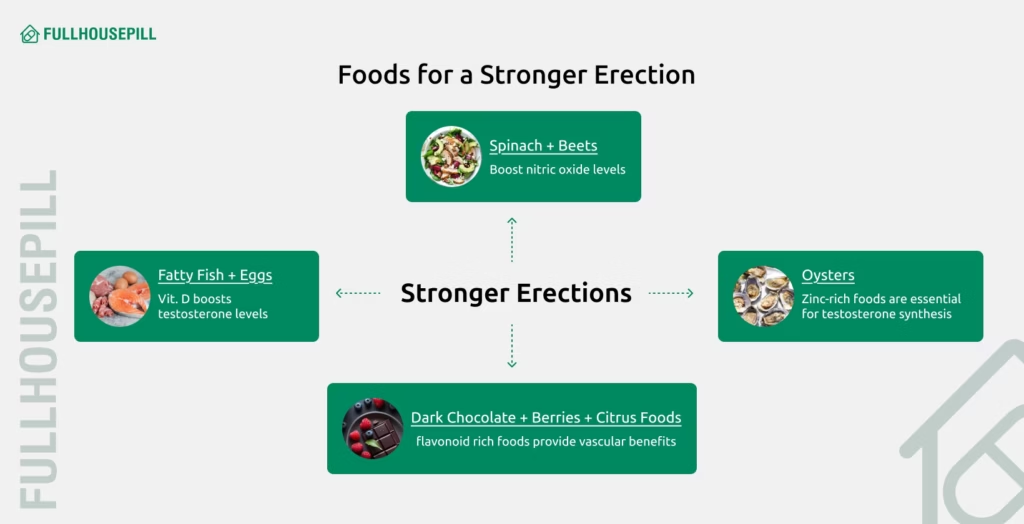
Eating the right foods plays a vital role in supporting healthy erections by enhancing blood flow and boosting testosterone, two crucial elements of erectile function. Foods rich in nitrates like spinach, beets, increase nitric oxide levels, which dilate blood vessels and improve circulation to the penis. A meta-analysis in a chemistry journal, Nitric Oxide (2014) found that inorganic nitrate from foods like beets and leafy greens significantly lowers blood pressure by boosting nitric oxide levels. Since nitric oxide is essential for blood flow to the penis, this suggests nitrate-rich foods may support stronger erections. Additionally, flavonoid-rich foods like berries, citrus fruits, and dark chocolate are linked to a lower risk of ED due to their vascular benefits, as per a study in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2016).
To help maintain optimal testosterone levels, incorporate foods high in zinc, vitamin D, healthy fats, and omega-3 fatty acids. Oysters, eggs, tuna, avocados, and nuts provide key nutrients that support hormone production and testicular health. A study in Hormone and Metabolic Research (2011) reported that men with low vitamin D levels were more likely to have reduced testosterone, suggesting a potential connection between vitamin D status and hormonal health. Similarly, zinc is essential for testosterone synthesis, as shown in a study in Nutrition (1996), where zinc-deficient men experienced significant testosterone declines. Prioritizing these nutrient-dense foods naturally enhances erection quality and sexual performance.
Exercises for Stronger Erections (Kegels + Cardio)
Pelvic floor exercises, or Kegels, are exercises that strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, which support the bladder, bowel, and sexual function. Kegels strengthen the muscles that regulate blood flow to and from the penis, supporting firmer and longer-lasting erections. Strengthening the pubococcygeus (PC) muscle enhances rigidity, improves ejaculation control, and facilitates the ability to maintain an erection. A randomized controlled trial published in BJU International (2005) found that pelvic floor training significantly improved erectile function in men with ED, with 40% regaining normal function and 35.5% showing improvement after three months. Kegels are especially beneficial for men with mild to moderate ED or those recovering from prostate surgery.
In addition to Kegels, aerobic exercise like brisk walking, jogging, or cycling plays a crucial role in supporting erectile health. Cardio enhances vascular function, lowers blood pressure, and improves nitric oxide availability, leading to harder erections. A meta-analysis in The Journal of Sexual Medicine (2023) found that aerobic exercise significantly improves erectile function in men with ED, especially when done regularly for at least 30 to 40 minutes, 4 times per week.
Physical Stimulation & Arousal Triggers
Physical stimulation is one of the most direct and effective ways to trigger an erection. Touching or stimulating erogenous zones, especially the penis, activates sensory nerves that send signals to the spinal cord and brain, initiating the release of nitric oxide, a chemical that relaxes penile blood vessels and allows blood to flow in. Nitric oxide (NO) is released locally by nerve endings within the penis during an erection, not directly from the brain. While the brain plays a role in initiating the signals that lead to an erection, the actual release of NO that causes the smooth muscle relaxation and subsequent blood flow into the corpora cavernosa comes from nerve endings in the penis itself. A study in the Journal of Sexual Medicine (2005) confirms that genital stimulation activates brain areas responsible for sexual arousal, reinforcing the mind-body connection in the erection process.
In addition to touch, mental and emotional arousal triggers, like visual stimuli, fantasies, and emotional intimacy, play a crucial role in erection quality. The brain is a major sex organ, and sexual thoughts or cues activate neural pathways that result in increased blood flow to the penis, even without direct contact. A study in Archives of Sexual Behavior (2010) notes that mood, attention, and emotional context affect how strongly someone feels aroused. Combining physical touch with emotional connection or erotic stimuli enhances erection strength and duration, especially when both partners are involved in the experience.
Relaxation & Breathing Hacks
Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation play a significant role in helping men achieve and maintain erections. Psychological stress activates the sympathetic nervous system, which triggers the body’s fight-or-flight response and restricts blood flow to the penis. In contrast, relaxation activates the parasympathetic nervous system, which is essential for initiating an erection. A European Society of Sexual Medicine – ESSM (2021) statement emphasizes that erectile dysfunction is best addressed through a biopsychosocial model, combining medical treatment with psychological support, like anxiety reduction, cognitive restructuring, and partner involvement, to enhance treatment effectiveness and relationship satisfaction.
Controlled breathing techniques such as diaphragmatic (belly) breathing or paced breathing lower cortisol levels, calm the mind, and enhance blood circulation. As per a study in Breathe (2017), slow breathing (4-10 breaths/min) enhances autonomic balance, heart rate variability, and blood pressure regulation in healthy individuals. It promotes efficient respiratory and cardiovascular function with potential therapeutic benefits. Practicing mindful breathing during arousal reduces performance anxiety and improves focus, helping stay relaxed and fully present during sexual activity, both of which support stronger, longer-lasting erections.
Supplements That Support Vascular Health
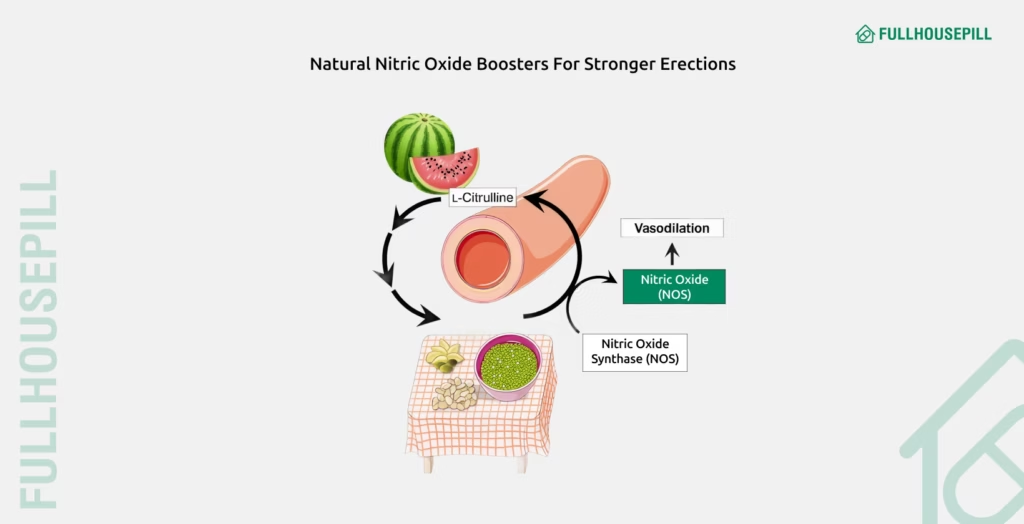
Certain dietary supplements support vascular function, a key factor in achieving and maintaining strong erections. L-citrulline and L-arginine are amino acids that act as precursors to nitric oxide (NO), which relax blood vessels and improve blood flow to the penis. A study published in Urology (2011) found that men with mild erectile dysfunction who took L-citrulline for one month showed improved erection hardness and satisfaction compared to those on placebo. Another study published in Frontiers in Endocrinology (2023) found that Pycnogenol, a potent antioxidant plant extract, significantly enhances endothelial function and erectile performance, especially when used in combination with L-arginine.
Other supplements like omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D may also benefit men with vascular-related ED by reducing inflammation and supporting cardiovascular health. A study in the Hormonal and Metabolic Research (2011) reported that vitamin D supplementation improved endothelial function and increased testosterone levels in vitamin D-deficient men. While these supplements may not replace medical treatments entirely, they serve as valuable supportive therapies to naturally enhance blood flow and erectile function.
Quitting Smoking & Reducing Alcohol
Smoking is a major risk factor for erectile dysfunction due to its harmful effects on vascular health and nitric oxide production. Cigarette smoke damages the endothelial lining of blood vessels, reduces blood flow, and impairs the relaxation of smooth muscle needed for erections. A review in Andrology (2015) reported that cigarette smoking is a significant and dose-dependent risk factor for erectile dysfunction, with higher levels of smoking associated with increased severity of the condition. The longer smoking continues, the greater the damage to penile arteries, making cessation a crucial step in restoring natural erectile response.
Excessive alcohol intake also contributes to weak erections by depressing the central nervous system, impairing testosterone production, and damaging liver function, which affects hormone metabolism. A study in the Journal of Psychosexual Health (2024) evaluated 170 men with alcohol dependence and found that 67% experienced sexual dysfunction, including erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, and reduced sexual desire. While moderate alcohol use may not cause issues in all men, cutting back or eliminating alcohol often leads to noticeable improvements in both erection quality and overall sexual performance.
Managing Stress with Mindfulness or Therapy
Chronic stress and anxiety are major psychological barriers to achieving and maintaining erections, as they increase cortisol levels and activate the sympathetic nervous system, which suppresses sexual arousal. Practicing mindfulness meditation and engaging in cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) significantly reduce performance anxiety and improve erectile function. A randomized controlled trial published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine (2011) found that guided internet-delivered CBT improved erectile function over six months. The treatment showed greater long-term benefits compared to an online discussion forum. A scoping review in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (2023) found that mindfulness improves men’s sexual well-being. It enhances sexual satisfaction, erectile and orgasmic function, desire, and genital self-image.
Medications for Better Erection
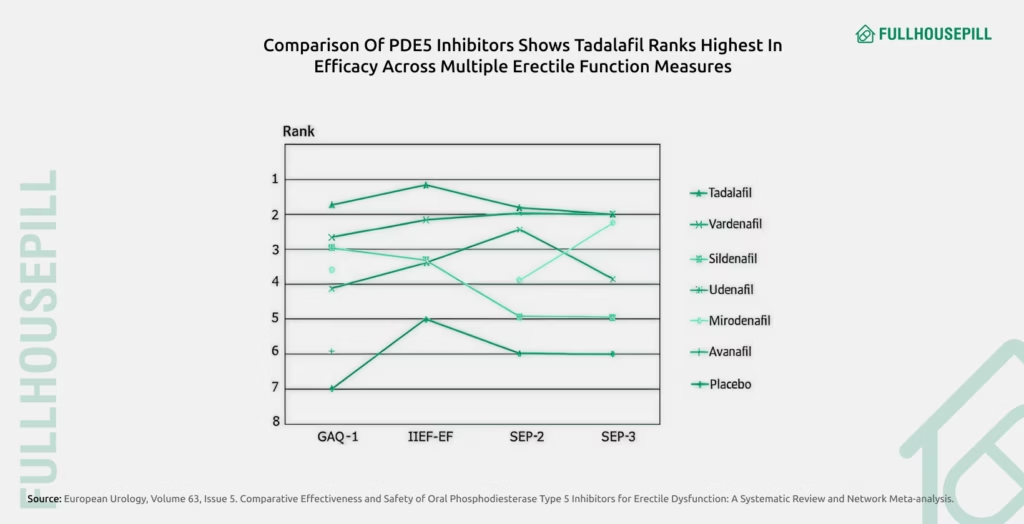
For men with erectile dysfunction, an erection medication, typically a phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor, is often the first line of treatment. Drugs like sildenafil (Viagra) and tadalafil (Cialis) are clinically proven to enhance blood flow to the penis by boosting nitric oxide activity. These medications are generally effective, safe, and well-tolerated in men with vascular, psychogenic, or mixed causes of ED. A meta-analysis published in European Urology (2013) found that PDE5 inhibitors significantly improved erectile function scores compared to placebo across multiple trials, with tadalafil showing the longest duration of action. However, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider to choose the most appropriate erection medication based on individual health conditions and medication compatibility.
Reduce Porn Consumption
Excessive pornography use has been linked to desensitization to sexual stimuli, decreased arousal during real-life sex, and a rise in porn-induced erectile dysfunction (PIED), particularly in younger men. Repeated exposure to high-intensity porn may alter the brain’s reward system, making it harder to achieve or maintain an erection without visual stimulation. A review in MDPI (2014) found that internet pornography’s unique features, like limitless novelty and ease of escalation, condition sexual arousal toward pornography and away from real-life partners. Clinical observations show that stopping porn use often reverses erectile dysfunction, low sexual desire, and orgasmic issues, underscoring the need for further investigation into porn cessation as a treatment strategy.
Sleep
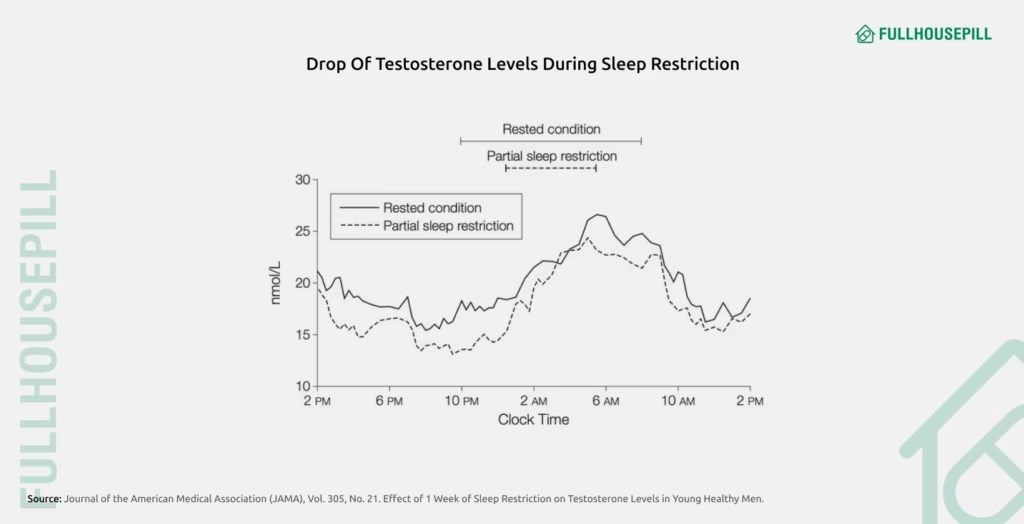
Quality sleep is essential for healthy erections, as it directly influences testosterone levels, hormonal balance, and nocturnal erections. Most testosterone is produced during deep sleep, and poor or insufficient rest lowers hormone levels and sexual function. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (2011) reported that young men who restricted their sleep to under five hours per night for one week experienced a 10-15% decline in testosterone levels, which was linked to decreased libido and weaker erections. Additionally, as per the study in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023), sleep disorders like obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) are strongly linked to erectile dysfunction due to disrupted oxygen flow and impaired nitric oxide activity. Consistently obtaining 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night is associated with improved erectile function and overall sexual health.
Can Food Enhance Erections Naturally?
Yes, food can enhance erections naturally by improving circulation, hormone balance, and vascular health. Regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress control work alongside diet to promote better sexual function. A nutrient-rich diet that includes foods for erectile dysfunction like leafy greens, beets, dark chocolate, walnuts, and oily fish raises nitric oxide levels. This molecule relaxes blood vessels and increases blood flow to the penis, which helps in achieving and maintaining firmer erections.
Medical treatments such as PDE5 inhibitors, sildenafil (Viagra) and tadalafil (Cialis) are also effective and often prescribed. However, the most sustainable improvement comes from combining these treatments with healthy lifestyle choices, especially a diet targeted at vascular health and hormone support.
What Are The Vitamins And Supplements That Help With Erection?
Vitamins and supplements that help with erection work by improving blood circulation, supporting testosterone production, and protecting vascular function. These nutrients can be beneficial for men experiencing mild to moderate erectile dysfunction, especially when used alongside lifestyle changes or medical treatments. One of the most essential vitamins for erectile strength is Vitamin D, which plays a direct role in testosterone synthesis and endothelial health. Low Vitamin D levels have been linked to a higher risk of erectile dysfunction in multiple studies. Similarly, Vitamin B3 (niacin) is known to enhance blood flow and reduce inflammation, particularly in men with elevated cholesterol levels.
Vitamin C supports vascular function by boosting nitric oxide production, which is critical for relaxing blood vessels and increasing blood supply to the penis. Vitamin E, though primarily an antioxidant, may also support hormonal balance and protect against oxidative stress that affects erectile performance.
Minerals like zinc are essential for testosterone metabolism and sperm quality, and deficiencies are commonly associated with sexual dysfunction. L-arginine, a nitric oxide precursor, helps widen blood vessels and may improve erection quality when used in the right doses. Finally, herbal remedies like Panax ginseng have shown efficacy in improving erectile function in controlled studies, likely due to their adaptogenic and vasodilatory properties.
These supplements are most effective when paired with regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and medical therapies if needed. Always consult a doctor to ensure compatibility with existing medications or conditions.
How To Get Morning Wood?
To get morning wood, also known as nocturnal penile tumescence (NPT), start by improving your sleep quality. Lowering stress levels is also important. Maintain healthy testosterone levels through balanced nutrition and regular exercise. Avoid alcohol or nicotine before bedtime, as they can interfere with NPT. These habits support the hormonal balance and blood flow necessary for consistent morning erections. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep, as erections typically occur during REM sleep cycles.
In addition, adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle of regular exercise, balanced nutrition (especially foods that support blood flow and testosterone), and staying hydrated. Keeping testosterone levels optimal through resistance training, adequate zinc intake, and stress reduction also increase the frequency of morning wood. If you’re consistently not experiencing morning erections, it may signal an underlying issue like low testosterone or vascular problems, and consulting a doctor is recommended.
What Causes Weak Erections?
Weak erections arise due to a combination of physical health problems, mental health challenges, and lifestyle habits. Common physical contributors include restricted blood flow, nerve-related issues, hormone deficiencies such as low testosterone, and long-term conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or cardiovascular disease. These conditions impair the vascular or nerve functions necessary for a long-lasting erection.
Psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, depression, or performance pressure also interfere with arousal and erection strength. Lifestyle habits like smoking, excessive alcohol use, lack of exercise, poor sleep, and an unhealthy diet further weaken erectile function. In many instances, improving erection quality is possible by targeting the root causes through natural remedies or medical treatment.
What Are The Reasons For Not Getting Hard During Sex?
Not getting hard during sex often results from a combination of physical and psychological factors. Poor blood flow due to conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or high cholesterol is a major cause. Hormonal issues, such as low testosterone, and nerve damage from injury or surgery, can also affect erectile function. Medications like antidepressants or antihypertensives may contribute to losing erection during sexual activity. Lifestyle habits, such as smoking, excessive alcohol use, or lack of sleep, further increase the risk. Psychological stressors like performance anxiety, depression, or unresolved relationship issues can create a feedback loop that worsens ED. In most cases, identifying and treating the root cause can restore sexual function.
How to Stay Hard or Maintain Erections Longer?
To stay hard and maintain erections longer, focus on improving blood flow, reducing performance anxiety, and supporting sexual stamina through lifestyle and medical strategies. Regular exercise, especially cardio and pelvic floor exercises, boosts circulation and strengthens the muscles involved in erections. Eating a diet rich in heart-healthy nutrients, like leafy greens, berries, nuts, and omega-3 fatty acids, also improves vascular function.
Managing stress, getting enough sleep, and limiting alcohol or smoking are equally important. Mental techniques such as mindfulness and open communication with your partner ease anxiety and improve sexual performance. For additional support, medically approved treatments like PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., Viagra or Cialis), testosterone therapy, or cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for sexual performance issues are effective under a doctor’s guidance. Combining physical and psychological strategies often produces the best results for lasting erections.
How To Treat Erectile Dysfunction?
The most effective treatment for erectile dysfunction depends on its underlying cause. Many men improve with lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, managing stress, and limiting alcohol. These actions enhance cardiovascular health and hormone balance, both essential for firm erections. Medically, treatment for erectile dysfunction often starts with PDE5 inhibitors like sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil, or avanafil, which increase blood flow to the penis. In cases where pills don’t work, alprostadil injections or vacuum erection devices may help. Psychological counseling benefits those with stress- or anxiety-related ED. Penile implants or vascular surgery are last-resort options for severe or treatment-resistant cases. Regardless of method, consultation with a doctor is essential to identify the safest, most effective approach.
