Sildenafil and vardenafil are PDE5 inhibitors primarily used for treating erectile dysfunction, but only sildenafil has additional approved and off-label uses. Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. Both sildenafil and vardenafil increase blood flow to the penis during sexual arousal, enabling a firm erection.
Sildenafil was approved by the FDA in 1998 and is also used under the brand Revatio to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a condition with elevated pressure in the pulmonary arteries. It is also prescribed off-label to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), Raynaud’s phenomenon, and sometimes cardiovascular issues such as heart failure. Vardenafil was approved in 2003 under the brand Levitra, which was discontinued in 2021 for commercial reasons. The active ingredient vardenafil is still available as a generic and under brand names like Vilitra and Staxyn. It is only FDA-approved for ED, with no secondary indications.
The following table compares sildenafil and vardenafil across key parameters such as onset time, duration, efficacy, and side effects.
| Aspect | Sildenafil | Vardenafil |
| Drug Class | PDE5 inhibitor | PDE5 inhibitor |
| Dosages | 25–100 mg oral tablets (once a day or as needed) | 5–20 mg oral tablets (once a day or as needed) |
| Onset of Action | ~30–60 minutes | ~25–60 minutes (often slightly faster than sildenafil) |
| Duration of Effect | About 4–6 hours | About 4–6 hours |
| Common Side Effects | Headache, flushing, stuffy nose, indigestion, visual disturbances (e.g., blue tinge) | Headache, flushing, stuffy nose, indigestion, less visual disturbance than sildenafil, has higher risk for QTc prolongation (abnormal heart rhythms) |
| Spontaneity/Flexibility Factor | Moderate, taken ~1 hour before intercourse | Moderate, taken ~1 hour before intercourse |
| Uses Other Than Erectile Dysfunction Treatment | Pulmonary arterial hypertension (as Revatio), off-label use includes BPH, Raynaud’s syndrome and heart problems | Erectile dysfunction only |
| Food Interactions | High-fat meals may delay absorption and onset of action | Less affected by food than sildenafil, but high-fat meals may still slow down absorption slight |
| Potency | PDE5 IC₅₀ of 4 nM | PDE5 IC₅₀ of 0.1–0.4 nM (higher than sildenafil, because, lower IC₅₀ = higher potency) |
| Selectivity for PDE5 | 1000-fold | 9300-fold (fewer side effects) |
What Is the Difference Between Sildenafil and Vardenafil?
Sildenafil and vardenafil are both PDE5 inhibitors used to treat erectile dysfunction, but they differ in potency, pharmacokinetics, and secondary indications. Sildenafil pills were approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1998 as the first oral treatment for erectile dysfunction. It increases cGMP levels and enhances NO-mediated vasodilation in the penile tissue. In addition to ED, sildenafil is also approved for treating pulmonary arterial hypertension under the brand name Revatio.
Vardenafil is another PDE5 inhibitor, approved in 2003 for ED treatment. Like sildenafil, it blocks the breakdown of cGMP and promotes penile erection through smooth muscle relaxation. However, a study by ElHady et al. (2023), published in Pharmaceuticals, claims that vardenafil exhibits the highest potency among all PDE5 inhibitors, with a reported IC50 value of 0.1–0.4 nanomolar, meaning lower doses may achieve equivalent effects. Unlike sildenafil, vardenafil is not approved for any indications beyond erectile dysfunction.
Both drugs enhance nitric oxide signaling by inhibiting PDE5, enabling better blood flow to the penis during arousal. Sexual stimulation triggers nitric oxide (NO) release in the penile corpus cavernosum. NO stimulates the production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which causes smooth muscle relaxation and dilates blood vessels. This process increases blood flow and allows for an erection.
PDE5, an enzyme found in the penis, breaks down cGMP. Sildenafil and vardenafil block PDE5, sustaining cGMP levels and prolonging erection duration. The drugs only work in the presence of sexual stimulation. The key difference in action is that sildenafil also inhibits PDE6, which plays a role in visual processing. This is why sildenafil has a higher incidence of vision-related side effects than vardenafil.
What Are the Medical Uses of Sildenafil and Vardenafil?
Sildenafil and vardenafil are primarily prescribed for erectile dysfunction (ED), with sildenafil having multiple additional medical applications. Both medications belong to the phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor class and work by enhancing blood flow to the penis during sexual stimulation. This helps men achieve and maintain erections sufficient for penetrative intercourse. The maximum approved dose for erectile dysfunction is 100 mg of sildenafil and 20 mg of vardenafil, taken once a day on an as-needed basis. These doses are typically reserved for patients who do not respond to lower strengths.
Sildenafil is also approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a condition characterized by elevated pulmonary artery pressure (≥25 mm Hg at rest). For PAH, the dosing regimen is higher and more frequent than for ED, up to 80 mg taken three times daily. This formulation is marketed under the brand name Revatio. In addition to PAH, sildenafil is used off-label for managing symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition involving enlargement of the prostate gland that impairs urinary function. Although not FDA-approved for this indication, clinical studies have shown that sildenafil may improve urinary tract symptoms associated with BPH. The maximum daily dose for this off-label use is typically 50 mg.
Sildenafil is also used off-label for secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon, a circulatory disorder that causes blood vessel spasms in the fingers and toes. In this context, the maximum dosage usually does not exceed 100 mg per day. Emerging studies are investigating additional uses of sildenafil, including possible applications in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and cardiovascular conditions like systolic heart failure. However, these uses are investigational and not currently supported by conclusive clinical data.
Vardenafil pills, in contrast, are approved only for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. It does not have FDA approval for any other indications and is not commonly prescribed off-label for conditions beyond ED.
How Does Sildenafil Work Compared to Vardenafil?
Sildenafil and vardenafil both improve erectile function by blocking the PDE5 enzyme, but vardenafil is more selective and less likely to affect vision. These medications work by enhancing the nitric oxide–cGMP pathway, which plays a central role in achieving and maintaining an erection during sexual stimulation.
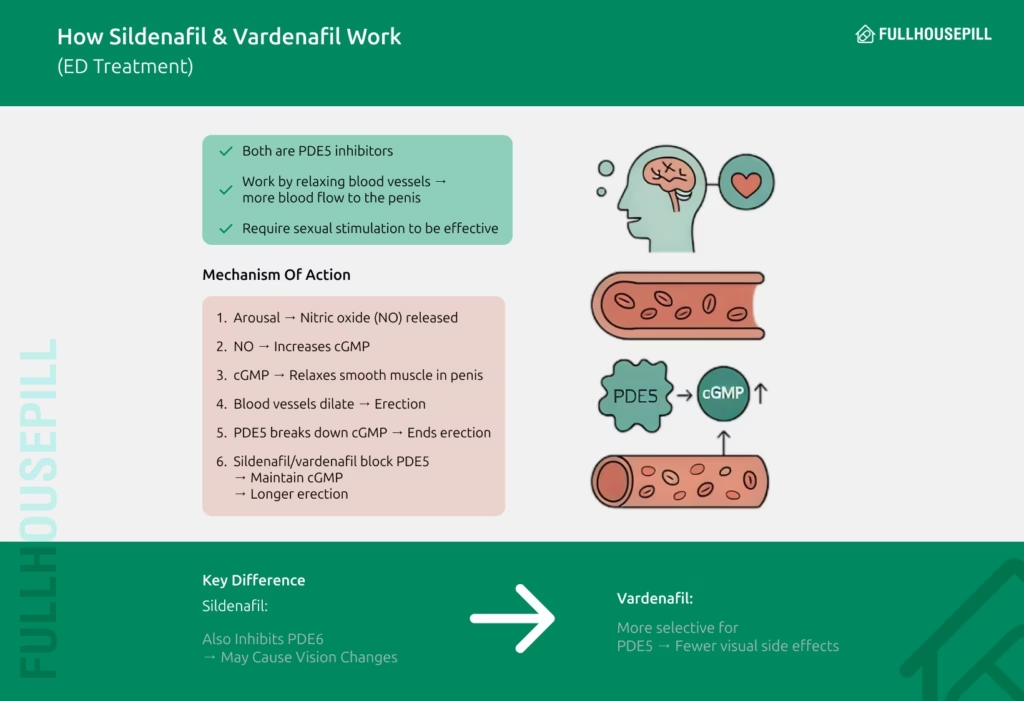
Sexual arousal triggers the release of nitric oxide (NO) in the penile tissues. NO stimulates the production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which relaxes the smooth muscle within the corpus cavernosum. This relaxation leads to vasodilation or widening of the blood vessels, allowing increased blood flow into the penis and resulting in an erection.
The enzyme phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) regulates this process by breaking down cGMP. When PDE5 acts too quickly, it reduces cGMP levels prematurely, limiting the duration and firmness of the erection. Sildenafil and vardenafil both inhibit PDE5, preventing the rapid breakdown of cGMP. This helps sustain the erection long enough for satisfactory sexual activity. However, sexual stimulation remains essential for these drugs to be effective, as they do not initiate erections on their own.
The core difference lies in enzyme selectivity. Vardenafil exhibits a higher degree of selectivity for PDE5, which means it is less likely to affect other phosphodiesterases in the body. Sildenafil also inhibits PDE6, an enzyme found in the retina. As a result, users of sildenafil may experience mild, temporary visual disturbances, such as a bluish tint or blurred vision, which are significantly less common with vardenafil.
Although the mechanisms of action are nearly identical, sildenafil and vardenafil differ slightly in pharmacokinetics. Vardenafil tends to act slightly faster and has marginally greater potency at lower doses, while sildenafil is more widely used and studied, with broader therapeutic applications.
How Fast Does Sildenafil Work Compared to Vardenafil?
Sildenafil and vardenafil both start working within 30 to 60 minutes, though vardenafil may act slightly faster in some users. These oral PDE5 inhibitors are rapidly absorbed and typically taken about one hour before sexual activity. However, individual responses may vary based on metabolism, food intake, and other physiological factors.
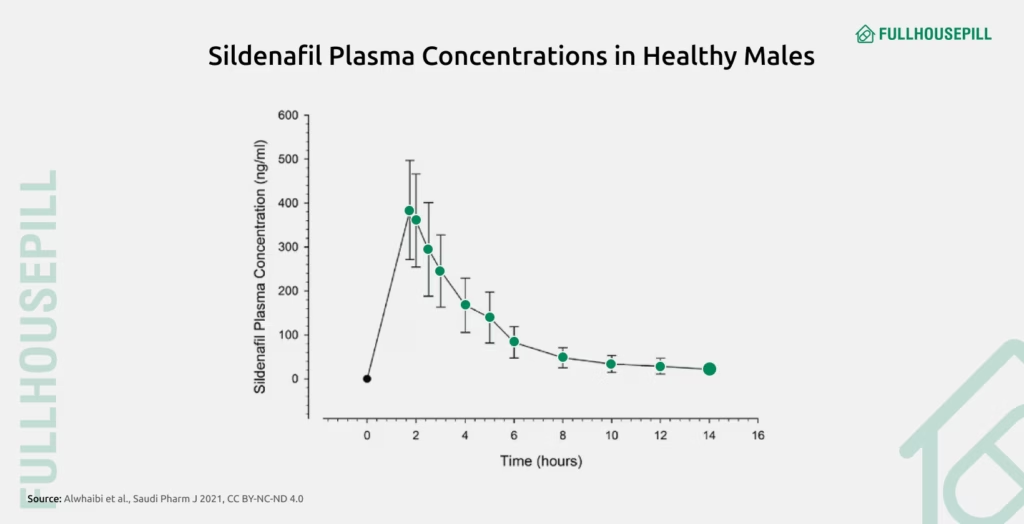
Vardenafil has been shown to begin working in as little as 10 minutes in some patients. Sildenafil, on the other hand, may start working as early as 12 minutes, although the average onset time is around 27 minutes. Both drugs usually reach their maximum plasma concentration, Cmax, within 1 hour: approximately 0.7 hours for vardenafil and 0.8 to 0.9 hours for sildenafil. This slight difference in absorption speed is not considered clinically significant for most men.
A key factor affecting onset time is food. High-fat meals can delay sildenafil absorption by about one hour and may reduce its overall effectiveness if taken too close to dosing. Vardenafil is also affected by high-fat meals, but to a lesser extent. Moderate-fat meals do not appear to delay its onset significantly. For optimal results, both medications are best taken on an empty stomach or after a light meal.
Overall, both drugs produce noticeable effects within an hour, with vardenafil having a slight edge in terms of rapid action in some cases.
Which Lasts Longer: Sildenafil or Vardenafil?
Sildenafil and vardenafil both remain effective for about 4 to 6 hours, though vardenafil may last slightly longer in some users. The duration of action for each drug is closely tied to its elimination half-life. Half-life is the time it takes for the concentration of the drug in the bloodstream to reduce by 50%.
Sildenafil has a half-life of approximately 4 hours. This means that four hours after ingestion, only half the drug remains active in the system. As the concentration drops, the drug’s effectiveness diminishes, though it may continue to offer some clinical benefit for up to 12 hours in certain individuals, depending on factors like metabolism, age, and dosage.
Vardenafil has a slightly longer half-life, ranging from 4 to 5 hours. This gives it a modest edge in terms of staying power, with effects sometimes lasting 8 to 10 hours. However, the difference is not dramatic enough to strongly favor one drug over the other in most treatment scenarios.
For men seeking longer windows of sexual activity, tadalafil may be a better option. Tadalafil has a half-life of 17.5 hours and remains active in the body for up to 36 hours, making it a preferred choice for spontaneity across an entire day or weekend.
While the peak effects of both sildenafil and vardenafil occur within the first few hours, residual efficacy can extend well beyond the standard 4 to 6-hour window, especially at higher doses or in men with slower metabolism.
Which Medication Gives a Harder Erection: Sildenafil or Vardenafil?
Sildenafil and vardenafil are equally effective in producing hard erections, with no significant difference in their ability to improve rigidity. Both medications enhance erectile function by increasing blood flow to the penis, and clinical trials show that they have similar efficacy and patient satisfaction rates.
Sildenafil (Viagra) demonstrates a success rate of up to 90% in clinical studies. Vardenafil (Levitra) also achieves comparable results, with many men reporting strong erections and successful penetration. While some studies note a patient preference for vardenafil due to its slightly faster onset or longer effect, others highlight better response with sildenafil. These variations often reflect individual differences rather than drug superiority.
In clinical terms, sildenafil and vardenafil are considered “non-inferior,” meaning they are equally effective in restoring erectile firmness and durability. However, there are cases where men who do not respond adequately to sildenafil may benefit from switching to vardenafil, especially if they have specific vascular conditions or side effect sensitivities.
What Are the Usual Dosages of Sildenafil or Vardenafil?
The standard dosages of sildenafil and vardenafil are customized based on individual needs. Sildenafil is typically started at 25 mg or 50 mg, depending on age, health status, and concurrent medications, and can be increased to a maximum of 100 mg per dose, not exceeding one dose per day.
Vardenafil is generally started at a lower dose, often 5 mg, with adjustments up to 20 mg per dose if needed. In some cases, especially in older adults or those with liver issues, the starting dose may be as low as 2.5 mg. Like sildenafil, it should be taken about one hour before anticipated sexual activity, with a maximum frequency of once daily.
Both drugs are prescribed as on-demand therapies, and dose adjustments are based on effectiveness, side effects, and patient-specific factors such as age, comorbidities, and drug interactions.
| Sildenafil | Vardenafil | |
| Usual Dose Range | 25 to 100 mg | 2.5 to 20 mg |
| Maximum Single Dose | 100 mg | 20 mg |
| How Often to Take | Once a day | Once a day |
| Usual Situations for Lower Doses | – Elderly patients (65 years and older): 25 mg- Liver problems: 25 mg- Severe kidney problems: 25 mg | – Elderly patients (65 years and older): 2.5 to 5 mg- Mild or moderate liver issues: start at 5 mg, max 10 mg- Kidney problems: usually no change needed |
| When to Take It | Approximately 1 hour before sex | Approximately 1 hour before sex |
What Are the Side Effects of Sildenafil vs Vardenafil?
Sildenafil and vardenafil share similar side effects, most of which are mild and short-lived, but they differ in visual impact and cardiac risk. Both medications can cause headaches, flushing, nasal congestion, indigestion, dizziness, or muscle aches. These symptoms typically resolve within a few hours and are not cause for concern unless they persist or worsen. Refer to the table below for the most common side effects of both the drugs.
| Side Effect | Sildenafil | Vardenafil |
| Headache | Common | Common |
| Flushing (warmth, redness in the face or the skin) | Common | Common |
| Upset stomach | Common | Common |
| Stuffy or runny nose | Common | Common |
| Muscle ache or back pain | Common | Common |
| Nausea | Common | Common |
| Dizziness/feeling lightheaded | Common | Common |
| Skin rash | Common | Less common |
| Flu-like symptoms | Not associated with sildenafil | Less common |
| Vision changes (blue tint, blurry, light sensitivity) | Rare, but possible | Less common than sildenafil |
| Nosebleeds | Less Common | Not associated with vardenafil |
| Severe allergic reaction | Rare | Rare |
| Painful, prolonged erection (priapism) | Rare | Rare |
| Sudden vision loss | Rare | Rare |
| Sudden hearing loss | Rare | Rare |
| Low blood pressure (hypotension) | Rare | Rare |
| Irregular heart rhythm (QT prolongation) | Not associated with sildenafil | Rare |
Sildenafil is more commonly associated with visual disturbances. These may include a blue tint to vision, blurred vision, or increased light sensitivity. This occurs because sildenafil inhibits not just phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), but also PDE6, an enzyme found in the retina. As a result, some men may notice temporary changes in color perception or clarity after taking sildenafil.
Vardenafil, in contrast, is more selective for PDE5 and has minimal impact on PDE6. Therefore, it is far less likely to cause vision-related side effects. Clinical data show that fewer than 10% of vardenafil users report any visual issues, making it a preferred option for men concerned about ocular effects.
What Drugs Should Not Be Taken With Sildenafil or Vardenafil?
Sildenafil and vardenafil should not be taken with certain medications due to dangerous drug–drug interactions that can lower blood pressure or increase toxicity. The most serious interactions occur with nitrates, guanylate cyclase stimulators, and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. These interactions may cause life-threatening drops in blood pressure, cardiac issues, or serious side effects. Below is a list of drugs you should avoid if you are receiving ED treatment with sildenafil or vardenafil.
| Drug Types | Examples | Possible Results of Interactions with Sildenafil or Vardenafil |
| Nitrates (used for treating heart diseases like angina/ chest pain) | Nitroglycerin, Isosorbide dinitrate/mononitrate, Amyl nitrite | Severe hypotension (a sudden, dangerous drop in blood pressure); increases nitrate effect. Absolutely contraindicated. |
| Guanylate Cyclase Stimulators (used for treating pulmonary arterial hypertension or PAH) | Riociguat (Adempas), Vericiguat (Verquvo) | Dangerous BP-lowering effects. Absolutely contraindicated. |
| Blood Pressure Medications (e.g., antihypertensive agents to treat high blood pressure) | Alpha-blockers (Prazosin), Calcium channel blockers (Amlodipine), angiotensin receptor blockers or ARBs (Losartan), Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists (Clonidine) | BP-lowering vasodilatory effects; may cause dizziness/fainting. Use with doctor’s guidance. |
| PDE5 Inhibitors or Other ED Drugs | Avanafil, Tadalafil | Risk of overdose and side effects. Do not combine. |
| Certain Antifungal Drugs | Ketoconazole and other CYP3A4 inhibitors, Itraconazole, Fluconazole, Posaconazole, Levoketoconazole | Increase sildenafil/vardenafil levels or toxicity. Use with caution. Dose adjustment may be needed. |
| Certain Antibiotics | Erythromycin or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors, Clarithromycin, Azithromycin | Increase sildenafil/vardenafil levels, toxicity or other symptoms e.g., irregular heart beat. Dose adjustment may be needed. |
| HIV Protease Inhibitors | Ritonavir and other strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, Atazanavir | Increase sildenafil/vardenafil concentration or adverse events.Lower doses may be required |
| QT interval Prolongation Drugs | Amiodarone and other CYP450 inhibitors, Sotalol, Haloperidol, Ziprasidone, Pimozide, Bepridil | Risk of arrhythmia, toxicity. Use with doctor’s advice. Vardenafil comes with a warning for QTc prolongation patients. |
| Medications for Treating Prostate Problems e.g., benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH | Alpha blockers like Tamsulosin, Alfuzosin | Risk of orthostatic hypotension. Use with doctor’s advice. |
| Herbal Remedies/Supplements | Not well studied | Unknown safety. Avoid unless approved by a doctor. |
Which Foods Interact with Sildenafil or Vardenafil?
Grapefruit, fatty meals, and alcohol are the primary food and beverage interactions to avoid when using sildenafil or vardenafil. These substances can alter how the body absorbs or metabolizes PDE5 inhibitors, reducing their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects.
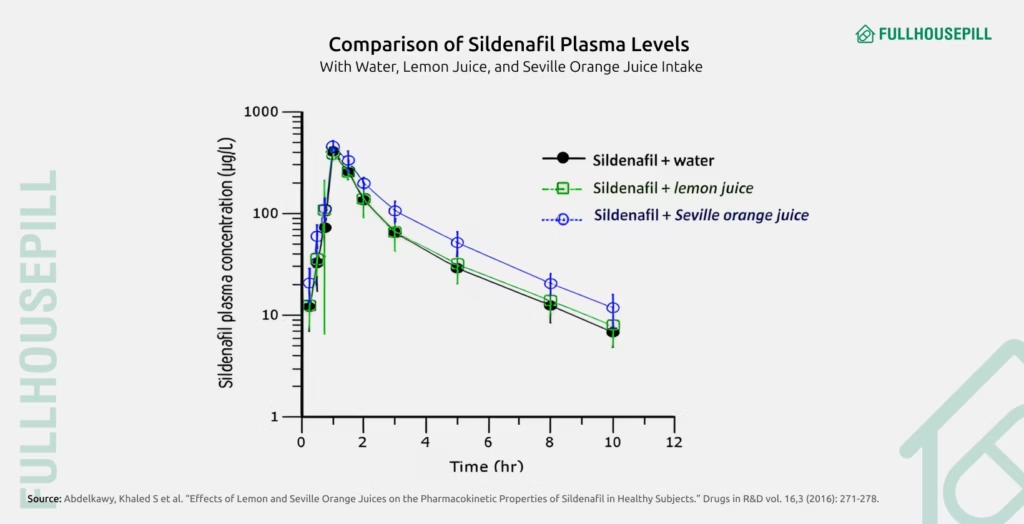
Grapefruit and similar citrus juices, including pomelo and pomegranate, contain compounds that inhibit the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A4. This enzyme helps break down sildenafil and vardenafil in the liver and intestines. When inhibited, blood levels of these drugs rise, potentially causing side effects like headache, flushing, or dangerously low blood pressure. Avoid taking Viagra or Levitra within 72 hours of drinking grapefruit or pomelo juice.
Seville orange juice may slightly accelerate drug absorption, but the effect is not clinically significant. Still, this juice is less commonly consumed and not recommended for consistent use with ED medications.
Heavy or high-fat meals like fried foods or rich dairy products can delay the absorption of sildenafil and vardenafil. This may slow the onset of action by up to one hour, making the medication less predictable. Sildenafil is best taken on an empty stomach for optimal results, as recommended by the UK’s National Health Service (NHS). Vardenafil is less affected by food overall, but a fatty meal may still slightly delay its onset.
Alcohol consumption while on PDE5 inhibitors increases the risk of side effects such as flushing, headache, dizziness, or orthostatic hypotension (sudden drops in blood pressure upon standing). Alcohol is a vasodilator like sildenafil and vardenafil, and the combination can intensify cardiovascular effects. Avoid excessive alcohol intake when using these medications.
Orally disintegrating tablet (ODT) forms of vardenafil do not require water or milk for ingestion. These formulations dissolve directly in the mouth and are unaffected by food or drink.
Which Is More Affordable: Sildenafil vs Vardenafil?
Sildenafil is usually more affordable than vardenafil with generic sildenafil starting at $5 per tablet and generic vardenafil costing around $20 per tablet. However, their brand name versions like Viagra and Levitra are more expensive, with costs starting from $65 per tablet.
Which Is Safer: Sildenafil or Vardenafil?
Vardenafil may be slightly safer than sildenafil for men concerned about vision changes, but both drugs are generally safe, effective, and well-tolerated in most patients.
The key safety distinction between the two lies in their enzyme selectivity. Sildenafil inhibits both PDE5 and PDE6, the latter of which is present in the retina. As a result, some users experience visual disturbances such as blurred vision or difficulty distinguishing blue and green shades. These effects are rare but are more likely with sildenafil than vardenafil. Vardenafil is more selective to PDE5 and does not significantly affect PDE6, making vision-related side effects less likely.
Outside of this visual safety margin, both drugs share a similar safety profile. They are FDA-approved for the treatment of erectile dysfunction and are widely used worldwide. Common side effects are typically short-lived and dose-dependent. These effects tend to subside within a few hours and rarely require discontinuation of the medication.
Both sildenafil and vardenafil are considered safe for use in men with serious health conditions, including diabetes, prostate cancer, or mild to moderate heart disease, under medical supervision. In patients with coronary artery disease, sildenafil may be used if nitrates and alpha-blockers are avoided, as combining these medications can cause dangerous drops in blood pressure.
Before using either drug, your healthcare provider must evaluate your medical history to reduce risk. Special precautions are needed for men with:
- Allergies to sildenafil, vardenafil, or excipients in the tablet
- Angina who are taking nitrate medications
- NAION (non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy) or vision loss
- Stomach ulcers or active gastrointestinal bleeding
- Anatomical penile abnormalities, such as Peyronie’s disease
- Cardiovascular disorders, including recent stroke or heart attack
- Diabetes, especially with complications like neuropathy
- Blood clotting disorders, such as sickle cell anemia or hemophilia
- Eye disorders, including retinitis pigmentosa
- Low blood pressure (hypotension) or unstable blood pressure
- Severe liver or kidney disease, which may require dose adjustment
Is Vardenafil Stronger Than Sildenafil?
Vardenafil is more potent and selective than sildenafil, but both have comparable efficacy in treating erectile dysfunction. Vardenafil is biochemically 20 times more potent as a PDE-5 inhibitor than sildenafil. This greater potency is due to its stronger binding affinity and higher selectivity for the PDE-5 enzyme, which plays a central role in regulating penile blood flow. Structurally, vardenafil and sildenafil differ only slightly, by two chemical groups, but these minimal differences significantly increase vardenafil’s molecular efficiency.
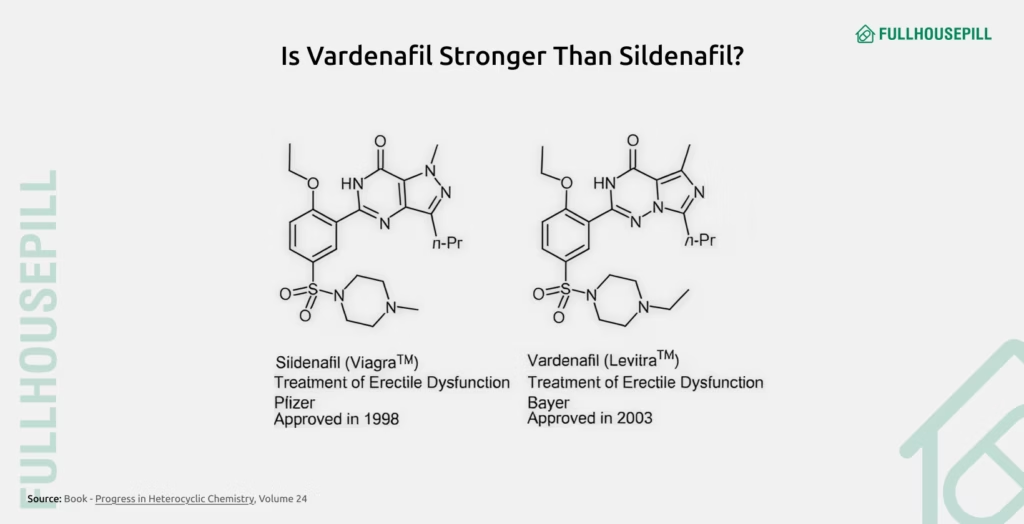
Because of its higher potency, vardenafil works effectively at lower doses. It is available in 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg oral tablet strengths. In contrast, sildenafil dosing typically starts at 25 mg and can be increased up to 100 mg based on individual response and tolerability. For example, a 10 mg dose of vardenafil may deliver the same level of therapeutic benefit as a 50 mg dose of sildenafil.
However, potency refers only to the amount of drug needed to trigger a response, not the strength or quality of that response. Efficacy is the ability of a drug to achieve its intended therapeutic effect, and on this front, both sildenafil and vardenafil perform equally well. Clinical studies consistently show that the two drugs result in similar rates of improved erections, successful intercourse, and overall sexual satisfaction.
This means higher sildenafil doses do not imply inferior results. Instead, it simply takes a bit more sildenafil to reach the same biochemical effect that a smaller amount of vardenafil can provide. Once the target dose is reached, both medications are equally effective in producing strong, reliable erections during sexual stimulation.
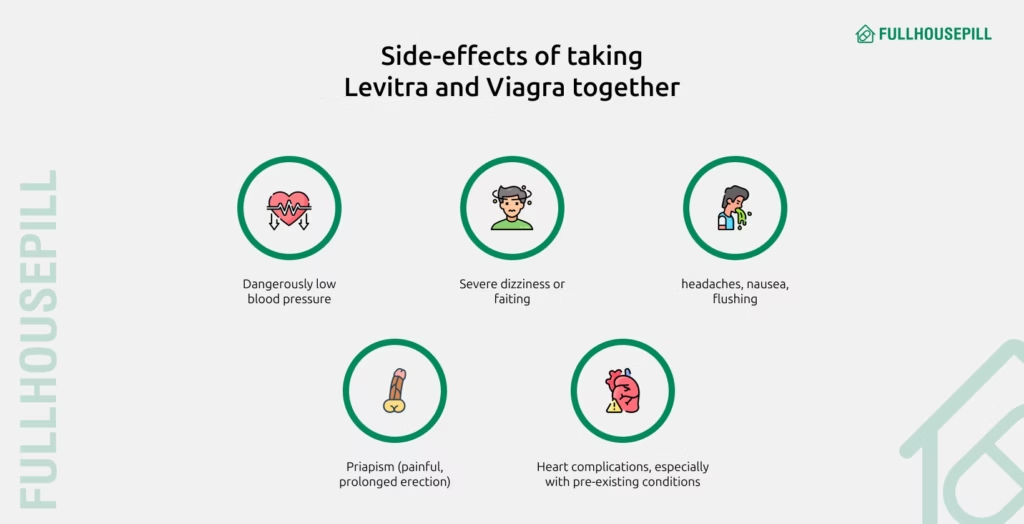
Can You Take Levitra and Viagra Together?
No, you should not take Levitra (vardenafil) and Viagra (sildenafil) together. Both medications belong to the same class, PDE5 inhibitors, and work by increasing blood flow to the penis. Taking them together increases the risk of side effects such as low blood pressure, severe headaches, dizziness, and even priapism. Each drug is potent on its own, and combining them offers no additional benefit but heightens the risk of harm. If one medication is not effective, consult your doctor before switching or adjusting the dose.
How to Choose the Right ED Pills?
Choosing the right medication depends on your health, lifestyle, and how long you want the effects to last. Some men prefer fast-acting drugs like sildenafil, while others opt for long-acting ones like tadalafil. Others may respond better to vardenafil, which is known for fewer vision-related side effects. When selecting the best erectile dysfunction pills, consider your medical history, current medications, and how quickly you need the drug to work. Consulting with a healthcare provider ensures a safe and personalized choice.
How Is Sildenafil Compared With Tadalafil?
Sildenafil is shorter-acting, while tadalafil offers a longer duration of action. Sildenafil vs tadalafil comparisons show that sildenafil (Viagra) typically works within 30–60 minutes and lasts for 4-6 hours, making it suitable for planned intercourse. Tadalafil (Cialis), on the other hand, can last up to 36 hours, offering more spontaneity. Both drugs are equally effective, but the choice depends on how often and when you want to be sexually active.
Is There a Generic Alternative to Levitra (Vardenafil)?
Yes, Vilitra is a generic alternative to brand-name Levitra. It contains the same active ingredient, vardenafil, and offers comparable efficacy and safety. Vilitra is often preferred by men looking for a more affordable option to manage erectile dysfunction. Other generic alternatives include Staxyn and Vivanza. These formulations all contain the same active ingredient and deliver similar results, but may vary in form, excipients, or pricing. Always ensure that generics are sourced from reputable pharmacies and approved by regulatory agencies.
Is There a Generic Alternative to Viagra (Sildenafil)?
Yes, Cenforce and Suhagra are generic versions of Viagra. Both contain sildenafil citrate and are used to treat erectile dysfunction by improving penile blood flow. Chttps://fullhousepill.com/erectile-dysfunction/sildenafil-citrate/cenforceenforce is available in various strengths, while Suhagra is often recommended for its consistent performance. These generics are widely available and cost-effective but should be taken under medical supervision. Below is a table with a list of generics of Viagra and their manufacturers.
| Brand Name | Manufacturer |
| Cenforce | Centurion Laboratories |
| Aronix | Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories |
| Liberize | Dexcel Pharma |
| Nipatra | Amdipharm Mercury |
| Kamagra | Ajanta Pharma |
| Suhagra | Cipla Ltd |
| Silagra | Cipla Ltd |
| Edegra | Sun Pharmaceutical |
| Penegra | Zydus Cadila |
| Generic Sildenafil | Torrent Pharmaceuticals |
How Do ED Drugs Compare in Terms of Duration?
Tadalafil lasts the longest, while sildenafil and vardenafil offer shorter durations. The answer to the general query, “How long does sildenafil last?” is about 4–6 hours. Vardenafil has a similar duration but may work better for some men with fewer side effects. Tadalafil stands out with a half-life of 17.5 hours and effectiveness lasting up to 36 hours. The best choice depends on how frequently you engage in sexual activity and whether you prefer spontaneity or scheduled dosing.
