Sildenafil (Viagra) typically lasts for 4 to 6 hours, with peak effects occurring around 1 hour after ingestion. Its onset, duration, and clearance from the body depend on factors such as dosage, metabolism, age, diet, and health conditions.
Sildenafil citrate, sold under brand names like Viagra, is the first FDA-approved phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor for treating erectile dysfunction (ED). At lower doses, doctors may also prescribe it for pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). The medication works by promoting vasodilation, which enhances blood flow to the penis and enables an erection in response to sexual stimulation.
When taken orally, sildenafil typically starts working within 30 to 60 minutes, with maximum effectiveness around the 1-hour mark. A clinical study published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology reported that 71% of men experienced an erection within 30 minutes when sexually stimulated. The effects are most noticeable during the 4 to 6-hour therapeutic window, but some men may still experience mild effects for up to 12 hours, though this is not consistent across all users.
The body metabolises sildenafil gradually, reducing its effectiveness over time. It has an average half-life of about 4 hours, which means half the dose is cleared from the system in that time. In most cases, the drug is almost entirely eliminated within 16 to 20 hours, although traces may remain for up to 24 hours depending on individual metabolic rates and organ function.
What is Sildenafil and How Does it Work?
Sildenafil citrate, the active compound in Viagra, belongs to the phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor class of drugs. According to the article by Benjamin P. Smith and Mary Babos published in StatPearls (Sildenafil), the drug works by inhibiting the phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) enzyme. PDE5 typically breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a key molecule in the erectile response.
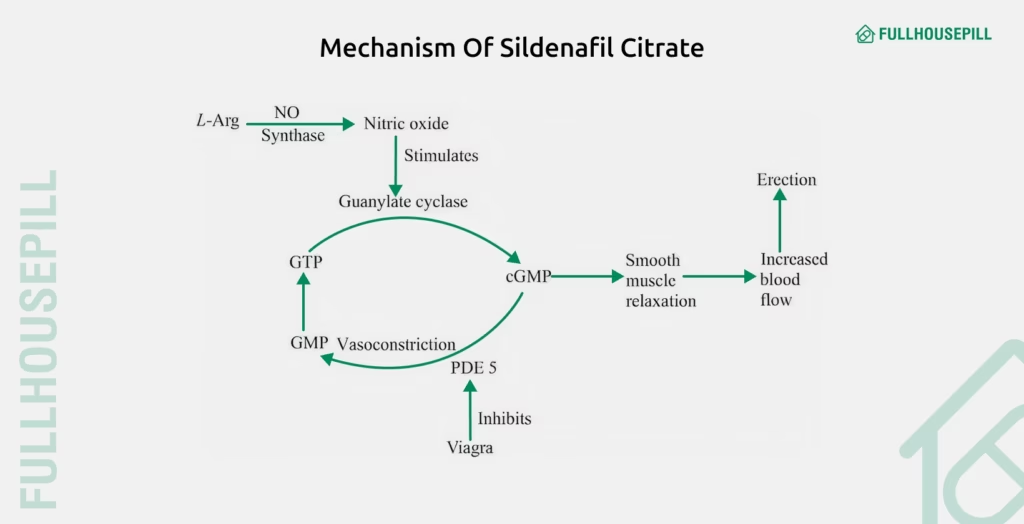
Sexual stimulation triggers the release of nitric oxide in the corpus cavernosum, which increases cGMP levels and promotes smooth muscle relaxation, allowing greater penile blood flow. When PDE5 rapidly degrades cGMP, it disrupts this process, often leading to erectile dysfunction. By mimicking the structure of cGMP, sildenafil binds to and blocks PDE5. Hence, preserving cGMP levels for longer durations.
This mechanism makes sildenafil tablets a widely trusted option for men seeking firmer, more sustained erections during sexual activity. Higher cGMP levels activate protein kinase G, which enhances muscle relaxation and facilitates adequate blood inflow into the penis.
How Fast does Sildenafil Work?
Sildenafil typically starts working within 30 to 60 minutes, with onset as early as 12 minutes in some men. This window depends on the individual’s metabolism, dose, and whether the drug is taken on an empty stomach. According to the 2002 study, the median time to erection onset after taking 50 mg sildenafil was 27 minutes, with a range of 12 to 70 minutes. In the group treated with sildenafil, about 80% of the patients responded to the drug within 45 minutes. Moreover, as many as 71% of the patients were able to achieve an erection within 30 minutes of dosing.
The study concluded that sildenafil citrate gives a penetrable erection to most patients within 12 minutes of intake, and the duration of action lasts at least 4 h. The peak action time is between half an hour to 2 hours. The effective duration of sildenafil, according to the original research study published in The Journal of Sexual Medicine in 2004, is 12 hours.
How Long does Sildenafil Last?
Sildenafil delivers peak effectiveness within 1 to 2 hours and remains clinically effective for at least 8 hours in most men. In some individuals, partial effects may persist up to 12 hours, but the maximum efficacy diminishes after 4 hours.
Data suggests that sildenafil remains effective for at least 8 hours, and it lasts for even 12 hours in some individuals. However, the effects are at full potency after 4 hours of ingesting a Viagra tablet. Of course, how fast the drug works and how long it lasts depend on a couple of factors-
- Food: Having sildenafil on an empty stomach helps it achieve the best efficiency
- Alcohol and grapefruit dampen sildenafil’s effect

How Long does Sildenafil Stay in Your System?
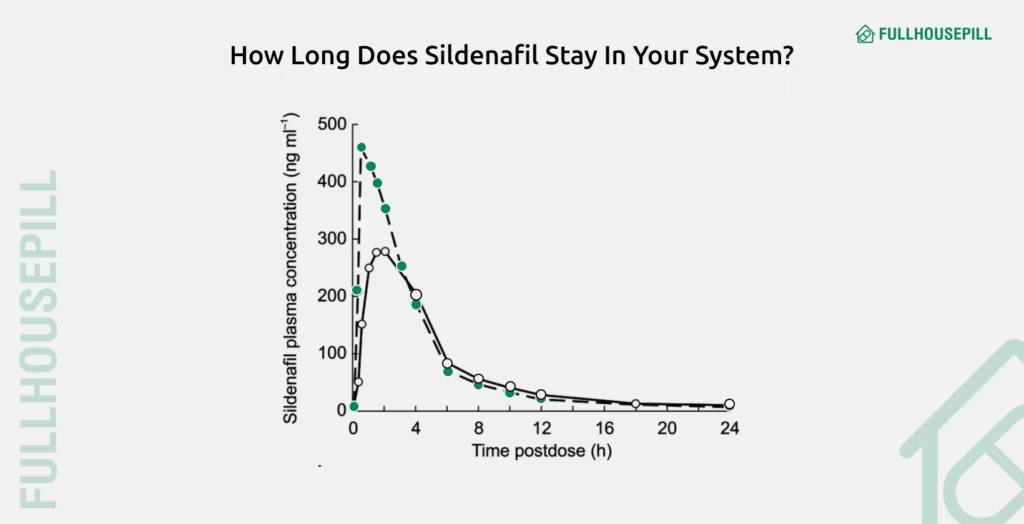
Sildenafil remains detectable in the bloodstream for up to 24 hours, although its clinical effect wears off much earlier. A 2002 BJCP study examined sildenafil’s pharmacokinetics and found that trace levels of the drug could still be identified up to 32 hours after administration. However, the concentration drops significantly, becoming negligible after 24 hours. This pharmacokinetic profile supports the standard recommendation of once-daily dosing and reinforces that sildenafil does not accumulate in the system when used as directed.
How Does Sildenafil Dosage Affect How Long It Lasts?
Higher doses of sildenafil produce longer-lasting effects, but they also increase the risk of side effects. This relationship is governed by the drug’s terminal half-life and dose-dependent pharmacokinetics.
According to the pharmacokinetic data from the 2002 British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology study, sildenafil has a terminal half-life of about 4 hours, meaning that after 4 hours, only 50% of the drug remains in circulation. This means higher doses (e.g., 100 mg) remain at effective concentrations longer than lower doses (e.g., 25 mg), although the elimination rate stays constant.
| Sildenafil Dose | Effective Lasting Time |
| 25 mg | 2 hours |
| 50 mg | 4 hours |
| 100 mg | 8 hours |
| 200 mg | 16 hours |
- 25 mg: Typically used in older adults or those with renal or hepatic impairment; wears off faster due to lower concentration.
- 50 mg: Standard starting dose for most patients; balances efficacy and tolerability.
- 100 mg: Often prescribed when 50 mg provides insufficient results; offers stronger and more sustained effect.
- 200 mg: Sometimes used as salvage therapy in patients unresponsive to 100 mg; not FDA-approved and linked with a significantly higher risk of adverse events like headaches, flushing, or vision disturbances.
Although higher doses may extend the duration of effect, they must be prescribed cautiously due to the increased potential for systemic side effects and drug accumulation.
What Affects the Effectiveness and Duration of Sildenafil?
Sildenafil’s potency and longevity depend on timing, food intake, interacting substances, concomitant medications, and sexual stimulation. It must be taken 30 to 60 minutes before engaging in sex for best results. Under no circumstances should it be taken more than four hours before sex, as it would have lost most of its potency by then.
Additionally, sildenafil absorbs fastest on an empty stomach; a fatty meal delays onset and reduces peak effect. Fatty meals (e.g., cheeseburger and fries) can postpone onset by 1–2 hours. Light meals (e.g., salad and grilled chicken) have minimal impact on absorption.
Similarly, alcohol and grapefruit juice lower sildenafil levels by accelerating metabolism, reducing both efficacy and duration. Alcohol (e.g., beer and wine) can impair blood flow and delay action. Grapefruit juice inhibits CYP3A4, accelerating drug breakdown.
Certain medications interfere with the working of sildenafil and hence, should be avoided. Refer to the list below for the medicines that can reduce or alter the effectiveness of sildenafil.
- Alpha-blockers (alfuzosin and doxazosin)
- Beta-blockers (atenolol)
- Oral antifungals (ketoconazole)
- HIV Protease inhibitors (ritonavir)
- Anticoagulants (warfarin)
- Cimetidine
- Amlodipine
- Erythromycin
- Efavirenz
- Nitroglycerin
Sildenafil’s onset and duration remain optimal when taken under fasting conditions 30-60 minutes before intimacy, avoiding alcohol, grapefruit, and interacting medications, and in conjunction with adequate sexual arousal.
Can You Make Sildenafil Last Longer?
Yes, you can make sildenafil last longer by optimizing how and when you take it. Take the tablet on an empty stomach, as fatty meals can delay absorption and reduce potency. Avoid alcohol and grapefruit juice, both of which interfere with sildenafil’s metabolism and can shorten its effective window. For best results, time the dose 30 to 60 minutes before sexual activity, and avoid using it more than four hours in advance, as its potency drops significantly after that. Always check for potential drug interactions, which can reduce effectiveness or increase side effects. Most importantly, sildenafil only works with sexual stimulation, so arousal is essential to trigger its mechanism. Making these adjustments won’t change the drug’s half-life, but they can help extend its effectiveness and improve results.
Does Viagra Make You Last Longer In Bed?
Viagra may help some men last longer in bed, but it is not a direct treatment for premature ejaculation. Viagra (sildenafil) works by improving blood flow to the penis, which enhances erectile firmness and allows men to maintain an erection for longer. While it is not approved by the FDA to treat premature ejaculation (PE), several clinical studies suggest it can offer meaningful benefits for men who experience both PE and erectile dysfunction (ED).
One clinical trial published in The Journal of Sexual Medicine followed 111 men with PE and found that those taking sildenafil experienced a greater increase in intravaginal ejaculatory latency time (IELT) than those on placebo. They also reported better control over ejaculation, increased confidence, and higher sexual satisfaction. Another six-month study published in International Journal of Urology (2007) compared sildenafil with paroxetine and the squeeze technique, showing that sildenafil produced the highest gains in IELT and intercourse satisfaction. A separate crossover study published in Human Reproduction, Volume 15, involving 20 healthy men, found that sildenafil reduced the post-ejaculatory refractory period from 10.8 ± 0.9 min to 2.6 ± 0.7 min, allowing men to get a second erection faster.
These results suggest that when men achieve consistently firm erections, they can better manage arousal and delay ejaculation. A shorter refractory period also supports repeat intercourse within a short timeframe. The drug’s impact may be partly psychological, as improved performance often reduces anxiety and builds confidence. Biologically, sildenafil boosts nitric oxide and cGMP levels, which may reduce penile sensitivity and prolong ejaculatory control. Although Viagra is not a dedicated PE medication, it can help men last longer if they struggle with both erection quality and early climax.
Does Viagra Help With Sexual Performance?
Yes, Viagra significantly improves sexual performance by enhancing erectile quality, maintaining erection duration, and reducing the refractory period between erections. The Archives of Internal Medicine meta-analysis reported that 78% of men using sildenafil experienced improved erections compared to 25% on placebo. The same review showed higher successful intercourse rates and overall sexual function improvement across varied populations, including men with diabetes, spinal cord injury, and post-prostatectomy.
Long-term studies published in PMC confirmed that these benefits persisted over 36-52 weeks, with high patient retention and 96% satisfaction regarding erectile effects. Viagra’s efficacy stems from its inhibition of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), which enhances the nitric oxide-cGMP pathway during sexual stimulation. This leads to increased blood flow, harder erections, and longer-lasting arousal responses.
Research in Nature Reviews Urology also found that men without diagnosed erectile dysfunction showed measurable improvements in erection duration and recovery time between erections. These physiological outcomes establish that Viagra contributes directly to sexual performance by improving the reliability, firmness, and consistency of erections in both ED and non-ED men.
How does Sildenafil Compares to Other Oral Medications?
Sildenafil is fast-acting and widely used, but it has a shorter duration than some newer erectile dysfunction (ED) medications. It belongs to a class of drugs called PDE5 inhibitors, which also includes vardenafil, avanafil, and tadalafil. These medications share a similar mechanism, enhancing blood flow to the penis, but differ in onset, duration and elimination time. Choosing the right one depends on your needs for onset speed, duration, flexibility, and side effect tolerance. The table below compares key pharmacokinetic properties of these oral ED medications:
| Drug | Half-life | Peak Response Duration |
| Sildenafil | 4 hours | 60-80 minutes |
| Vardenafil | 4 hours | 30-60 minutes |
| Avanafil | 6 hours | 20-40 minutes |
| Tadalafil | 17.5 hours | 120 minutes |
Tadalafil Vs Sildenafil: Which Is Better?
Tadalafil is often preferred for its longer duration, while sildenafil may work better for shorter windows of intimacy. Both are effective phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors that treat erectile dysfunction by increasing blood flow to the penis. However, when comparing sildenafil vs tadalafil, the decision often comes down to how long you want the medication to last and how frequently you plan to engage in sexual activity. Tadalafil stays active for up to 36 hours, making it more flexible for spontaneous use. Sildenafil, on the other hand, works for 4 to 6 hours and is ideal for planned encounters. Your choice should align with your lifestyle and expectations around timing.
Vardenafil Vs Sildenafil: Which is more effective and longer-lasting?
Vardenafil and sildenafil are equally effective for most men with erectile dysfunction, but subtle differences may make one a better fit than the other depending on individual needs. Both are PDE5 inhibitors that enhance blood flow to the penis and typically last 4 to 6 hours. However, vardenafil may be slightly less affected by food intake and has been shown in some studies to have a marginally stronger effect at comparable doses. When comparing sildenafil vs vardenafil, men who experience inconsistent results with one may benefit from trying the other, especially if dietary timing or mild gastrointestinal side effects are a concern. The right choice often comes down to personal response and tolerability.
Can Sildenafil Be Taken With Alcohol?
It is generally safe to consume small amounts of alcohol while using sildenafil, but excessive drinking can reduce its effectiveness and increase side effects. Alcohol is a central nervous system depressant that can interfere with the blood flow needed for an erection. It may also lower blood pressure, which, when combined with sildenafil, can lead to dizziness, headache, or fainting. When combining Viagra and alcohol, moderation is key. Limiting intake to one or two drinks can help maintain erectile function while minimizing health risks.
Does Sildenafil Help You Last Longer During Sex?
No, it can only treat erectile dysfunction, that is, help you achieve an erection during sex. But it cannot enhance your stamina or make you last longer.
How Much Sildenafil is Too Much?
If you are on a prescription (50 or 100 mg per day), do not take more than one tablet within 24 hours. Although 200 mg is prescribed by some doctors, it is not a safe dose. An overdose of sildenafil may result in severe side effects (nausea, rashes, breathlessness, palpitations, priapism, loss of vision, etc.) and should be avoided at all costs.
How Much Sildenafil Is Too Much?
The maximum recommended sildenafil dosage for erectile dysfunction is 100 mg within 24 hours. Taking more than this increases the risk of side effects such as headaches, dizziness, vision changes, and dangerously low blood pressure. Overdose can lead to serious complications, including priapism (a prolonged, painful erection) that requires urgent medical attention. Higher doses do not guarantee stronger or longer-lasting effects and may actually reduce sexual performance due to discomfort or side effects.
How Long Does Sildenafil Last Before It Expires?
Unopened sildenafil remains effective until the expiration date on its packaging, typically 2–3 years from manufacture. Once opened, sildenafil’s expiry depends on storage conditions. Heat, moisture, and light can degrade the active ingredient faster, lowering potency. Expired sildenafil is unlikely to be harmful but may not work effectively. To maintain strength, keep tablets in their original blister packs, stored in a cool, dry place. Do not use if the tablets appear discolored, crumbled, or have an unusual odor. For safety and effectiveness, replace expired medication with a fresh prescription from a healthcare professional.
