Vardenafil is a phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor prescribed for erectile dysfunction. It is sold under the brand names Levitra and Staxyn. It works by blocking the breakdown of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). This increases blood flow to the penis during sexual stimulation. Vardenafil is available as film-coated tablets in 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg strengths. It is also available as orally disintegrating tablets in 10 mg strength. The usual starting dose is 10 mg taken about 60 minutes before sexual activity. The maximum approved dose is 20 mg. Vardenafil starts working within 15-30 minutes. Peak concentration occurs at about 0.7 hours when fasting and 1.2 hours with food. Its clinical effect lasts about 4-5 hours. The elimination half-life is 4-5 hours, and most of the drug is cleared from the body within 24 hours. Vardenafil can be taken on demand or as a daily low dose of 2.5-5 mg. Food may delay absorption, but overall exposure remains unchanged. Alcohol does not change drug levels but can increase the risk of low blood pressure.
What is Vardenafil?
Vardenafil is a selective phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor that is marketed under the brand names Levitra and Staxyn. It is used as a first-line oral treatment for erectile dysfunction by enhancing the natural physiological process of penile erection. According to the study “Efficacy and safety of vardenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction” by Hellstrom et al. (2002), vardenafil showed significant improvement in erectile function compared to placebo, confirming its role as an effective treatment option.
Vardenafil works through selective inhibition of PDE5, an enzyme located in penile vascular smooth muscle cells. During sexual stimulation, nitric oxide (NO) is released from nerve endings in the penis, which activates guanylate cyclase. This activation increases production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a messenger that promotes smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation in the corpus cavernosa. According to the study “The role of cyclic GMP in mediating smooth muscle relaxation” by Lincoln and Cornwell (1993), cGMP plays a central role in penile erection through vascular smooth muscle relaxation.
PDE5 normally hydrolyzes cGMP to 5′-GMP, which terminates the erectile response and causes detumescence. By selectively inhibiting PDE5, vardenafil prevents the degradation of cGMP, leading to prolonged smooth muscle relaxation, increased blood flow to the penis, and sustained erection. According to the study “Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors: current status and future directions” by Corbin and Francis (2002), PDE5 inhibition maintains higher cGMP levels, thereby improving erectile function in men with erectile dysfunction.
What Are the Available Dosage Forms and Strengths of Vardenafil?
Vardenafil is available as film-coated oral tablets in 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg strengths, marketed as Levitra. According to the RELY-II trial, doses between 5–20 mg taken on demand achieved a 72% first-dose efficacy rate in men receiving 10 mg. It is also formulated as orally disintegrating tablets, marketed as Staxyn, in a 10 mg strength that dissolves on the tongue without water. These formulations and dosing regimens allow individualized therapy based on the timing of sexual activity and patient comorbidities.
Vardenafil2.5 mg
Vardenafil 2.5 mg is used as a once-daily low-dose regimen for daily erectile function support, especially in men with mild erectile dysfunction. According to the study by Santi et al. (2015), a 12-week randomized trial in men with type 2 diabetes showed that 2.5 mg once daily improved International Index of Erectile Function scores compared with placebo. It has lower efficacy than on-demand doses of 5–20 mg but provides continuous therapeutic plasma levels with fewer peak-related adverse events.
Vardenafil 5mg
Vardenafil 5 mg is the on-demand starting dose for as-needed sexual activity in patients with mild-to-moderate erectile dysfunction. According to the Overview of Clinical Evidence (2009), Phase II dose-finding studies showed significant improvement in erection hardness at 5 mg compared with placebo, with fewer side effects than 10 mg. It has less efficacy than 10 mg but better tolerability, making it suitable for dose escalation.
Vardenafil 10mg
Vardenafil 10 mg is the standard on-demand starting dose, taken about 60 minutes before intercourse. According to the RELY-II study by Stief et al. (2013), the first-dose success rate was 72% at 10 mg compared with 25% for placebo. It balances efficacy and tolerability and is the preferred initial dose over 5 mg in men without significant comorbidities.
Vardenafil 20 mg
Vardenafil 20 mg is the maximum recommended as-needed dose for patients requiring higher potency. According to the ENDURANCE trial by Pérez et al. (2008), this dose resulted in longer erection duration and higher intercourse success rates compared with placebo. It offers superior efficacy compared with 10 mg but with an increased incidence of headache and flushing.
Vardenafil 40 mg
Vardenafil 40 mg has been investigated as a supratherapeutic dose in early pharmacological studies. According to the Pharmacology Overview (2009), Phase I dose-escalation trials showed that single doses up to 40 mg produced incremental increases in cyclic GMP and erection rates. It provided insights into dose-response relationships but was not adopted as a standard regimen. Compared with 20 mg, it demonstrated no proportional increase in efficacy but a higher rate of treatment-related adverse events.
Vardenafil 60 mg
Vardenafil 60 mg has been studied only in investigational settings to establish pharmacokinetics and safety margins. According to the Pharmacology Overview (2009), Phase I trials using single doses up to 60 mg showed incremental increases in cGMP and erectile response. However, efficacy gains plateaued beyond 20 mg, while adverse events such as headache and flushing became more frequent. This confirmed 20 mg as the optimal maximum recommended dose, with 60 mg reserved for research and not clinical practice.
Vardenafil ODT
Vardenafil ODT is available as a 10 mg orally disintegrating tablet for patients seeking discreet dosing without water. According to a crossover study by Porst et al. (2011), the 10 mg ODT had comparable bioavailability to the 10 mg film-coated tablet, with similar onset and efficacy. It provides ease of administration and rapid absorption, and its efficacy parallels the 10 mg film-coated tablets. Another randomized crossover study by Porst et al. (2011) confirmed bioequivalence of the supralingual vardenafil tablet to conventional tablets, with rapid dissolution and reliable pharmacokinetics.
What Is the Recommended Dosage of Vardenafil?
The recommended on-demand dosage of vardenafil is 5–20 mg, taken about 60 minutes before sexual activity, with a maximum single dose of 20 mg and no more than one dose in 24 hours. The typical starting dose is 10 mg, which balances efficacy and tolerability for most patients. For men who prefer daily dosing, low-dose regimens of 2.5–5 mg once daily are available. These daily doses provide sustained improvement in erectile function with consistent therapeutic levels and good tolerability.
What Is the Maximum Dose of Vardenafil?
The maximum recommended single dose of vardenafil is 20 mg taken as needed, with at least 24 hours between doses. This limit provides the best balance of efficacy and tolerability, since higher doses did not result in proportional clinical benefits. A study also evaluated supratherapeutic doses of 40 mg and 60 mg in Phase I trials to assess pharmacokinetics and safety. The research showed that these higher doses produced more frequent headaches, flushing, and visual disturbances without meaningful additional improvement in erectile response. This confirmed 20 mg as the maximum effective and safe dose.
Is 40 mg of Levitra safe?
No, 40 mg of Levitra (vardenafil) is not safe and is not recommended for clinical use. Clinical studies have established the safety and efficacy of vardenafil only at doses of 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg. At these doses, the most common adverse effects were mild to moderate and transient, including headache, flushing, and rhinitis, with no reports of abnormal color vision. According to the study by Keating and Scott published in Drugs, vardenafil is generally well tolerated up to 20 mg, which remains the clinically recommended maximum.
There is no clinical evidence supporting the safety or efficacy of a 40 mg dose. Reviews such as Vardenafil by Keating and Scott and Levitra: Multiple Action, Prospects for Application by Vertkin et al. do not mention doses above 20 mg, and the flexible-dose study by Seftel in The Journal of Urology also lacks data on doses higher than 20 mg. Higher doses of PDE5 inhibitors like vardenafil increase the risk of serious adverse events, including cardiovascular complications and severe hypotension, particularly when combined with other medications. Literature consistently emphasizes that the maximum safe and effective dose is 20 mg.
How Should You Take and Use Vardenafil?
Vardenafil should be taken orally with water and may be used with or without food. High-fat meals delay absorption, increasing the time to peak concentration from 0.7 to 1.2 hours and reducing peak plasma levels by about 30%. For on-demand use, the recommended dose is 5-20 mg taken about 60 minutes before sexual activity. A minimum interval of 24 hours between doses is required to prevent accumulation and adverse effects, as noted in the Clinical Monograph for Drug Formulary Review (2005). In once-daily regimens, low-dose vardenafil at 2.5-5 mg provides continuous plasma levels.
Can I take Vardenafil daily?
Yes, vardenafil can be taken daily at low doses, but its use depends on the patient’s condition and tolerability. Clinical research shows that daily dosing provides benefits for erectile dysfunction and some related conditions. According to the study EDATE by Rosen et al. (2010), 5 mg once daily improved erectile function consistently in men with ED and was well tolerated. In men with type 2 diabetes and ED, the study by Santi et al. (2015) confirmed that 2.5 mg daily improved both erectile and endothelial function without significant adverse effects.
Daily vardenafil has also been investigated in other conditions. The study Vardenafil for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (2005) reported that a twice-daily regimen improved exercise capacity and was safe. In terms of safety, the study Effects of Daily Vardenafil on Reproductive Function by Hellstrom et al. (2003) showed that daily use up to 20 mg for six months did not impair semen quality or reproductive hormones. Adverse effects in most trials were mild to moderate, with headache being the most common.
Research also supports its role in special populations. The study Post-Prostatectomy Recovery with PDE5 Inhibitors by Montorsi et al. (2008) found that daily vardenafil aided erectile function recovery after prostate surgery. However, higher daily doses did not yield better results and sometimes increased side effects. These findings confirm that daily vardenafil can be effective, but dosing must be individualized.
Does food or alcohol affect vardenafil dosage?
Yes, food and alcohol can affect how vardenafil works in the body. A high-fat meal can lower the maximum concentration of vardenafil by about 18% and delay absorption by around one hour. According to the study Effect of High-Fat Breakfast and Moderate-Fat Evening Meal on the Pharmacokinetics of Vardenafil by Rajagopalan et al. (2003), these changes were not clinically significant and did not affect the need for dosage modification. Moderate-fat meals showed no meaningful effect on pharmacokinetics or efficacy. The study Pharmacokinetics of a New Orodispersible Tablet Formulation of Vardenafil by Heinig et al. (2010) also confirmed that vardenafil may be taken with or without food.
Alcohol has also been studied with vardenafil. According to the study Effects of Food and Alcohol on the Pharmacokinetics of Vardenafil by Zhan-ju He (2005), moderate alcohol intake of 0.5 g/kg ethanol did not significantly change the pharmacokinetics of the drug. The same observation was made in the study Simultaneous Administration of Vardenafil and Alcohol Does Not Result in a Pharmacodynamic or Pharmacokinetic Interaction in Healthy Male Subjects by Wensing et al. (2006), which reported that the combination was well tolerated. These findings confirm that food and alcohol do not meaningfully affect vardenafil dosage.
What Are the Drug Interactions of Vardenafil?
Vardenafil’s pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic interactions include:
- Nitrates
Vardenafil must not be taken with organic nitrates such as nitroglycerin or isosorbide mononitrate. According to the Clinical Monograph for Drug Formulary Review (2005), this combination can cause profound hypotension and is contraindicated. - Alpha-blockers
Caution is required when combining vardenafil with α₁-adrenergic antagonists such as doxazosin or tamsulosin. According to Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor Differentiation (2004), this interaction may lead to symptomatic hypotension. Stabilizing blood pressure and using the lowest vardenafil dose is recommended. - CYP3A4 inhibitors
Strong inhibitors such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, and ritonavir can raise plasma concentrations of vardenafil. The dose should be reduced to 2.5 mg and must not be repeated more than once every 48 hours. - CYP3A4 inducers
Strong inducers such as rifampin and carbamazepine can lower vardenafil plasma levels and decrease efficacy. Dose escalation may be considered but only with caution. - Other vasodilators
Concomitant use with antihypertensives such as β-blockers or diuretics can increase the risk of hypotension. According to the Clinical Monograph for Drug Formulary Review (2005), blood pressure should be monitored when initiating or adjusting therapy. - Other PDE inhibitors
Use with other phosphodiesterase inhibitors such as sildenafil or tadalafil has not been studied. It is not recommended due to the potential for additive adverse effects.
How Long Does Vardenafil Last in the Body?
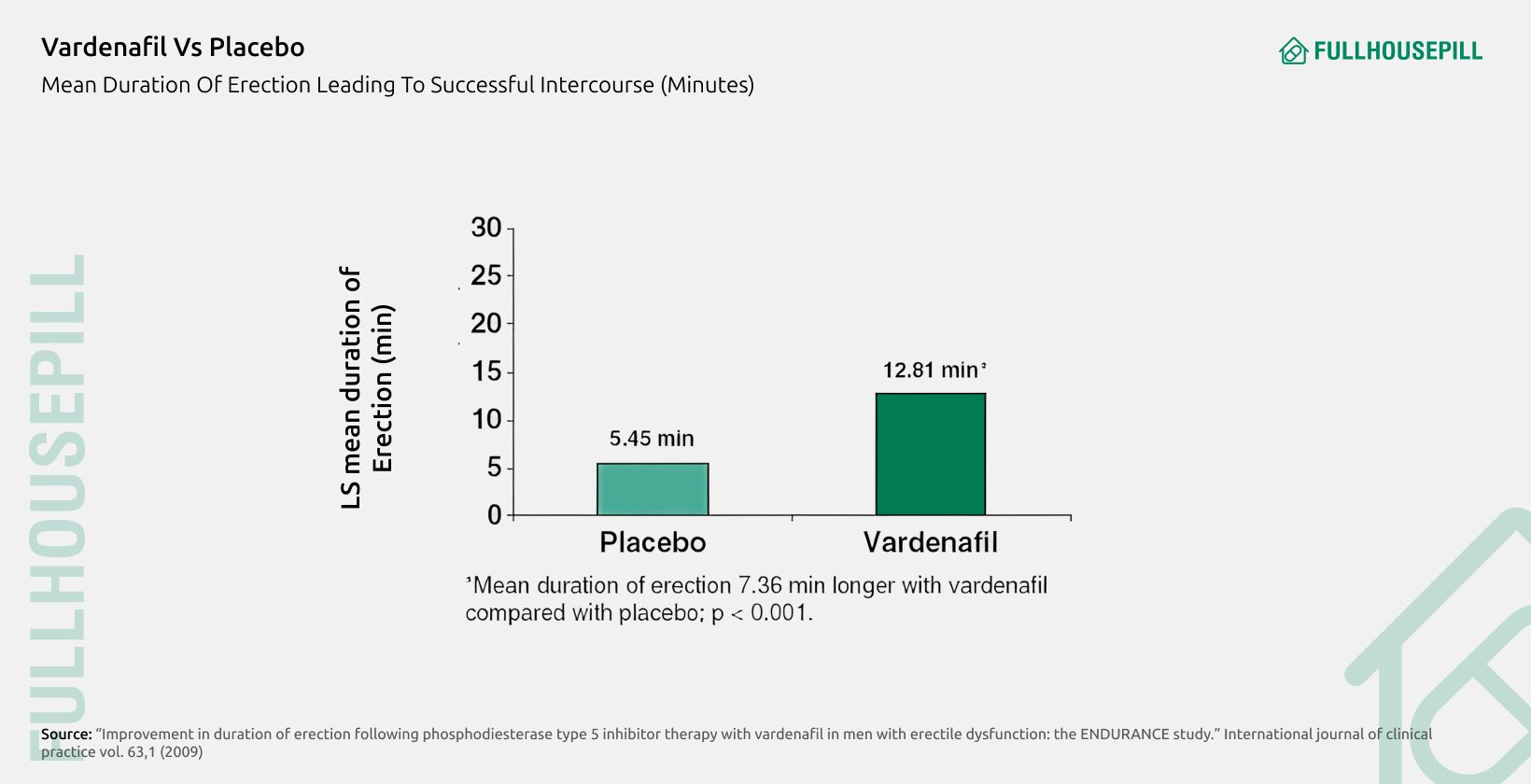
Vardenafil generally lasts for 4-5 hours, during which erectile response to sexual stimulation is most effective. Its elimination half-life is about 4 to 5 hours, and plasma levels decline to negligible amounts within 24 hours, marking complete elimination. Clinical data show that its duration is shorter than tadalafil’s extended 36-hour window but comparable to sildenafil. According to the ENDURANCE study, vardenafil 10 mg produced significantly longer erection duration than placebo, with patients averaging 12.81 minutes versus 5.45 minutes. The EROS study confirmed sustained improvements in erection duration and International Index of Erectile Function scores over 8 weeks of therapy. Extended testing, such as the trial by Porst et al., demonstrated that vardenafil could remain effective up to 8 hours in select cases.
How long does it take for vardenafil to start working?
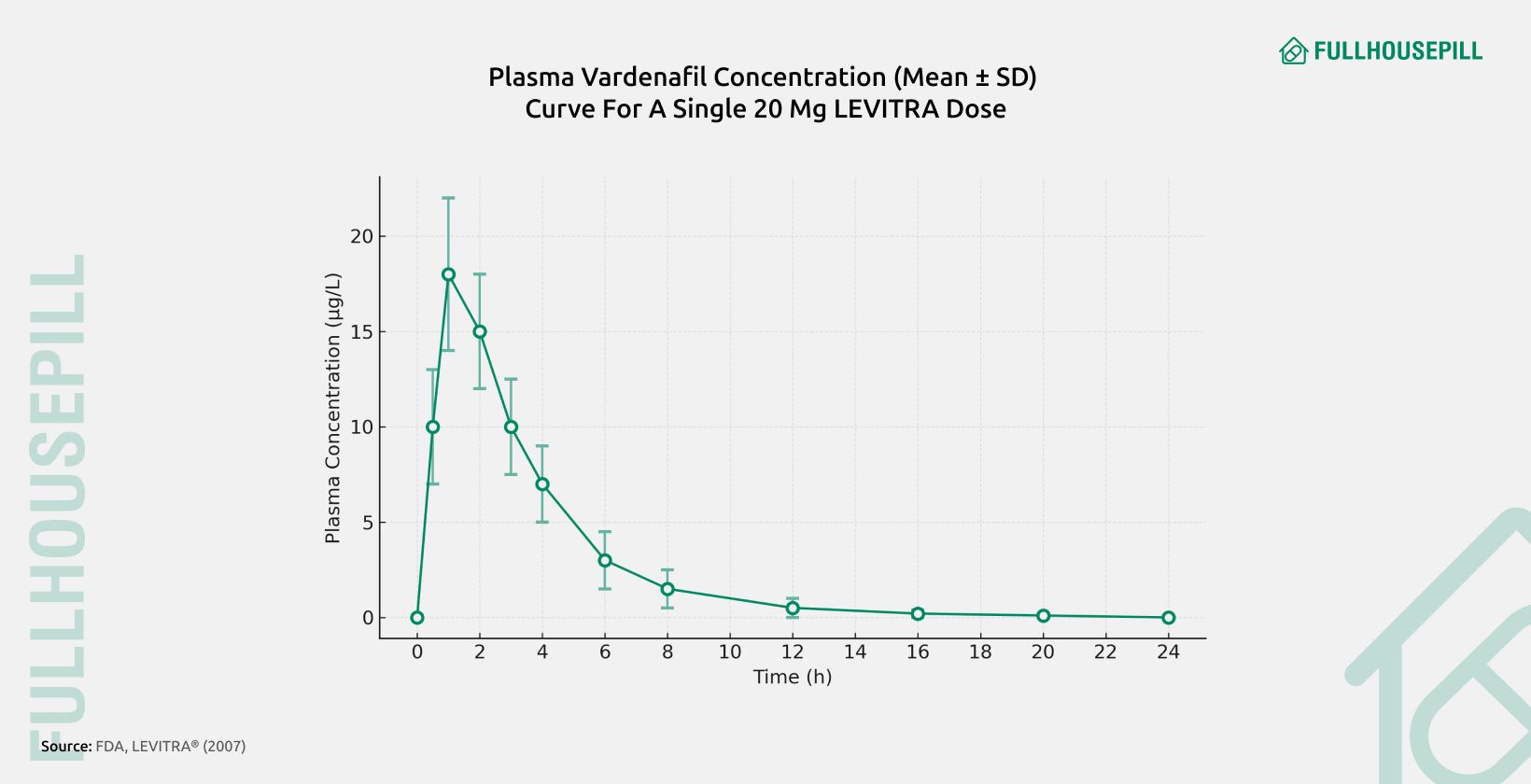
Vardenafil starts working within 15 to 30 minutes after dosing. Its median time to peak plasma concentration is 0.7 hours when taken on an empty stomach and 1.2 hours when taken with food. In the RELY-II study, a subset of men taking 10 mg reported significant erections as early as 30 minutes after the first dose.
What Are the Side Effects of Vardenafil?
Below is a list of common, rare and serious side effects caused by Vardenafil.
Common side effects
- Headache
- Flushing
- Dyspepsia
- Nasal congestion
- Dizziness
- Back pain
These effects are usually mild and temporary. You should continue treatment if they remain tolerable, but consult your doctor if they persist or worsen.
Serious side effects
- Priapism
- Sudden hearing loss
- Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
These conditions require immediate medical attention. You must stop taking vardenafil and seek urgent care if you develop a prolonged erection, sudden vision changes, or hearing problems.
Rare side effects
- Myocardial infarction
- Stroke
- Severe hypotension
These events are uncommon but can be life-threatening. They are more likely if vardenafil is taken with nitrates or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. You should avoid such combinations and inform your healthcare provider about all your medications before starting vardenafil.
What Is the Recommended Vardenafil Dosage for Women?
There is no recommended dosage of vardenafil for women. Vardenafil is approved only for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in men and has not been studied in women. Clinical trials have included only male participants, and no randomized controlled studies have evaluated its safety, pharmacokinetics, or efficacy in female subjects. For this reason, vardenafil is not indicated for use in women, and no dosage guidelines exist. Women should not take vardenafil, especially if they are pregnant or breastfeeding, since its effects during these conditions remain unknown. In some cases, doctors may prescribe Vardenafil (Levitra) off-label for female sexual dysfunction.
How Does Vardenafil Compare to Other ED Medications?
Vardenafil, sildenafil, and tadalafil are all PDE5 inhibitors, but they differ in absorption time, duration of action, and selectivity. Vardenafil has the fastest onset and higher selectivity for PDE5 over PDE6 compared to sildenafil, which lowers the risk of visual side effects. Sildenafil and vardenafil have similar durations of action, lasting around 4–5 hours, whereas tadalafil lasts up to 36 hours, allowing greater spontaneity. Clinical trials show first-dose success rates are slightly higher for vardenafil than for sildenafil and tadalafil. Adverse events such as headache and flushing are reported across all three, but tadalafil also causes muscle pain in some patients. These differences often guide patient preference, with some favoring vardenafil for its rapid onset and others choosing tadalafil for its long duration.
| Feature | Vardenafil | Sildenafil | Tadalafil |
| Onset (Tₘₐₓ) | 0.7 hrs (fasted) / 1.2 hrs (fed; ↓Cₘₐₓ 30%) | 1.0 hr (fasted) / 1.2 hrs (fed; ↓Cₘₐₓ 50%) | 2.0 hrs (fasted) / 2.5 hrs (fed; no effect) |
| Duration of Action | 4–5 hours | 4–5 hours | Up to 36 hours |
| PDE5 vs PDE6 Selectivity | Higher selectivity (fewer visual side effects) | Lower selectivity (more visual side effects) | Moderate selectivity |
| First-Dose Success | 72% at 10 mg (RELY-II) | 66% at 50 mg (registration trials) | 68% at 10 mg |
| Adverse Events | Headache 13%, flushing 7% | Headache 16%, flushing 10% | Headache 16%, myalgia 5% |
How is vardenafil different from sildenafil (Viagra)?
Vardenafil differs from sildenafil (Viagra) in selectivity, onset, and side-effect profile. It shows greater PDE5 versus PDE6 selectivity, which lowers the chance of visual disturbances that are more common with sildenafil. It also reaches peak plasma levels faster, with a Tₘₐₓ of about 0.7 hours when fasted, compared to sildenafil’s Tₘₐₓ of around 1.0 hour, leading to a quicker onset of erectile response. In clinical trials, vardenafil achieved a first-dose success rate of 72% at 10 mg, while sildenafil reached 66% at 50 mg. When comparing Viagra vs Vardenafil, the incidence of flushing was slightly lower for vardenafil at 7% compared to sildenafil at 10%.
How is vardenafil different from tadalafil (Cialis)?
Vardenafil differs from tadalafil (Cialis) in both duration and onset of action. Tadalafil has a longer half-life of about 17.5 hours, giving up to 36 hours of effectiveness and supporting once-daily or extended dosing. Vardenafil, by comparison, has a shorter half-life of 4–5 hours, keeping its benefits within the same period. Food does not affect tadalafil’s absorption, but its onset is slower, with a Tₘₐₓ of around 2 hours. Vardenafil reaches peak levels faster, with a Tₘₐₓ of 0.7 hours when fasted. In the comparison of Vardenafil VS Tadalafil, vardenafil is favored for its faster action in on-demand situations.