High cholesterol can lead to erectile dysfunction (ED). When cholesterol builds up, it narrows the arteries and slows blood flow to the penis. Erections depend on healthy circulation, so blocked vessels make them weaker or inconsistent. Cholesterol itself is a fatty substance that supports hormone balance and cell health. In excess, it harms arteries and raises risks for both heart disease and sexual problems. Research shows men with uncontrolled cholesterol often experience erectile issues, while lowering cholesterol can improve function over time.
A study in the American Journal of Epidemiology found that higher total cholesterol raised the risk, while higher HDL cholesterol lowered it. Each 1 mmol/litre increase in total cholesterol increased the risk by 1.32 times. Each 1 mmol/litre increase in HDL reduced the risk by 0.38 times. Men with HDL over 1.55 mmol/litre had only 0.30 times the risk compared to those with HDL below 0.78 mmol/litre. Men with total cholesterol above 6.21 mmol/litre had 1.83 times the risk compared to those below 4.65 mmol/litre. These results show that high total cholesterol and low HDL cholesterol are important risk factors for erectile dysfunction. Managing cholesterol may help reduce this risk.
Medicines for cholesterol rarely cause erectile dysfunction. Lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, and quitting smoking, can help improve both cholesterol levels and erectile function. Some men see benefits within months of healthier routines. Treatments for ED, including Viagra, are generally safe if cholesterol is controlled with medical advice. The article highlights How High Cholesterol Leads to Erectile Dysfunction, treatment options, the safety of Viagra, and whether exercise helps erectile dysfunction caused by cholesterol.
What is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a natural fatty substance found in every cell of the body. It plays a key role in hormone production, vitamin D synthesis, and the liver’s creation of bile acids that aid in food digestion. Without cholesterol, many vital processes would not function properly.
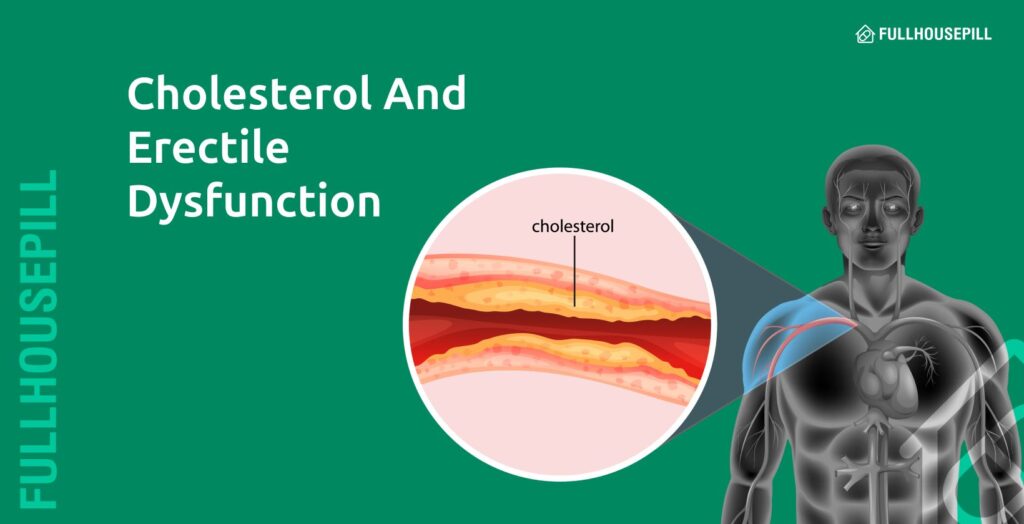
When cholesterol levels are balanced, the body works smoothly. Problems begin when cholesterol rises too high in the blood. Excess cholesterol attaches to artery walls, forming deposits called plaque. This process is known as atherosclerosis. Plaque makes arteries hard and narrow, which restricts blood flow. Poor circulation increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and erectile dysfunction.
A study in the European Heart Journal explored how plaques prone to rupture develop. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) builds up under the artery lining, supplying cholesterol that cells convert into free cholesterol (FRC). When HDL transport is impaired, FRC can accumulate, crystallise, and damage cells. Cholesterol crystals trigger inflammation through IL-1β and raise C-reactive protein, destabilising plaques. Targeting IL-1β or preventing crystal formation may help stabilise vulnerable plaques and reduce rupture risk.
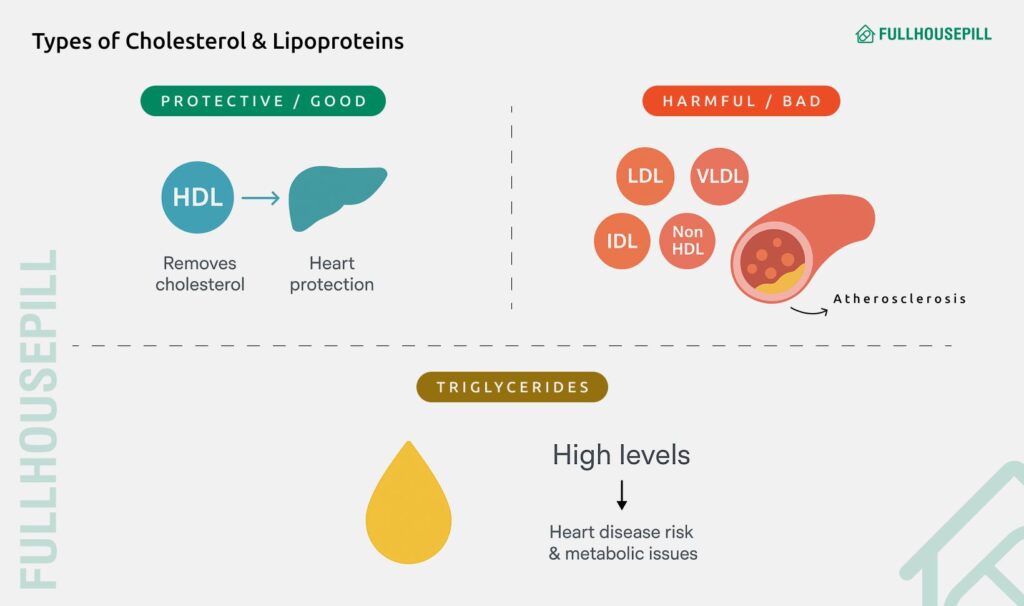
Doctors measure cholesterol through a lipid panel. This test gives a breakdown of different cholesterol types:
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein): This is known as “good” cholesterol because it removes extra cholesterol from the bloodstream and transports it back to the liver for disposal. Higher HDL levels protect against heart disease.
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein): This is called “bad” cholesterol because it contributes to plaque buildup in arteries. High LDL is a leading risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
- VLDL (Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein): This is another harmful type that primarily carries triglycerides. It also plays a role in plaque formation.
- Non-HDL Cholesterol: This is a measure that adds together all the harmful types (LDL, VLDL, IDL) and is considered a strong predictor of risk.
- IDL (Intermediate-Density Lipoprotein): It is a transitional particle formed when VLDL breaks down, also linked with plaque deposits.
- Chylomicrons: These are large particles that carry dietary fat and triglycerides from food through the bloodstream.
- Triglycerides: This is not a cholesterol particle but always measured with the panel. High triglycerides increase the chance of heart disease and are often associated with metabolic issues.
Understanding the balance between HDL, LDL, and non-HDL cholesterol is more important. High HDL is protective, but high LDL, VLDL, or triglycerides can be harmful even if total cholesterol looks normal.
Can High Cholesterol Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Yes, high cholesterol can directly cause erectile dysfunction. Elevated cholesterol leads to plaque buildup inside blood vessels, narrowing them and slowing blood flow to the penis. Erections depend on strong circulation, so reduced flow makes it harder to get or keep one. The link is primarily vascular. When LDL and VLDL cholesterol rise, they damage the artery lining. This reduces the release of nitric oxide, a chemical that relaxes vessels so blood can enter the penile tissue. Without enough nitric oxide, arteries stay tight, and the blood supply is limited. Even if desire is present, the body struggles to respond.
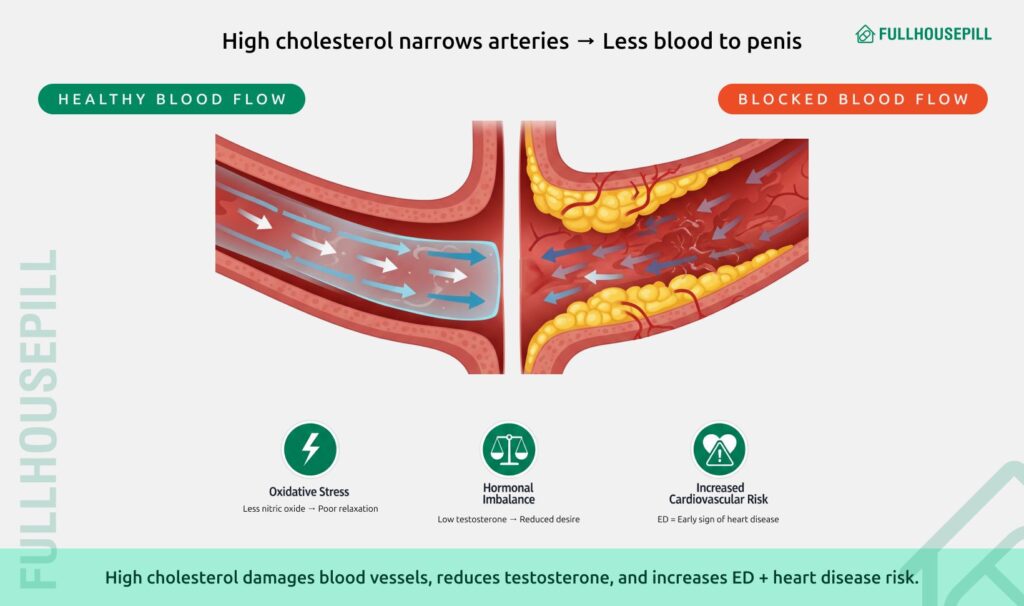
According to a study in The Journal of sexual medicine, Hypercholesterolemia increases oxidative stress and impairs endothelial function in the penis. Researchers found that NAD(P)H oxidase is an initial source of reactive oxygen species, leading to eNOS uncoupling and endothelial dysfunction. LDLR-null mice on a Western diet showed reduced erectile response, increased NAD(P)H oxidase activity, oxidative stress, and decreased endothelial function. Treatment with the inhibitor apocynin preserved erectile function and reversed these changes. The study shows that targeting NAD(P)H oxidase could help prevent ED caused by high cholesterol.
High cholesterol can disrupt the hormonal balance which may contribute to erectile dysfunction. Cholesterol is needed to make testosterone, but excess cholesterol disrupts how the body regulates hormones. Low testosterone levels can worsen sexual function, reducing both desire and erection quality. Doctors emphasise that erectile dysfunction linked to cholesterol is often an early sign of wider health risks. Studies show that men with high cholesterol and ED are at greater risk of heart attack and stroke. This makes ED not just a quality-of-life issue but also a warning signal of cardiovascular disease. Treating cholesterol through lifestyle changes or medication can improve erectile health and protect the heart at the same time.
A study in The Journal of sexual medicine examined the link between erectile dysfunction (ED) and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). ED and cardiovascular disease share common risk factors such as age, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and dyslipidemia. Researchers also explored whether living in rural or urban areas affects MACE risk. Using a large population-based database, men with and without ED were followed for cardiovascular outcomes. ED was linked to a higher risk of MACE, even after accounting for other health conditions. Rural men with ED had an even greater risk than urban men. The study highlights that ED is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular events. Healthcare providers should address cardiovascular risk when managing men with ED, especially those in rural areas.
How High Cholesterol Leads to Erectile Dysfunction?
High cholesterol can lead to erectile dysfunction by damaging blood vessels and reducing circulation. When cholesterol levels rise, fatty deposits build inside artery walls and cause them to narrow. This narrowing, known as plaque buildup, slows down blood flow throughout the body. Since erections rely on a sudden rush of blood into the penis, even a small drop in circulation can make it harder to achieve and maintain firmness.
A study in Lipids in Health and Disease explored the link between remnant cholesterol (RC) and erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with diabetes. ED is known to be associated with dyslipidemia, but the role of RC remained unclear. Using data from 215 men in the NHANES survey (2001–2004), RC was calculated by subtracting HDL-C and LDL-C from total cholesterol, and ED was based on self-reports. Logistic regression analyses showed a strong correlation between higher RC levels and ED in diabetic men (OR 7.49, 95% CI 1.98–28.37). A trend of increasing ED risk with higher RC levels was also observed. The study suggests that elevated RC may predict ED in men with diabetes. Further research is needed to confirm these findings.
The process starts with cholesterol particles, especially LDL and VLDL. When levels rise, they stick to artery walls and form fatty streaks. Over time, these deposits harden into plaque in a process called atherosclerosis. Arteries become narrower and less flexible, which means blood has less room to pass through. Since penile arteries are smaller than those in the heart, they show signs of trouble sooner. Even mild plaque can restrict the surge of blood needed for an erection.
Another key factor is endothelial dysfunction. The endothelium is a thin lining inside blood vessels that produces nitric oxide. This chemical is vital because it relaxes arteries and lets blood rush into the penis during arousal. High cholesterol inflames and damages endothelial cells, cutting down nitric oxide release. With less nitric oxide, arteries stay tense, and blood cannot fully enter the erectile chambers.
A narrative review in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences examined the role of oxidative stress (OS) in erectile dysfunction (ED), a common condition affecting male sexual health. ED arises from multiple factors, including psychological, hormonal, neurologic, cardiovascular, and lifestyle influences. OS, caused by an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidants, disrupts endothelial function, reduces nitric oxide availability, and contributes to vascular problems.
The review highlights key ROS sources such as NADPH oxidase, xanthine oxidase, uncoupled nitric oxide synthase, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and lifestyle factors like smoking and obesity worsen ED through oxidative damage. Emerging evidence suggests that antioxidants and lifestyle interventions may restore redox balance, improve endothelial function, and slow ED progression. Further research is needed to clarify molecular pathways and develop targeted therapies.
Hormones and nerves are also part of the picture. Cholesterol is necessary to make testosterone, but when it is too high, it can disrupt hormone regulation. Low testosterone reduces sexual desire and weakens erections. At the same time, reduced blood flow starves penile nerves of oxygen. Oxygen-poor nerves become less responsive, which slows the communication between the brain and penis.
This is why erectile dysfunction is often called an early warning system. The penile arteries are smaller than the coronary arteries, so ED may appear years before heart disease or stroke. In many cases, men notice erection issues before they realise their cholesterol or cardiovascular health is at risk.
Does Cholesterol Medicine Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Yes, some cholesterol-lowering medications can cause erectile dysfunction. Statins, such as atorvastatin (Lipitor), simvastatin, and rosuvastatin, have been linked to sexual side effects in certain men, including reduced libido and difficulty maintaining erections.
Statins work by lowering LDL cholesterol, which helps prevent plaque buildup in arteries. While this protects the heart and improves circulation over time, some reports suggest that statins may reduce testosterone slightly in certain individuals, potentially contributing to erectile difficulties. The mechanism is not fully understood, but it may involve hormonal changes or subtle effects on nerve signalling.
According to Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine, Lipid-lowering therapy remains central to reducing cardiovascular risk. Statins effectively lower cholesterol and significantly reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. While some benefits may come from cholesterol reduction, other cholesterol-independent effects are also possible. Advances in cardiac imaging, including intravascular ultrasound and coronary CT angiography, have improved our understanding of statins’ impact on atherosclerotic plaques. Statins not only reduce plaque lipid content but also stabilise plaques by thickening fibrous caps and promoting calcification, helping prevent plaque rupture and cardiovascular events.
Despite these concerns, the majority of research indicates that statins do not cause widespread erectile dysfunction. In fact, some studies show that improving cholesterol levels with statins can enhance blood flow and even improve sexual function in men with high cholesterol and ED.
A study in the Journal of Hypertension explored the link between erectile dysfunction (ED) and dyslipidemia and the effect of statins on ED. 100 men with high cholesterol and ED were divided into two groups: one received atorvastatin for three months, the other received no treatment. Erectile function and lipid levels were measured before and after treatment. Men on statins showed significant improvement in both IIEF scores (16.3 vs 11.4) and lipid profiles compared to controls. The findings suggest statins may improve erectile function in men with high cholesterol, though they are not recommended for ED in men with normal lipid levels.
It is also important to note that reported cases of statin-induced ED are relatively rare. Atorvastatin (Lipitor) is the most studied, and while some men report mild sexual side effects, these are often reversible when the medication is adjusted or switched.
Does Lowering Cholesterol Improve Erectile Dysfunction?
Yes, lowering cholesterol can significantly improve erectile dysfunction. High cholesterol causes fatty deposits to accumulate in arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow. Since erections depend on a rapid and sufficient flow of blood into the penis, any restriction can make it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection.
In The Journal of Urology, this study evaluated whether statin therapy could improve erectile function in men whose only risk factor for ED was high cholesterol. Nine men with hypercholesterolemia were treated with atorvastatin to lower total cholesterol below 200 mg/dl and LDL below 120 mg/dl. Erectile function was assessed using RigiScan and the Sexual Health Inventory in Men questionnaire. After an average of 3.7 months, eight of nine men achieved erections sufficient for intercourse. Questionnaire scores improved from 14.2 to 20.7, and total and LDL cholesterol levels decreased significantly. RigiScan measurements showed increased penile rigidity at both the base and tip. The study concludes that lowering cholesterol with atorvastatin can improve ED while supporting cardiovascular health.
Reducing cholesterol, whether through medications like statins or lifestyle measures such as diet and exercise, helps restore arterial health. When LDL cholesterol drops, plaque buildup stabilises or decreases, allowing blood vessels to function better. The endothelium, the inner lining of arteries, begins producing more nitric oxide, which relaxes the vessels and improves blood flow. Improved circulation directly supports stronger and more reliable erections.
According to The Journal of Urology, men with ED linked to high cholesterol often notice gradual improvements after several months of treatment. The recovery is not instant because it takes time for arterial walls to heal and for blood flow to normalise. Both lifestyle changes, like regular exercise and a heart-healthy diet, and statin therapy can contribute to these improvements.
Lowering cholesterol also has the added benefit of reducing cardiovascular risk. Since erectile dysfunction and heart disease often share the same vascular causes, improving cholesterol addresses both issues at once. In this way, treating high cholesterol not only enhances sexual health but also strengthens overall heart and artery function.
How Quickly Can ED Improve After Reducing Cholesterol?
Erectile dysfunction can start improving within weeks to months after cholesterol levels are lowered. The exact timeline depends on the severity of arterial damage, the type of cholesterol management, and overall vascular health. Men with milder blockages or early-stage atherosclerosis often notice changes sooner, sometimes within a month or two. In contrast, those with significant plaque buildup may need several months before improvements become noticeable.
According to Hospital Pharmacy, Lipid-lowering therapy (LLT) includes medications that reduce cholesterol and triglyceride levels to prevent cardiovascular diseases. Common drugs include statins, PCSK9 inhibitors, ezetimibe, bile acid sequestrants, fibrates, niacin, omega-3 fatty acids, bempedoic acid, and combination therapies. Statins are the first-line treatment and generally safe, though muscle-related side effects are common. Effects on male reproductive health are rare and often underreported. The study reports a case of a 50-year-old man with no prior sexual or testicular issues who developed loss of libido, erectile dysfunction, and testicular pain while on multiple LLT drugs. Symptoms resolved after stopping therapy. This case emphasises the need to monitor male patients for sexual side effects when prescribing LLT.
Improvements occur gradually because arterial healing and plaque stabilisation take time. Lowering LDL cholesterol reduces inflammation in blood vessels and supports endothelial recovery. A healthy endothelium produces more nitric oxide, a chemical that relaxes arteries and allows blood to flow efficiently into the penis. This gradual restoration of blood flow is the key mechanism behind improved erectile function.
Lifestyle factors can accelerate recovery. Regular exercise, a balanced heart-healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol all enhance vascular health. When combined with statin therapy, these changes not only improve erectile function but also reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other vascular complications.
It is important to understand that improvements in erectile function usually mirror improvements in overall cardiovascular health. Men may notice partial improvements first, such as firmer erections or increased libido, before full recovery occurs. Continuous monitoring and cholesterol management are essential to sustain these benefits over the long term.
What Are the Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction Caused by High Cholesterol?
Erectile dysfunction caused by high cholesterol can be treated effectively through multiple approaches. These treatment options improve blood flow, restore vascular health, and support hormonal and nerve function.
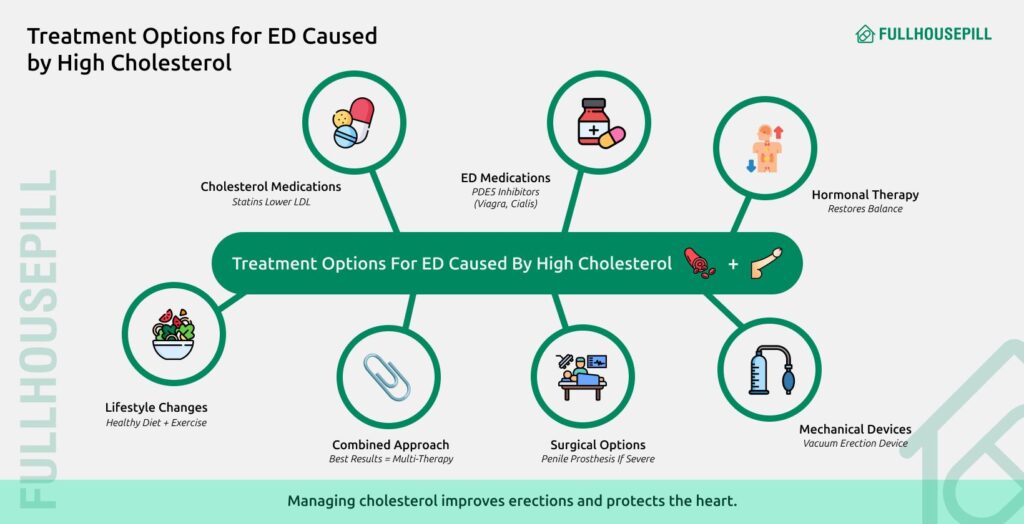
1. Lifestyle Modifications
The most natural approach is to change lifestyle habits. A heart-healthy diet with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats lowers LDL cholesterol and reduces arterial plaque. Exercise improves circulation and boosts nitric oxide, which is essential for erections. Maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol also enhance sexual function over time. Vascular Health and Risk Management examines the effectiveness of different diets and strategies for nutritional counselling, helping patients adopt heart-healthy eating habits. The review also highlights barriers such as food insecurity, limited access, and socioeconomic challenges. Emphasis is placed on a multidisciplinary, team-based approach, including nutrition specialists, to implement culturally tailored dietary recommendations.
2. Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
Statins such as atorvastatin (Lipitor), simvastatin, and rosuvastatin reduce LDL cholesterol and stabilise plaque in arteries. By improving endothelial function and blood flow, these medications can indirectly support erectile performance. Some men notice improved erections after several weeks or months of consistent therapy.
3. ED-Specific Medications
According to European Urology, Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors include sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra). These enhance blood flow to the penis. They work best when arteries are partially healthy. Combined with cholesterol-lowering treatments, these medications can help men with persistent erectile difficulties.
4. Hormonal Therapy
High cholesterol can affect testosterone production, leading to reduced libido and weaker erections. According to Atherosclerosis, testosterone replacement therapy may help men with confirmed hormonal deficiencies. Balancing hormones improves sexual desire and erectile quality while supporting vascular improvements from cholesterol management..
5. Mechanical Devices
Vacuum erection devices create suction to draw blood into the penis. This was supported by Reviews in Urology. They are particularly useful for men with significant arterial narrowing or severe ED. While not permanent, these devices provide immediate results and support sexual activity while other treatments take effect.
6. Surgical Options
For severe cases where other treatments fail, surgical options such as penile implants or vascular reconstructive surgery can restore erectile function. According to Annals of The Royal College of Surgeons of England, the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED) has been transformed by orally active phosphodiesterase inhibitors, which are effective in 70–80% of men. For those who do not respond, surgical penile prosthesis implantation may be necessary. Historically, this surgery faced technical challenges and high complication rates, but advances in prosthesis design and surgical techniques have rapidly improved outcomes. One key development is the use of antimicrobial coatings on prostheses, which significantly reduce infection rates. This review focuses on the major advancements in penile prosthesis reported over the past five years. These procedures are usually reserved for irreversible arterial damage.
7. Combined Approach
The most effective strategy often combines lifestyle changes, cholesterol management, ED medications, and, when needed, hormonal or mechanical interventions. Addressing vascular, hormonal, and nerve factors together improves erections and reduces cardiovascular risk.
What Foods Lower Cholesterol and Improve Erections?
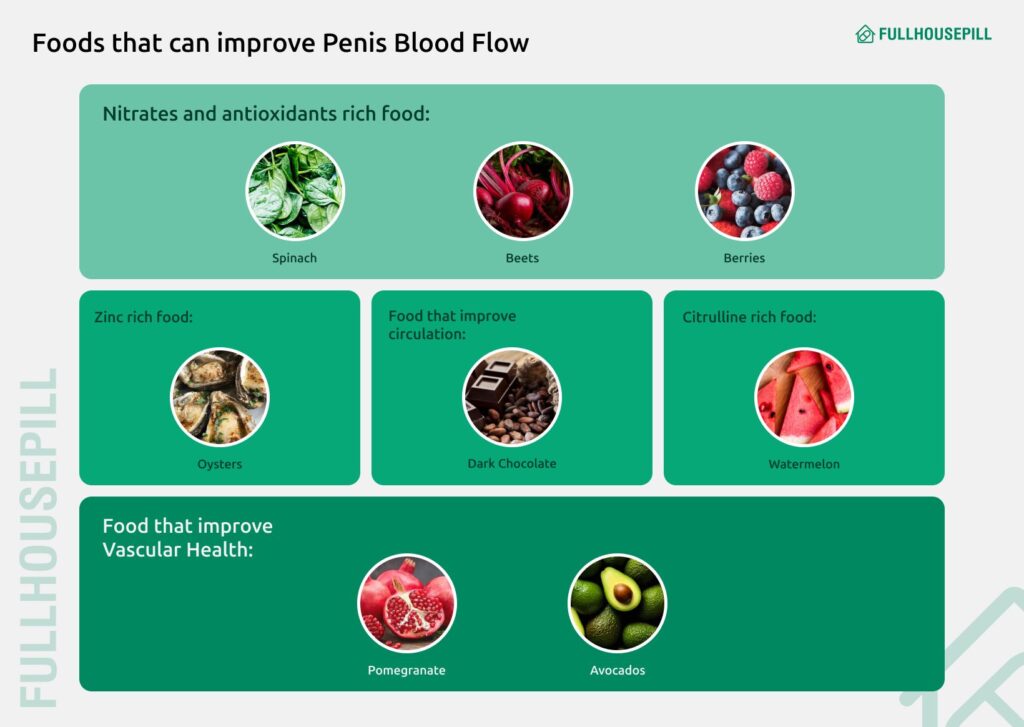
Image reference- This image highlights eight foods that can support blood flow and endothelial health, potentially improving erectile function. Foods such as spinach, beets, and berries are rich in nitrates and antioxidants, which boost nitric oxide levels. Oysters provide zinc, which is important for testosterone production. Dark chocolate contains flavonoids that improve circulation, while watermelon is high in citrulline, which may relax blood vessels. Pomegranate and avocado also support vascular health through antioxidant and healthy fat content. Regular inclusion of these foods in a balanced diet can enhance blood flow and overall cardiovascular health.
Yes, certain foods can lower cholesterol and improve erectile function. Eating a heart-healthy diet reduces LDL cholesterol, enhances blood flow, and supports nitric oxide production, all of which are vital for erections. A meta-analysis in the Asian Journal of Andrology highlights a significant link between diet and erectile dysfunction, indicating that low-fat or Mediterranean diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and nuts may help improve ED.
High cholesterol can narrow arteries and limit blood flow to the penis, making erections difficult. Including specific cholesterol-lowering foods in your diet helps restore vascular health and supports sexual performance.
Key Foods That Help:
- Oats and Barley: Rich in soluble fibre, these grains reduce LDL (“bad”) cholesterol. They help arteries stay clear and improve blood flow to the penis.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines contain omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s reduce inflammation, prevent plaque buildup, and support nitric oxide, which relaxes blood vessels.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia, and flaxseeds are packed with healthy fats and plant sterols. They help balance cholesterol and improve vascular flexibility for better erections.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Berries, citrus fruits, spinach, and broccoli are full of antioxidants. They protect blood vessels from oxidative damage and enhance overall circulation.
- Olive Oil and Avocados: These provide monounsaturated fats that improve blood vessel health and reduce cholesterol, supporting stronger erections.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are high in fibre and plant proteins. They lower LDL cholesterol and contribute to healthy blood flow.
- Dark Chocolate (in moderation): Contains flavonoids that improve endothelial function and boost nitric oxide, helping arteries relax and blood flow efficiently.
Incorporating these foods consistently, along with exercise and proper hydration, can gradually lower cholesterol and improve erectile health.
Does Exercise Help Erectile Dysfunction Caused by Cholesterol?
Yes, regular exercise can significantly improve erectile dysfunction linked to high cholesterol. According to Sexual Medicine, physical activity lowers LDL cholesterol, raises HDL, enhances blood flow, and supports vascular and endothelial health.
High cholesterol can narrow arteries and reduce blood flow to the penis, making erections harder to achieve. Exercise counteracts this by improving circulation, reducing arterial plaque, and boosting nitric oxide production. Nitric oxide relaxes blood vessels, allowing more blood to enter the erectile tissue.
Both aerobic and resistance exercises have benefits. Aerobic activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling improve heart and vascular health. Resistance training, such as weight lifting, supports testosterone levels, which play a key role in sexual desire and erectile function.
Exercise also helps manage weight, reduce inflammation, and lower blood pressure, all of which contribute to healthier arteries and better erections. Combining regular physical activity with a heart-healthy diet and cholesterol-lowering medications can enhance erectile function over time.
Consistency is essential, as the benefits of exercise on erectile function and cholesterol develop gradually over several weeks to months. Combining cardiovascular activities with strength training enhances blood flow, supports testosterone levels, and improves vascular health. Regular exercise not only helps with erectile function but also strengthens overall cardiovascular health, making it highly effective for men managing high cholesterol and sexual health concerns.
Does Ejaculating Lower Cholesterol?
No, ejaculating does not meaningfully lower cholesterol. While sexual activity burns a small number of calories, it has no significant impact on LDL or HDL cholesterol levels or long-term cardiovascular risk. Some men wonder if frequent ejaculation can influence cholesterol, but research shows it does not. Sexual activity, including ejaculation, is a natural bodily function that involves short-term cardiovascular and muscular activity. While it slightly increases heart rate and calorie expenditure, these effects are minimal compared to structured exercise or dietary changes. Cholesterol levels are primarily influenced by diet, physical activity, genetics, and medications. However, regular sexual activity may still have indirect benefits for cardiovascular and mental health, such as reducing stress, improving mood, and promoting healthy blood flow. These factors support overall heart health, but they do not directly lower LDL or raise HDL cholesterol.
Can ED Medications Help Men With ED Caused by High Cholesterol?
Yes, ED medication can help men with cholesterol-related erectile dysfunction. According to a 2004 study published in the Journal of Urology, PDE5 inhibitors like sildenafil and tadalafil effectively treat ED, while statins improve cholesterol levels and enhance ED medication effectiveness simultaneously.
Sildenafil citrate tablets and other ED medications effectively treat erectile dysfunction caused by high cholesterol through multiple mechanisms. High cholesterol damages blood vessels and reduces nitric oxide availability, leading to poor penile blood flow. PDE5 inhibitors work by blocking phosphodiesterase enzymes, allowing increased blood flow to the penis regardless of underlying cholesterol issues.
Is it Safe to Take Viagra with High Cholesterol?
Yes, the sildenafil citrate tablet is generally safe for men with high cholesterol. A comparative study published in The Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology shows no increased cardiovascular risks, and the medication may actually improve lipid profiles when combined with statin therapy.
Sildenafil citrate tablet demonstrates excellent safety in hypercholesterolemic patients. According to a comprehensive safety review of 67 double-blind studies involving over 14,000 patients, sildenafil shows no increased cardiovascular risks even in men with existing risk factors. Another randomized controlled trial published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine, examining combined therapy, men receiving both atorvastatin and sildenafil achieved significantly greater improvements in erectile function compared to sildenafil alone, reducing LDL cholesterol by 43%.
Does sildenafil increase cholesterol levels?
No, sildenafil citrate tablet does not significantly increase cholesterol levels in most patients. A study, Effect of long-term administration of sildenafil on lipid profile and organ functions in hyperlipidemic rats, examining sildenafil’s effects on lipid profiles, shows mixed results depending on patient population and dosing. In hyperlipidemic rats, long-term sildenafil administration actually decreased total cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL cholesterol levels.
The cardiovascular safety profile of sildenafil remains excellent across multiple patient populations. Analysis of over 67 double-blind placebo-controlled trials, published in the International Journal of Clinical Practice, confirmed sildenafil’s good tolerability without significant lipid metabolism concerns. Men with existing high cholesterol can safely usethe sildenafil citrate tablet under medical supervision without worrying about substantial cholesterol increases.
Does tadalafil affect cholesterol levels?
Tadalafil demonstrates favorable effects on cholesterol and lipid profiles compared to other ED medications. Studies show chronic tadalafil treatment significantly reduces triglycerides, non-HDL cholesterol, and VLDL cholesterol levels. Men receiving combined tadalafil and atorvastatin treatment achieved greater improvements in both lipid profiles and sexual function compared to statin therapy alone. This combination therapy also reduced inflammatory markers more effectively than single-drug treatment.
Tadalafil’s longer half-life may contribute to its metabolic benefits compared to shorter-acting PDE5 inhibitors. The drug’s anti-inflammatory properties may also contribute to improved cardiovascular risk profiles.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.