Lidocaine is one of the most widely used treatments for premature ejaculation. It helps men last longer during sex. It works by numbing the surface nerves of the penis, which reduces sensitivity and allows greater control over climax. Topical lidocaine extends the time to ejaculation. It is safe when applied correctly and remains one of the most practical medical approaches to this condition.
A study in the International Journal of Impotence Research found that topical lidocaine-prilocaine spray significantly prolongs ejaculation time. Men with PE applied the spray to the glans 10-15 minutes before intercourse and wiped it off before penetration. The results were striking. Average intravaginal ejaculation latency time (IVELT) increased from 1 minute 24 seconds to 11 minutes 21 seconds, an eight-fold improvement (P=0.008). Mild glandular numbness occurred in only two cases and did not affect orgasm. A few men reported minor difficulty maintaining an erection while waiting the 15 minutes between application and intercourse.
Lidocaine use comes with clear benefits, but it also requires careful application. Side effects such as temporary numbness or reduced erection quality may occur. The article highlights lidocaine’s role in premature ejaculation, its benefits, safe use, and possible risks. This article was compiled from peer-reviewed medical sources and guidelines. All health information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare provider before starting any new treatment, supplement, or lifestyle change, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking prescription medications.
What is Lidocaine?
Lidocaine is a class Ib antiarrhythmic and local anaesthetic. It is an amino amide type anaesthetic and has been in medical use since the mid-20th century.
Lidocaine functions as a local anaesthetic by obstructing the body’s nerve signals. Blocking the transmission of nerve impulses at the application site reduces pain when applied topically or injected. This effect makes it possible to relieve pain during a variety of medical procedures without unconsciousness.
Lidocaine is used as a class Ib antiarrhythmic agent to treat ventricular arrhythmias and other abnormal heart rhythms. It helps to restore normal rhythm and avoid potentially fatal arrhythmias by stabilising the heart’s electrical activity.
A study in Clinical and Translational Science on lidocaine shows that lidocaine is a class Ib anti-arrhythmic that blocks voltage- and pH-dependent sodium channels. It primarily binds to inactivated sodium channels, reduces action potential duration, and increases the refractory period. This action raises the ventricular fibrillatory threshold and can stop life-threatening tachycardias caused by re-entrant mechanisms, especially in ischemic tissue. Lidocaine was the anti-arrhythmic of choice for ventricular arrhythmias for decades. Its use declined with the rise of amiodarone and modern electrical devices, but has recently regained attention for treating acute sustained ventricular tachyarrhythmias.
Lidocaine is a drug that can be used for both heart and pain relief. Because of its quick onset and efficacy, it is frequently utilised in clinical settings. Lidocaine also help men by reducing penile sensitivity to delay ejaculation and treat premature ejaculation (PE).
How Lidocaine Works to Treat PE?
Lidocaine works to treat premature ejaculation as a topical anaesthetic that slightly reduces the sensitivity of the penis. When applied as a cream or spray about 10-20 minutes before sex, it blocks nerve signals in the skin. This lowers the feeling of arousal and helps delay ejaculation, giving men more control over when they climax.
Lidocaine works by numbing the penile skin. It blocks sodium channels in the nerve endings of the penis. These channels normally send fast signals of stimulation to the brain. When they are blocked, the nerves transmit fewer signals, which lowers penile sensitivity. This temporary desensitisation allows men to maintain sexual activity longer without reaching orgasm too quickly.
For safety and effectiveness, the cream or spray should be washed off before intercourse, or a condom should be used to prevent transferring numbness to a partner. This simple approach makes lidocaine a practical and popular option for managing PE.
What are the Benefits of Using Lidocaine for Premature Ejaculation?
Lidocaine helps men control premature ejaculation by numbing the penile skin, which lowers sensitivity and delays climax. The Benefits of using lidocaine are listed below.
- Longer-lasting performance. Slightly numbs the penis, which helps delay ejaculation and extends the time before climax.
- Better ejaculatory control. Reduces sensitivity which allows men to have more control during intercourse.
- On-demand use. Applied as sprays and creams shortly before sex, making it a practical and flexible option.
- Low risk of systemic effects. Applied topically, the effect stays local and does not usually impact the rest of the body.
- Fast-acting and convenient: Works quickly, making it suitable for spontaneous sexual activity without long preparation.
- Different forms available. Available as sprays, creams, and gels, it gives men a choice of what suits them best.
These physical benefits make lidocaine a reliable option for men who want to manage premature ejaculation safely and effectively. However, it is important to know how to use lidocaine properly and safely on the penis.
How to Use Lidocaine Safely on the Penis?
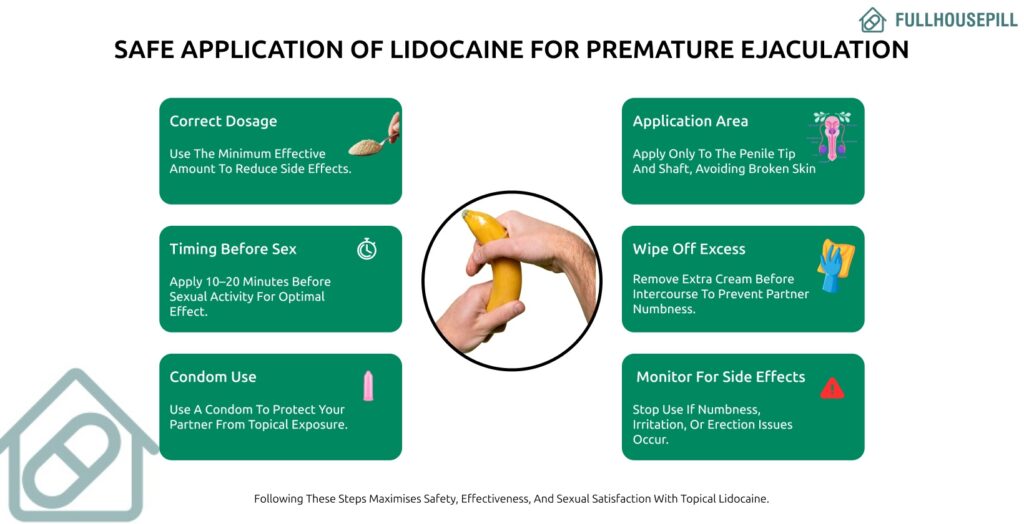
To use lidocaine safely, apply a small amount directly to the sensitive areas of the penis shortly before sex. Lidocaine comes in creams, gels, sprays, or wipes. Creams and gels are applied in a thin layer to the glans, allowing them to spread evenly and absorb quickly. Sprays are convenient because they cover the area without needing direct contact. Wipes are easy to use and work well for a one-time application. Regardless of the form, the aim is to reduce sensitivity without completely taking away sensation.
Timing is also crucial. Lidocaine usually works best when applied 10-20 minutes before sexual activity. After waiting, any excess should be wiped away to prevent passing numbness to a partner. It’s also a good idea to wash your hands after applying it.
Topical lidocaine spray effectively prolongs ejaculation with 2 to 5 sprays on the head and base of the penis. Creams or gels typically require just a pea-sized amount on the glans or the underside near the frenulum. These amounts can delay ejaculation without causing excessive numbness.
The different forms of creams, gels, sprays, and wipes make lidocaine a practical and discreet option. It is helpful for men who want a safe, on-demand way to manage premature ejaculation.
Can You Put Lidocaine on the Foreskin?
Yes, you can safely apply lidocaine to the foreskin. It is a topical anaesthetic that numbs the skin and provides pain relief during certain medical situations, but it is not for treating premature ejaculation.
Lidocaine cream or gel is often used in procedures like adult circumcision to relieve pain. In a study in the Journal of Clinical Medicine at Xiangya Hospital, nearly all patients (99.1% of 649) required only a single application of compound lidocaine cream. The anaesthesia acted quickly, typically within 2-5 minutes, though it took slightly longer for severe phimosis cases. Pain during application was minimal, with 96.7% of patients reporting scores of 3 or lower. The anaesthetic effect lasted about an hour, covering the entire surgical procedure, and 98.7% of patients experienced minimal pain during surgery. Side effects were rare, and patient satisfaction was high, with 98.9% rating their experience 7 or above. Overall, lidocaine cream proves to be a safe, fast, and effective anaesthetic for simplifying adult circumcision procedures.
Applying lidocaine beforehand helps reduce discomfort. It is also useful for treating paraphimosis, which is a painful condition where the foreskin becomes stuck behind the glans. In these cases, lidocaine alleviates pain and makes the reduction process easier. You can also use it before minor surgeries on the foreskin to avoid needing stronger anaesthesia.
Creams, gels, and combination products like lidocaine-prilocaine are popular choices because they spread evenly and absorb quickly. You should always apply it to intact skin and never on healing wounds or open cuts.
Safe use relies on the right timing and dosage, so it’s best to have medical supervision. Usually, the cream is applied shortly before the procedure to achieve effective numbing. This increases comfort without the risks of systemic side effects.
Where should lidocaine not be used?
Lidocaine should not be used on broken skin, open wounds, or inside the urethra. If it is used in these areas, it can cause irritation and burning. It may also cause infection or excessive numbness, which can be uncomfortable or unsafe. It should also be avoided in sensitive areas outside the penis, like the testicles or mucous membranes, unless a healthcare professional specifically advises its use. Overusing or spreading lidocaine beyond the intended area raises the risk of side effects.
Men should be careful about partner contact, as the drug can transfer during intercourse and temporarily reduce sensation for their partner. Using the right amount only on the head and base of the penis ensures that lidocaine works where it is needed. Proper application helps maintain sexual pleasure, prevents irritation, and allows the medication to achieve its purpose safely. Avoid injecting it into inflamed or infected tissue, and do not cover treated skin tightly, as this can increase absorption and the risk of systemic effects.
How Long Does Lidocaine Last and How Fast Does It Work?
Lidocaine starts working in about 10 to 20 minutes after application, depending on the form and method used. Once it takes effect, the numbing sensation can last from 30 minutes to 3 hours. This rapid onset happens because lidocaine is absorbed directly through the skin, allowing it to block nerve signals quickly and effectively.
Topical forms, like creams, gels, and sprays, usually take 10 to 20 minutes to begin working, although the full effect may take up to 30 to 60 minutes. The peak effect depends on how much is applied, the type of product, and the area covered. Using more than recommended does not speed up its action or extend its duration, but it can lead to side effects like excessive numbness or irritation.
Proper timing and application let men use it as needed without impacting overall sexual function. This approach maximises the benefits related to premature ejaculation.
What are the Side Effects and Risks of Using Lidocain?
The side effects and risks of lidocaine can range from mild skin irritation or redness to more serious reactions such as allergic responses or numbness spreading beyond the treated area. These effects depend on the dose, form, and individual sensitivity. When used correctly, lidocaine is generally safe, and being aware of its potential risks helps prevent complications and ensures proper use.
Common Side Effects:
- Redness, itching, or irritation at the application site
- Mild numbness or tingling beyond the intended area
- Temporary burning or stinging sensation
Moderate Side Effects:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Blurred vision or ringing in the ears
- Feeling unusually hot or cold
Serious or Rare Risks:
- Severe allergic reactions, including hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing
- Methemoglobinemia, a rare blood disorder that reduces oxygen in the body
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Confusion, drowsiness, or fainting
- Respiratory depression or slowed heart rate, especially if large doses are used in medical settings
Overuse or applying lidocaine to large areas increases the risk of serious side effects.
Avoid using on broken skin, open wounds, or sensitive areas like the urethra unless prescribed. Seek immediate medical attention if severe reactions occur, such as swelling of the face, lips, or throat, or sudden dizziness and fainting. Lidocaine is effective and generally safe, but understanding the potential side effects ensures it can be used responsibly without risking harm.
Does Lidocaine Affect Erection Quality?
Yes, lidocaine affects erection quality by causing temporary erectile dysfunction or weaker erections. As a local anaesthetic, it numbs the area where it is applied. Using too much or leaving it on for too long can lead to excessive numbness. This makes it more challenging to achieve or keep a firm erection.
The effect on erections is usually short-lived and manageable. Using the right amount, wiping off any excess before intercourse, or wearing a condom can help reduce these problems. Applying lidocaine about 20 minutes before sexual activity allows it to work well without dulling sensation too much.
Is lidocaine safe for regular use?
No, lidocaine is not safe for regular use. Lidocaine is meant for short-term, occasional use only. Using it repeatedly or on large areas can lead to serious health issues. Overuse increases absorption into the bloodstream, which can cause confusion, dizziness, seizures, slow heart rate, and even loss of consciousness. Long-term use may also lead to rare allergic reactions.
Topical lidocaine should never be applied to broken skin, burns, or open wounds. Covering the treated area or using more than recommended raises the risk of toxicity. Safe use means following instructions carefully, limiting the area of application, and consulting a healthcare professional if there are any concerns. Regular use without guidance is unsafe and can have dangerous effects.
Will Lidocaine Numb My Partner Too?
Yes, lidocaine can numb your partner if it transfers during sex. Lidocaine is a strong local anaesthetic. Any residue on the penis can temporarily reduce sensation in your partner’s genitals. This is more likely with creams or gels, which can be messy. Sprays can also transfer if not handled carefully. To prevent this, wipe off any excess before penetration. Wash your hands thoroughly after applying it, or use a condom. These steps keep the numbing effect focused where it’s needed while protecting your partner’s sensation.
Which is better: benzocaine or lidocaine?
Lidocaine is better than benzocaine when considering strength, duration, and effectiveness. While benzocaine acts faster, its effect lasts only about 12–15 minutes and is suited for small, localized areas. Topical lidocaine or lidocaine spray provides longer-lasting numbness, usually 30 minutes to 3 hours, making it more reliable for larger areas or extended use.
For men, lidocaine for premature ejaculation is clearly more effective. It helps reduce sensitivity, last longer in bed, and maintain better erectile quality, which benzocaine cannot reliably provide. Overall, lidocaine offers stronger, longer-lasting relief and greater versatility, making it the superior choice when both speed and duration matter. The choice between benzocaine and lidocaine depends on your needs and how long you want the numbing effect to last
