Cialis is a popular Erectile Dysfunction (ED) drug and has some hypotensive effects (lowers blood pressure), though its clinical significance is widely discussed. In healthy men, Cialis causes modest reductions in blood pressure. The minimal blood pressure changes do not pose any serious risks or are not clinically significant. However, in hypertensive patients, a 20 mg dose of Cialis is known to significantly reduce blood pressure. The average reduction in systolic/diastolic blood pressure was found to be 4.8/2.9 mmHg. Individuals with uncontrolled hypertension exhibited maximum reductions of 7.5/4.3 mmHg. Cialis is not contraindicated in men with stabilised or treated hypertension and is generally considered safe to take while on some medications.
Nevertheless, combining Cialis with nitrate medication is absolutely contraindicated due to the risk of life-threatening hypotension. That’s why it is advised to wait at least 48 hours before combining doses of Cialis and nitrates. Combining Cialis with alpha-blockers also requires careful monitoring of the hemodynamic stability, but overall, the cardiovascular safety profile of Cialis shows a low incidence of serious adverse events compared to placebo.
You should also exercise caution when mixing excess alcohol with Cialis, as it can amplify the hypotensive effects and may lead to an increase in side effects, even orthostatic hypotension.
If you happen to experience any symptoms of hypotension while on Cialis, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting, you should immediately seek medical attention. Continue reading to learn more about what Cialis is, how it lowers blood pressure, its drug interactions, and side effects.
What is Tadalafil (Cialis)?
Cialis (branded version of Tadalafil) is a phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor approved by the FDA in 2003 for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is the recurrent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. Tadalafil is also approved to treat the symptoms of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). BPH is a condition that enlarges the prostate and can lead to difficulties in urination. Tadalafil, marketed as Adcirca, is prescribed for individuals with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). PAH is a condition where persistently elevated blood pressure in the lungs causes breathlessness and fatigue.
Tadalafil is the active ingredient in Cialis. Tadalafil has the longest half-life of 17.5 hours due to subtle differences in its chemical structure. The pharmacokinetics of tadalafil influence its selectivity, bioavailability, and metabolism. Tadalafil acts as a PDE5 inhibitor. PDE5 inhibition prevents the breakdown of cGMP in the penile smooth muscles. Increased cGMP causes local vasodilation and improves blood flow, which results in stronger erections.
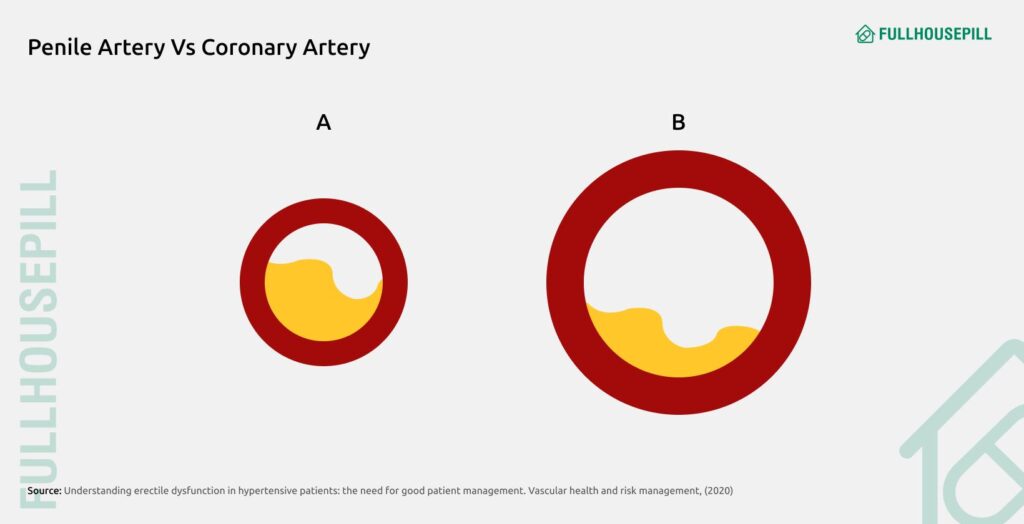
Both ED and cardiovascular disease (CVD) share common risk factors, including hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and smoking. According to a 2013 review published in Sexual Medicine Reviews, it was found that erectile dysfunction shares its pathophysiology with cardiovascular and endothelial function, preceding adverse cardiovascular events by 2-5 years. Penile arteries are much smaller than coronary arteries, making them more susceptible to the early signs of vascular impairment. Therefore, ED has recently emerged as a significant independent risk factor for adverse cardiovascular events, especially in younger men and diabetics.
Since Tadalafil has been one of the most preferred ED medications, owing to its longest duration of effect, it is important to uncover what Cialis actually affects our blood circulation and overall cardiovascular health.
Does Cialis Help Blood Circulation?
Yes, Cialis helps improve blood circulation through its mechanism as a PDE5 inhibitor. Cialis helps inhibit the PDE5 enzyme, a kind of protein found in various tissues throughout the body. PDE5 enzyme is present in the corpus cavernosum (erectile tissue of the penis), smooth muscle cells of the lungs, kidneys, and brain. PDE5 is also found in the systemic arteries and veins throughout the body. According to a 2004 study published in the Circulation journal, PDE5 inhibitors like Cialis have mild vasodilator effects that help improve blood circulation by widening the arteries. Cialis promotes the relaxation of the smooth muscle cells of the arteries and veins, enhancing the circulation throughout the vascular system.
Tadalafil is highly selective for PDE5 relative to other PDE isoforms. Tadalafil inhibits the PDE5 enzyme in the lungs, causing the arteries to widen and relax. When the pulmonary artery relaxes, it reduces the cardiac pressure in the lungs, making it easier for the heart to pump blood efficiently through the lungs.
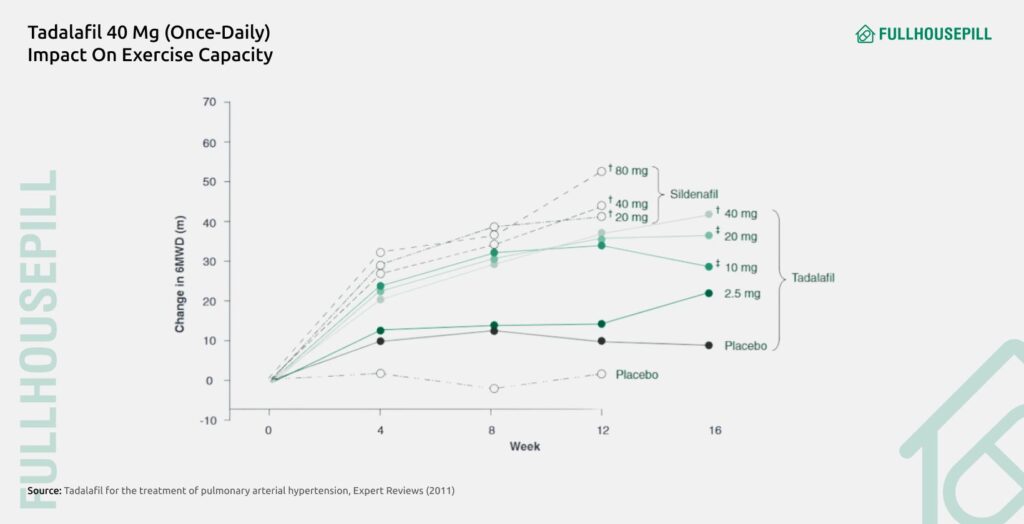
Even though Cialis is not authorised as a circulatory drug, current treatment guidelines by the World Health Organisation (WHO) recommend Tadalafil (once-daily) for treatment of class II or III PAH. Clinical trials published in the National Library of Medicine demonstrated that Tadalafil 40 mg (once-daily) significantly improved exercise capacity, with patients showing a 33-meter improvement in a 6-minute walking distance compared to placebo. A 2011 review published in the Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine also notes that Tadalafil reduces clinical worsening by 68% in patients with PAH. Tadalafil’s longer half-life of 17.5 hours also allows for convenient once-daily dosing, with headache being the most common adverse effect.
Does Cialis Increase or Raise Blood Pressure?
No, Cialis does not increase blood pressure. Cialis might cause a mild drop in your blood pressure. In most healthy people, low blood pressure is not a common side effect of Cialis when taken alone. When used alone, Cialis can cause minute, temporary decreases in blood pressure ranging from up to 7 mm reduction in systolic pressure and 5 mm in diastolic pressure, which can last up to 12 hours.
During the clinical trials of Cialis, healthy male participants were administered 20 mg Tadalafil, and their blood pressure was measured while standing up and lying down. Compared to placebo, Tadalafil 20 mg showed minimal difference: 0.2/4.6 mmHg while standing and 1.6/0.8 mmHg while lying down. A literature search in PubMed of more than 60 Tadalafil clinical trials with more than 4000 participants revealed that healthy participants who took Tadalafil 20 mg daily for 26 weeks reported no significant differences in their SBP (systolic blood pressure) and DPB (diastolic blood pressure) compared to placebo.
Due to Cialis’s vasodilatory effects and concurrent blood flow, flushing and headaches are the most commonly reported side effects in its studies. Headaches and flushing are also symptoms of hypertension or high blood pressure, which can confuse Cialis consumers into thinking that it raises blood pressure. Consult a healthcare professional to determine if your headaches and flushing are caused by hypertension and pursue any necessary treatment.
How Does Cialis Affect Blood Pressure?
Cialis causes mild reductions in blood pressure, which, in general, is not clinically concerning. Cialis, a PDE5 inhibitor, causes systemic vasodilation, creating small blood pressure changes in healthy men, according to a study published in the American Journal of Cardiology in 2003. However, in hypertensive patients, the hypotensive effects of Tadalafil can become more pronounced, especially if it is taken in combination with other anti-hypertensive agents. A multicentre, randomised, double-blind placebo study published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, analysing 114 patients with hypertension, reported that 20 mg Tadalafil lowered the average 26-hour ambulatory blood pressure (blood pressure readings at regular intervals) by 4.8/2.9 mmHg when taken along with multiple antihypertensive agents.
Extra caution is advised to avoid combining Cialis and nitrates. Their drug interaction is contraindicated due to the risk of severe hypotension, which can be life-threatening. A clinical trial examining the drug interaction between nitrate and Tadalafil analysed 150 male participants receiving daily Tadalafil (20 mg) and nitroglycerin (0.4 mg). The hemodynamic interaction reported greater mean decreases in systolic blood pressure up to 24 hours after administration compared to placebo. The interaction between the drugs was not observed at 48, 72, a nd 96 hours after administration, hypothesising that Tadalafil’s long half-life (17.5 hours) plays a critical role in this contraindication.
How Much Does Cialis Lower Blood Pressure?
When used alone, Cialis produces modest reductions in blood pressure due to its mild systemic vasodilatory effects. Typically, Cialis lowers systolic blood pressure by 7mmHg and diastolic blood pressure by 5 mmHg. These minor decreases in blood pressure are temporary and generally last up to 12 hours. In healthy men, these non-significant reductions are not clinically relevant and should generally not pose any severe risks. A 2022 clinical trial, the PASTIS trial, found that healthy men receiving 20 mg of Tadalafil twice within 15 days showed no significant effects on systolic and diastolic blood pressure without any incidence of serious adverse events.
A 2006 study published in Current Hypertension Reports examined the effect of Tadalafil in treated and untreated hypertensive patients. The study observes greater declines in the blood pressure of treated and untreated hypertensive patients, with the modest additive effect of Tadalafil. The study also reports on contraindications between Cialis and nitrate medication (vasodilators) or α-blockers (alpha blockers), which can cause dangerous drops in blood pressure. These drug interactions can also increase the risk of orthostatic hypotension (profound decline in blood pressure leading to dizziness, fainting, and falls).
Why Does Cialis Drop My Blood Pressure Too Much?
Cialis acts as a vasodilator and can cause minor blood pressure reductions due to vasodilation and reduced vascular resistance.
If you are taking Cialis and experiencing severe hypotension, dizziness, fainting episodes, or blurred vision, you may be combining nitrates, alcohol, and strong antihypertensive medication with Cialis. Here’s why these combinations are contraindicated and not recommended by the FDA:
Nitrates
Nitrates such as nitroglycerin or isosorbide dinitrate are used to treat angina (chest pain) and its symptoms, like pain in your jaw, down your arm, etc. Nitrates work by dilating the blood vessels and improving oxygen delivery to the heart.
Cialis demonstrates extended hemodynamic interactions with nitroglycerin up to 48 hours. Due to Cialis’s long half-life and extended elimination timeline (3-4 days), its drug interactions can cause significant blood pressure reductions during co-administration. A 2005 study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology examined these interactions and reported that compared to placebo, co-administration of Cialis and sublingual nitroglycerin lowered systolic blood pressure below 85 mmHg (severe hypotension) starting from 4 hours up to 24 hours.
| Medication | Mechanism of Action | Effect on Blood Pressure |
| Nitrates | Increases nitric oxide→ relaxes blood vessels | Lowers blood pressure |
| Cialis | Inhibits PDE5→ increases cGMP→ relaxes blood vessels | Lowers blood pressure |
When nitrates are combined with Cialis, the vasodilatory effects are amplified and may overwhelm the body’s homeostatic ability to regulate pressure.
Real-world prescription data show low (3.31%) rates of Cialis and Nitrate co-administration, suggesting a high degree of physician adherence to the contraindication guidelines. Despite these reports, clinical trials of Cialis demonstrate a favourable cardiovascular safety profile in healthy patients or patients not receiving nitrate therapy.
Alcohol
Mixing Cialis and alcohol can be risky, especially if you drink in excess. Both alcohol and Cialis are vasodilators and can augment the resultant hypotensive effect. When working in tandem, Cialis and alcohol can cause severe drops in blood pressure and orthostatic hypotension in men (above 65 years of age). Therefore, limit yourself to 1-2 drinks if you are planning on taking or have already taken Cialis. Other potential risks of mixing Cialis with Alcohol are:
| Effect | Why it happens |
| Low blood pressure | Both relax and widen blood vessels, causing a severe drop in BP, if alcohol is taken in excess. |
| Dizziness or fainting | Sudden drops in blood pressure reduce blood flow to the brain. |
| Headaches or Flushing | Common side effects of Cialis can be intensified by excess alcohol intake. |
| Rapid heartbeat | The body compensates for low BP |
| Reduced sexual performance | Excess alcohol with Cialis can cause the medication to not take effect properly, impairing arousal and the quality of erection. |
Anti-hypertensive agents
Both nitrates (Nitroglycerin, Isosorbide) and alpha-blockers (Prazosin, Doxazosin) are antihypertensive agents. They help lower the blood pressure, similar to Cialis. Cialis also demonstrates hypotensive effects by reducing systolic blood pressure by 7-10mmHg on average. When combined with other anti-hypertensive drugs, the hypotensive effects can become more pronounced and may lead to fatal hypotension. A 2021 retrospective study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine reports that in healthy individuals, co-possession of Tadalafil and anti-hypertensive agents like nitrates does not significantly increase the risk of hypotensive cardiac outcomes.
However, in patients with uncontrolled hypertension on multiple antihypertensive agents, studies have noted larger reductions in average ambulatory blood pressure (7.5/4.3mmHg), making this combination absolutely contraindicated. The FDA also lists nitrates and alpha-blockers as contraindications, advising against using either for at least 48 hours after Cialis use.
| Medication Class | Examples | Risk |
| Alpha-blockers | Prazosin, Doxazosin | High risk of orthostatic hypotension when combined with Cialis |
| Nitrates | Nitroglycerin, isosorbide | Contraindicated– can cause a life-threatening drop in blood pressure. |
Avoid combining Cialis with nitrates, alcohol, and other anti-hypertensive agents to minimise their amplified effect on blood pressure. All of these agents are vasodilators. Their combined effect can be dangerous for men with autonomic dysfunction or on other contraindicated medications.
Should you take Cialis with low blood pressure?
You should exercise caution while taking Cialis if you already have low blood pressure. You should tell your doctor if you have uncontrolled low blood pressure before you start ED treatment with Cialis because Cialis relaxes the blood vessels and lowers blood pressure by about 7-10mmHg. However, if your baseline blood pressure is already low (below 90/60 mmHg), the combined vasodilation effects of Cialis can lead to:

[Add sophisticated infographic next to side effects, can include emoticons too to show fatigue, blurred vision]
- Dangerous drop in blood pressure
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fainting
- Blurred Vision
- Fatigue
Despite a large pooled analysis of 22,825 patients showing no significant increases in hypotension-related events when mixed with anti-hypertensive medication compared to placebo, important exceptions also exist. For patients with a history of cardiovascular diseases, an important marker of ED, a complete diagnostic workup and optimised hemodynamic stability must be achieved for longer periods before Cialis can be safely prescribed.
If you still want to use Cialis safely, you need to receive your doctor’s approval and start with a lower dose of Cialis (2-2.5mg). You should avoid combining Cialis with other vasodilators and monitor your blood pressure regularly. You should also stay hydrated and rise slowly from sitting or lying positions, especially if you are older (above 60 years).
Can You Take Cialis with High Blood Pressure?
Yes. Cialis can generally be taken by people with high blood pressure, but there are important caveats to improve its safety and efficacy. Cialis may slightly lower systolic blood pressure by 7-10 mmHg, which can be beneficial and generally considered safe for patients with controlled hypertension.
A recent 2022 pooled analysis of 72 Phase II-IV clinical studies of Tadalafil published in the Journal of Clinical Hypertension reported no significant increase in hypotensive and major cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients. As hypertension persists as a modifiable risk factor of ED and a prognostic marker in the development of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), modest lowering of blood pressure through Cialis can be beneficial in improving blood pressure control along with adherence to anti-hypertensive therapies.
However, men who are suffering from uncontrolled hypertension and those on Nitrates and alpha-blocker therapy should not start taking Cialis until their physician has stabilised the dosage.
Certain scenarios can arise if Cialis is taken with uncontrolled hypertension or high blood pressure (not stabilised).
| Scenario | Recommendation (for Cialis) | Rationale |
| Concurrent Ntrate therapy | Contraindicated | Life-threatening BP drop when the vasodilatory effects of nitrates and PDE5 inhibitors mix |
| Alpha-blocker | Use a very low dose, monitor blood pressure regularly | High Risk of Orthostatic Hypotension and Fainting Episodes |
| Uncontrolled Hypertension | Postpone Cialis use until blood pressure is stabilised on a daily dose | Increased cardiovascular strain during sexual activity |
| Recent heart attack, stroke, or unstable angina | Contraindicated | Sexual exertion may increase the risk of adverse events, as the effects on blood pressure are unpredictable. |
What Happens If You Take Cialis with High Blood Pressure?
Most classes of blood pressure medications, such as beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), can be safely combined with Cialis without serious interactions, provided your hypertension can be stably controlled.
A 2012 clinical trial demonstrates that combining Cialis with Losartan (Cozaar Brand name) can provide enhanced therapeutic benefits for ED symptoms. Published in the International Journal of Impotence Research, the study showed minute blood pressure differences (8/4 mmHg) compared to placebo. The clinical trial was also the first to show that losartan, administered together with Cialis, can significantly improve erectile function and sexual performance scores and was more effective than monotherapy.
Another recent 2022 study looked at the pharmacokinetic interactions between Cialis and Amlopidine (Norvasc Brand name), a calcium channel blocker and antihypertensive. The study found that coadministration of 5 mg Tadalafil (Cialis) and 10 mg Amlodipine increased tadalafil exposure by 57% and peak plasma concentration by 34%, increasing its bioavailability and efficacy. The interaction was well-tolerated and resulted in only mild adverse events.
An ACE inhibitor, Lisinopril, when combined with Cialis, can cause dangerous hypotensive effects (blood pressure below 85 mmHg), leading to side effects such as dizziness, headache, or fainting. A 2003 Phase 3 clinical trial of Tadalafil revealed that combination with anti-hypertensive agents like ACE inhibitors can cause mild blood pressure drops in healthy men, which are not clinically concerning. However, caution should be maintained while taking Cialis with anti-hypertensives for symptoms of dizziness and severe hypotension.
| Medication Class | Examples | Notes |
| Beta blockers | Metoprolol, Atenolol | Monitor for fatigue or a very low heart rate |
| ACE inhibitors | Lisinopril, Enalapril | Additive Blood pressure-lowering effects–watch out for dizziness. |
| ARBs | Losartan, Valsartan | Mild additive effect on Vasodilation |
| Diuretics | Hydrochlorothiazide | Ensure adequate hydration to avoid blood pressure drops |
What are the other side effects of Tadalafil (Cialis)?
Tadalafil (Cialis) is generally well-tolerated, but it can produce a spectrum of side effects ranging from mild and common to rare but serious.
| Side effects category | Examples | Notes |
| Common | Headaches, indigestion, back pain, muscle aches, flushing, and a stuffy nose | Typically mild-moderate symptoms, often temporary. |
| Less Common (Mild) | Dizziness, nausea, diarrhea | Often resolved without treatment |
| Rare (Serious) | Severe hypotension, sudden change in vision and hearing, chest pain or irregular heartbeat, priapism (prolonged erection for >4 hours) | Infrequent events require immediate medical attention. |
How Does Viagra Compare With Cialis?
Viagra vs Cialis shows clear differences in duration and effectiveness. Viagra typically works within 30 to 60 minutes and lasts 4 to 6 hours. Cialis offers much longer-lasting effects, remaining active for up to 36 hours. This longer duration makes Cialis known as the “weekend pill” while Viagra serves as an “evening pill”.
Both medications are PDE5 inhibitors that work similarly by increasing blood flow to the penis. Neither medication affects sexual desire but helps facilitate erections when sexually aroused. Viagra requires more precise timing before sexual activity, needing to be taken within a specific timeframe. Cialis provides greater flexibility and spontaneity due to its extended duration. Cialis also comes in a daily 2.5mg dose option for continuous effectiveness.
Side effects differ between the medications. Viagra may cause blue-tinted vision and nausea. Cialis commonly causes back pain and upper respiratory symptoms. Both medications can cause headaches, flushing, and nasal congestion.
Does Generic Viagra Lower BP?
Yes, generic viagra can lower blood pressure through vasodilation effects. Sildenafil works by blocking the PDE-5 enzyme, which causes blood vessels to relax and widen. This vasodilation effect reduces blood pressure in most users. Research shows sildenafil decreases systolic blood pressure by approximately 8 mmHg and diastolic pressure by about 5 mmHg. These reductions are typically small and clinically insignificant for healthy individuals. The blood pressure lowering effects do not differ significantly between normotensive and hypertensive men. Erectile dysfunction medication like sildenafil is actually used in higher doses as Revatio to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension. The hypotensive effects are generally temporary and return to normal within 4 hours.
Which ED Medications Are Safest For Men With Low BP?
ED medications require careful consideration for men with low blood pressure. All FDA-approved PDE5 inhibitors, including sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil, and avanafil, are generally safe but can lower blood pressure further.
Men with very low blood pressure (below 90/50 mmHg) should use sildenafil with caution. Patients with dehydration or heart conditions face increased risks when using generic viagra pills. The combination of existing low blood pressure and the hypotensive effects can cause dizziness or fainting.
The safest approach involves starting with the lowest effective dose and monitoring blood pressure responses. Daily tadalafil at 5mg may be safer for some men with hypotension as it provides consistent low-dose effects rather than higher peak concentrations. Your healthcare providers will evaluate cardiovascular status before prescribing any ED medication.
Generic viagra pills should never be combined with nitrate medications or alpha-blockers in hypotensive patients, as this can cause dangerous blood pressure drops. Men with low blood pressure need medical supervision when starting ED treatments to ensure safety and effectiveness
