Sildenafil (Viagra) and tadalafil (Cialis) are the two most prescribed pills for erectile dysfunction (ED). ED is a common condition in men where getting or keeping an erection is difficult. It can be caused by physical or psychological factors. Both drugs are phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors. They improve blood flow to the penis through the nitric oxide–cGMP pathway during sexual stimulation.
PDE5 is an enzyme found in the smooth muscle of blood vessels in the penis and lungs. It breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). cGMP helps relax blood vessels and increase blood flow. Blocking PDE5 allows cGMP to build up. This relaxes the smooth muscle in the corpus cavernosum and makes it easier to have a firm erection.
Sildenafil, launched by Pfizer in 1998, works quickly and lasts for 4 to 6 hours. Tadalafil, launched by Eli Lilly in 2003, lasts up to 36 hours and is called “the weekend pill.” Clinical data shows sildenafil peaks in 1 to 1.5 hours, while tadalafil peaks at about 2 hours and has a longer half-life of 17.5 hours.
Tadalafil offers more flexibility and spontaneity because of its long duration. Sildenafil may cause vision changes more often, while tadalafil may cause back or muscle pain. Both drugs are also approved for pulmonary arterial hypertension, and tadalafil is approved for benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Knowing the differences in duration, side effects, cost, and interactions can help you choose the better option for your needs.
For a better understanding of the differences between the drugs, refer to the table below.
| Drug Details | Sildenafil (Viagra) | Tadalafil (Cialis) |
| Drug Class | PDE5 inhibitor | PDE5 inhibitor |
| Dosage | 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg (once daily or as needed) | 2.5 mg, 5 mg (daily); 10 mg, 20 mg (as needed) |
| Onset | 30-60 minutes | 30-45 minutes |
| Duration Of Effect | 4-6 hours | 24-36 hours |
| Side Effects | Headache, flushing, nasal congestion, visual disturbances. | Headache, back pain, dyspepsia, myalgia. |
| Suitability For Spontaneous Sex | Moderate – timed use needed. | High – long duration allows spontaneity. |
| Also Approved For | Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) – Sildenafil, Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) – brand name Revatio | Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) – Cialis, Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)- brand name Adcirca |
| Food Interactions | High-fat meals may delay the effect; grapefruit increases side effects. | Grapefruit increases drug levels and side effects; minimal impact from other foods. |
What Is the Difference Between Sildenafil (Viagra) and Tadalafil (Cialis)?
Sildenafil (Viagra) and tadalafil (Cialis) are PDE5 inhibitors used for erectile dysfunction. They differ in onset, duration, and dosing. Sildenafil works within an hour and lasts 4-6 hours. Tadalafil can last up to 36 hours, offering more flexibility. Understanding the key differences mentioned below, will help you make a better choice.
Sildenafil (Viagra) vs. Tadalafil (Cialis): Key Differences
- Onset of action: Sildenafil usually starts working within 30-60 minutes, while tadalafil can take about 30 minutes but may be slower in some men.
- Duration: Sildenafil lasts 4-6 hours, whereas tadalafil can last up to 36 hours, earning it the nickname “the weekend pill.”
- Dosing: Sildenafil is typically taken as needed before sexual activity, while tadalafil can be taken either as needed or in a lower daily dose for more spontaneity.
- Food effect: A heavy or fatty meal can delay sildenafil’s effect, but tadalafil is less affected by food.
- Best suited for: Sildenafil is good for men who want a shorter, one-time effect. Tadalafil is better for those who prefer a longer window of effectiveness or daily treatment.
Sildenafil: Sildenafil citrate is a medicine called a PDE5 inhibitor. It works by helping the blood vessels in the penis relax, so more blood can flow in during sexual stimulation. This makes erections easier to achieve. Pfizer first developed sildenafil in the early 1990s to treat chest pain (angina). During testing, researchers noticed it caused erections. Because of this, the sildenafil citrate tablets were approved to treat ED. - Tadalafil: Tadalafil is also a PDE5 inhibitor. It improves erections in the same way, by increasing blood flow to the penis. The main difference is that tadalafil lasts much longer in the body. This is why it is often called “the weekend pill.” It was developed by ICOS Corporation with Eli Lilly after Viagra’s success. The FDA approved tadalafil in November 2003 under the brand name Cialis.
Sildenafil: Sildenafil citrate is a medicine called a PDE5 inhibitor. It works by helping the blood vessels in the penis relax, so more blood can flow in during sexual stimulation. This makes erections easier to achieve. Pfizer first developed sildenafil in the early 1990s to treat chest pain (angina). During testing, researchers noticed it caused erections. Because of this, the sildenafil citrate tablets were approved to treat ED.
Tadalafil: Tadalafil is also a PDE5 inhibitor. It improves erections in the same way, by increasing blood flow to the penis. The main difference is that tadalafil lasts much longer in the body. This is why it is often called “the weekend pill.” It was developed by ICOS Corporation with Eli Lilly after Viagra’s success. The FDA approved tadalafil in November 2003 under the brand name Cialis.
What Are the Medical Uses of Sildenafil and Tadalafil?
Sildenafil and tadalafil are both FDA-approved PDE5 inhibitors primarily used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED). Both drugs have received approval under the names – Revatio for sildenafil and Adcirca for tadalafil, for treating pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Both are also used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), either alone or in combination with ED. These extended uses leverage the vasodilatory effects of the drugs on smooth muscle in the lungs and lower urinary tract.
Some off-label uses for these drugs occur in conditions like Raynaud’s phenomenon, Female Sexual Arousal Disorder (FSAD), and altitude sickness / High-Altitude Pulmonary Edema (HAPE).
To better illustrate the dosage differences between the two drugs, see the table below.
| Condition | Sildenafil | Tadalafil |
| Erectile Dysfunction | 100 mg, once per day. | 5-10 mg, once per day. |
| Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension | 20 mg, three times daily (60 mg/day) | 40 mg, once per day. |
| Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia | 25-50 mg, once per day. (rare, usually tadalafil is used) | 5 mg, once per day. |
| Raynaud’s Phenomenon | 50 mg, twice per day | 20 mg, on alternate days. |
| Female Sexual Arousal Disorder | 25-50 mg, once per day. | 5 mg, once per day. |
| Altitude Sickness / High-Altitude Pulmonary Edema | 50 mg, every 8 hours | 10 mg, twice per day. |
How Does Sildenafil Work Compared to Tadalafil?
Sildenafil blocks the PDE5 enzyme to boost blood flow to the penis. It works in 30-60 minutes and lasts about 4-6 hours. A heavy meal can delay its effect. Tadalafil works the same way but lasts up to 36 hours. Food has little impact on its absorption
When a man is sexually aroused, the body releases nitric oxide (NO) in the penis. This happens in the corpus cavernosum, a spongy tissue that fills with blood during an erection. NO helps the body make more cGMP. This chemical relaxes the smooth muscles in the penis and widens the blood vessels, allowing more blood to flow in. By stopping cGMP from breaking down, sildenafil and tadalafil keep its levels higher. This helps men get and keep firmer erections during sexual activity.
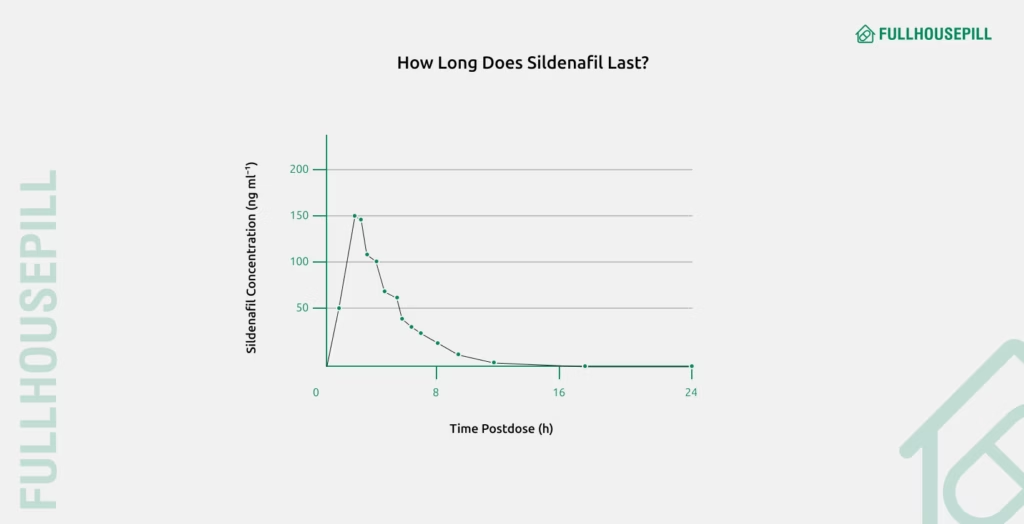
A study published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2002) looked at how sildenafil works in healthy men. It found that taking a 50 mg dose of sildenafil led to the highest blood level of the drug (about 159 ng/mL) in 1 to 1.5 hours. The drug’s half-life was about 4 hours. Eating a high-fat meal slowed down how quickly the drug was absorbed and lowered the peak level by about 29%. However, it did not significantly change the total amount of the drug absorbed.
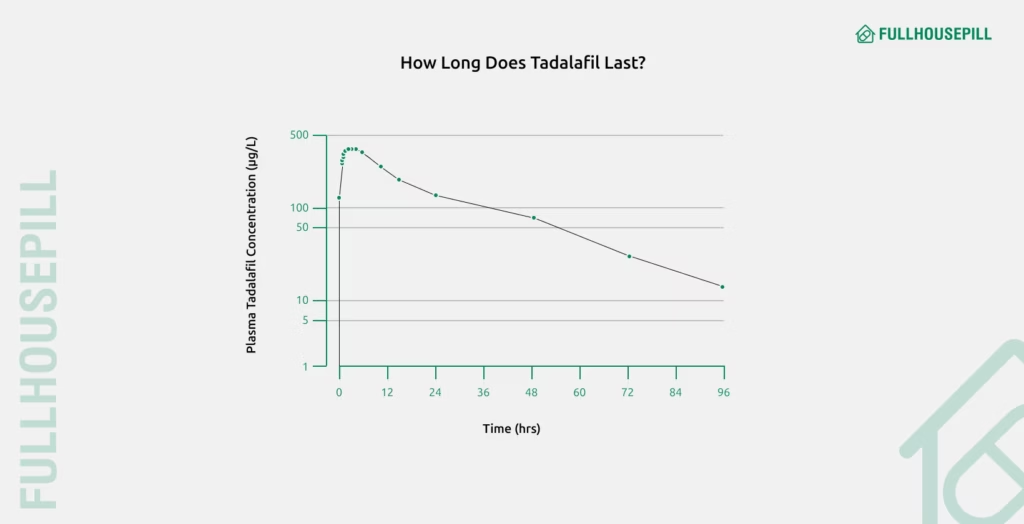
A study in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2005), conducted pharmacokinetic assessments in healthy adults after single and multiple doses of tadalafil (2.5-20 mg). It found that tadalafil reached a mean peak plasma concentration of approximately 378 µg/L around 2 hours after a 20 mg dose, followed by a half-life of 17.5 hours. The research confirmed dose- and time-linear pharmacokinetics, unaffected by food intake, with relatively slow systemic clearance compared to other PDE5 inhibitors.
How Fast Does Sildenafil Work Compared to Tadalafil?
Sildenafil usually starts working in 30-60 minutes. Some men may feel it as early as 12 minutes in ideal conditions. High-fat meals can delay its effect, so it works best on an empty stomach.
Tadalafil usually starts working in 30-45 minutes. Food does not slow it down much.
In studies, sildenafil began working in 12-30 minutes, with peak effect at about 60 minutes. Tadalafil started in 30-45 minutes and peaked in the blood after 2 hours.
In real life, most men notice sildenafil working in 45-60 minutes. Tadalafil usually works in 30-60 minutes. Its effects build slowly, last much longer, and feel smoother compared to sildenafil’s faster but shorter effect.
Sildenafil is better for quick, short-term results, while tadalafil is better for longer-lasting, more flexible performance.
Which Lasts Longer: Sildenafil or Tadalafil?
When it comes to duration of action, tadalafil outlasts sildenafil. Sildenafil (Viagra) remains effective for about 4 to 6 hours after ingestion, though its peak effect usually occurs around the 1-hour mark. After this window, its blood concentration declines rapidly due to a shorter half-life of approximately 4 hours. This makes sildenafil a suitable choice for on-demand use, but it requires careful timing around sexual activity.
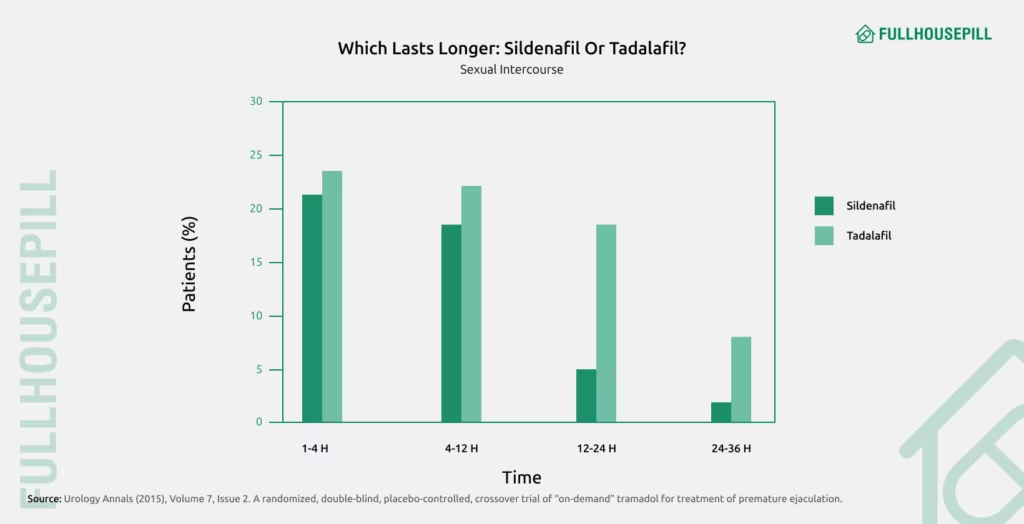
Tadalafil (Cialis) lasts significantly longer – up to 36 hours, earning it the nickname “the weekend pill.” It allows sustained plasma levels and therapeutic effects over an extended period of time. This prolonged action supports both on-demand and daily low-dose regimens, offering more flexibility and spontaneity in sexual activity.
Which Medication Gives a Harder Erection: Sildenafil or Tadalafil?
Both sildenafil and tadalafil are effective at improving erection hardness by enhancing blood flow to the penis, but neither has been proven to consistently produce a “harder” erection over the other.
Sildenafil produces a more intense peak effect due to its faster onset and shorter duration, making it feel more potent to some users. In contrast, tadalafil offers more natural-feeling, longer-lasting erections, which results in greater overall satisfaction and improved consistency, especially when taken daily. The effect differs from user to user. User preference is driven by timing flexibility, rather than erectile strength.
What Is the Usual Dosage of Sildenafil or Tadalafil?
The usual dosage of sildenafil is 50 mg, one hour prior to sexual activity. If ineffective, the dose may be increased to 100 mg per day. The standard dose of tadalafil is 10 mg, 30 minutes before sexual activity. The dose is reduced to 5 mg if necessary. Tadalafil has a longer duration of action (up to 36 hours), so a daily dose may not be required.
For the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED), both sildenafil and tadalafil are taken orally, but their dosing regimens differ based on their pharmacokinetics and duration of action. Consult your doctor to determine your dose based on your age and health.
What Are the Side Effects of Tadalafil vs Sildenafil?
Sildenafil and tadalafil are usually safe for most people, and both are well-tolerated. They can cause similar side effects because they work the same way as PDE5 inhibitors.
The differences in how long they stay in the body and how they affect other PDE enzymes can cause some changes in side effects. Sildenafil can affect PDE6, which is found in the eyes, so it is more likely to cause vision changes. Tadalafil stays in the body longer and can affect PDE11, which is linked to muscles. This is why some people get muscle aches or back pain when using tadalafil.
Below is a table comparing common side-effects for both drugs.
| Side Effects | Sildenafil (Viagra) | Tadalafil (Cialis) |
| Headache | Very Common | Very Common |
| Flushing (redness) | Common | Less Common |
| Nasal Congestion | Common | Common |
| Dyspepsia (indigestion) | Common | Very Common |
| Muscle or back pain | Rare | Common |
| Visual Disturbances (blurred vision, tinged vision) | Common | Rare |
| Hypotension | Rare | Common |
| Dizziness | Common | Common |
| Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) | Common | Less Common |
| Rash | Common | Less Common |
Some adverse reactions reported for both drugs are priapism (prolonged erection lasting over 4 hours), sudden hearing loss, non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) – more commonly associated with sildenafil, severe hypotension – when combined with nitrates or alpha-blockers.
Sildenafil and tadalafil remain safe for consumption despite the side-effects listed above. But, always consult your doctor if the medication or dosage does not agree with you.
What Drugs Should Not Be Taken With Sildenafil or Tadalafil?
Sildenafil and tadalafil can be dangerous if taken with certain medicines or substances. This is because they widen blood vessels and lower blood pressure. The biggest risks are with nitrates and alpha-blockers. Taking them together can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure, which may lead to dizziness, fainting, or even heart problems.
A study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2000) looked at men with stable angina who took sildenafil (50 mg) and nitrates. It found the combination caused a much greater drop in blood pressure, raising the risk of severe hypotension. Because of this, sildenafil should never be used with nitrate medicines.
For men taking alpha-blockers, sildenafil or tadalafil should only be used if a doctor says it’s safe. The mix can also cause low blood pressure.
Tadalafil is mainly broken down in the liver by an enzyme called CYP3A4. This enzyme is found in the liver and intestines and helps break down many medicines. Some drugs, like ticagrelor, ketoconazole, itraconazole, or ritonavir, block CYP3A4. This slows the breakdown of tadalafil, so more of it stays in the blood. This can increase the risk of side effects such as headaches, flushing, low blood pressure, and long-lasting erections.
Other drugs, like rifampin, speed up CYP3A4. This makes tadalafil break down faster, lowering its level in the blood and making it less effective. In such cases, the dose may need to be changed.
A case report in the Journal of Forensic and Legal Medicine (2023) described a rare death from brain bleeding caused by heavy alcohol use and sildenafil. Drinking a lot of alcohol while using sildenafil or tadalafil is unsafe. It can make side effects worse, such as dizziness and low blood pressure.
For a comprehensive list of drugs to be avoided, refer below.
- Nitrates (eg. nitroglycerin, isosorbide dinitrate) – can cause dangerous drops in blood pressure
- Alpha-blockers (eg. tamsulosin, doxazosin) – may lead to low blood pressure and dizziness
- Protease inhibitors (eg. ritonavir, saquinavir) – can raise drug levels and side effects
- Antifungal medications (eg. ketoconazole, itraconazole) – may increase blood levels of the drug
- Macrolide antibiotics (eg. erythromycin, clarithromycin) – can also increase blood levels
- Certain seizure medications (eg. carbamazepine, phenytoin) – may reduce effectiveness.
- Other ED medications – combining with other PDE5 inhibitors increases side effect risk
Which Food Interacts With Sildenafil or Tadalafil?
Sildenafil is known to be affected by food, especially high-fat meals, which delays its absorption and reduces its maximum plasma concentration. Tadalafil has low water solubility, but it is efficiently absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract and its absorption is not affected by food when taken orally. Grapefruit and grapefruit juice can interact with both sildenafil and tadalafil by increasing their blood levels, which may heighten the risk of side effects.
A pharmacokinetic study in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2002), reported that taking sildenafil with food, especially a high-fat meal, delayed its peak concentration by about one hour and reduced the maximum concentration by approximately 29%, while overall exposure dropped around 11%. These changes, though measurable, are generally not deemed clinically significant, but taking sildenafil on an empty stomach helps ensure faster onset.
Another study in the same journal described the pharmacokinetic effects of tadalafil. It showed that tadalafil follows a dose and time-dependent linear pharmacokinetic profile, meaning its absorption and concentration in the body increase proportionally with the dose. Unlike some other ED medications, its absorption is not influenced by food intake, and it is cleared from the body more slowly than most other PDE5 inhibitors.
Which Is Better: Sildenafil or Tadalafil for Erectile Dysfunction?
Both sildenafil (Viagra) and tadalafil (Cialis) are effective treatments for erectile dysfunction (ED), but the better option depends on individual needs, lifestyle, and health factors.
Sildenafil typically starts working in 30-60 minutes and lasts about 4-6 hours, making it a good option for occasional, planned use. However, it may be less effective if taken after a high-fat meal.
Tadalafil, on the other hand, begins to work in 30-45 minutes and lasts up to 36 hours, offering more spontaneity. It’s also approved for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Men who want a longer window of effectiveness or who experience urinary symptoms prefer tadalafil over sildenafil.
Which Is More Affordable: Cialis (Tadalafil) or Viagra (Sildenafil)?
Tadalafil might be slightly more affordable, due to its longer duration of action. However both drugs are priced approximately in the same range, and choice largely depends on user intent and convenience.
Cenforce 100 mg (Sildenafil) is generally priced at $0.85-$2.00 per tablet on most online pharmacy websites. It’s a common generic version of Viagra manufactured by Centurion Laboratories.
Vidalista 20 mg (Tadalafil) usually costs around $0.90-$2.00 per tablet, and is manufactured by Centurion Laboratories as well. Since tadalafil lasts longer, some users take it less frequently, which reduces overall cost.
Which Is Safer Sildenafil or Tadalafil?
Both sildenafil and tadalafil are considered safe and well-tolerated PDE5 inhibitors when used as prescribed, but they differ in duration, side-effects profile, and individual tolerability. A direct meta-analysis in the Journal of International Urology and Nephrology (2017), comparing tadalafil and sildenafil found no significant difference in erection firmness or success of intercourse between the two drugs. However, tadalafil’s longer half-life (~17.5 hours) offers a longer window of action (up to 36 hours), which many patients report as more natural and flexible. Tadalafil users also reported an increased occurrence of muscle pain, however flushing was noticeably lower than sildenafil users.
Can You Take Sildenafil and Tadalafil Together?
No, sildenafil and tadalafil should not be taken together. Both drugs belong to the same class, phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, and combining them significantly increases the risk of adverse effects such as severe hypotension, dizziness, syncope, priapism, and cardiovascular events. Since both medications work by enhancing nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation, their effects are additive and potentially dangerous when used together. Clinical guidelines and pharmacological reviews explicitly advise against combining PDE5 inhibitors due to the lack of safety data and the risk of synergistic vasodilatory effects.
What Are The Best ED Treatments?
The best ED treatments include oral medications, lifestyle changes, therapy, and medical devices, with oral PDE5 inhibitors like sildenafil and tadalafil offering the fastest and most reliable results.
| Treatment | Mechanism | Onset | Duration | Best For |
| Sildenafil (Viagra) | Increases blood flow by inhibiting PDE5 enzyme | 30–60 minutes | 4–6 hours | Occasional use, quick onset |
| Tadalafil (Cialis) | Longer-acting PDE5 inhibitor for improved blood flow | 30–45 minutes | Up to 36 hours | Regular use, spontaneity |
| Avanafil (Stendra) | Fast-acting PDE5 inhibitor with fewer side effects | 15–30 minutes | 6–8 hours | Men wanting faster action and milder effects |
| Vardenafil (Levitra) | Enhances blood flow via PDE5 inhibition | 30–60 minutes | 4–5 hours | Men with diabetes or mild ED |
| Vacuum Erection Devices | Create suction to draw blood into the penis | 5–15 minutes | As long as ring is on | Men who can’t take medication |
| Penile Injections | Directly trigger erection via vasodilation | 5–20 minutes | 30–60 minutes | Severe ED, non-responders to pills |
| Lifestyle Changes | Improve blood flow and hormone balance | Gradual | Ongoing | All ED types, long-term improvement |
| Therapy (Sex or Psych) | Reduces anxiety, improves performance and confidence | Gradual | Ongoing | ED with psychological causes |
What Are The Best ED Pills?
The best ED pills include sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), vardenafil (Levitra), and avanafil (Stendra), each offering different onset times, durations, and side effect profiles. Sildenafil is one of the best ED pills for rapid onset and short-term use. It begins working in 30 to 60 minutes and remains effective for about 4 to 6 hours. It’s ideal for men who want a fast-acting option for planned sexual activity.
Tadalafil offers a longer window of effectiveness, up to 36 hours, and can be taken daily at a lower dose. This makes it suitable for men who want more spontaneity or prefer a regular dosing schedule. Vardenafil is similar to sildenafil but may work better in men with diabetes or certain cardiovascular risks due to its slightly different chemical structure. It typically lasts 4 to 5 hours. Avanafil, the newest option, acts quickly (within 15–30 minutes) and has fewer side effects for some men.
All four options require sexual stimulation to work and are available by prescription. A healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate pill based on age, health status, and frequency of use.
Which ED Medication Has The Longest-Lasting Effects?
Tadalafil (Cialis) lasts the longest of all ED medicines. It can stay active in the body for up to 36 hours. This gives men more flexibility and spontaneity for sexual activity.
Sildenafil (Viagra) lasts upto 4 to 6 hours. How long it works can depend on metabolism, food, and other factors. Vardenafil (Levitra) lasts about the same as sildenafil, around 4 to 5 hours. It may work a little better for men with diabetes.
Avanafil (Stendra) is a newer ED drug. It works fast, in about 15 to 30 minutes, and lasts around 6 hours. This makes it a good middle option between quick action and moderate duration.

Which Is More Effective: Sildenafil Or Vardenafil?
Sildenafil and vardenafil are both effective PDE5 inhibitors, but their subtle differences can affect which one works better for a specific user. Clinical data suggest that for many men, sildenafil vs vardenafil comparisons show similar success in achieving erections, though vardenafil may offer greater efficacy in individuals with diabetes or high cholesterol. Both drugs typically take effect within 30 to 60 minutes and last about 4 to 6 hours. However, vardenafil binds more selectively to the PDE5 enzyme, which may reduce side effects like visual changes that are sometimes reported with sildenafil. On the other hand, sildenafil is more widely available and often more affordable, making it a first choice for many doctors. Choosing between sildenafil vs vardenafil depends on how your body responds, what side effects you experience, and whether you have coexisting health conditions. A healthcare provider can help tailor the treatment based on personal needs.
Which Is More Powerful, Vardenafil Or Tadalafil?
Vardenafil is more powerful; in vardenafil vs tadalafil, vardenafil delivers higher biochemical potency and stronger first-dose efficacy. Vardenafil shows superior PDE5 inhibition in laboratory tests. Corbin et al. measured an IC50 of 0.091 nM for vardenafil compared to 1.8 nM for tadalafil, demonstrating nearly twenty-fold greater potency. This biochemical strength translates into more effective early response rates. Clinical trials show vardenafil 20 mg achieved 81% first-dose success on SEP2 and 70% on SEP3. In contrast, tadalafil 20 mg reached about 62% on SEP2 and 55% on SEP3. These results indicate that vardenafil consistently outperforms tadalafil in both laboratory potency and initial clinical outcomes.
What is the recommended sildenafil dosage for ED?
The usual sildenafil dosage for erectile dysfunction is 50 mg taken about one hour before sexual activity. Depending on effectiveness and tolerance, the dose may be reduced to 25 mg or increased to 100 mg. It should not be taken more than once in 24 hours. Sildenafil works best on an empty stomach and with sexual stimulation. Factors such as age, health conditions, and other medications can affect the correct dose. A doctor will determine the safest and most effective amount based on individual needs to ensure optimal results while minimizing the risk of side effects.
What Are the Generic Options of Sildenafil Citrate?
Cenforce, commonly referred to as the “Blue Pill,” is the generic option of sildenafil citrate used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men. Manufactured by Centurion Laboratories, it contains 100 mg of sildenafil citrate, the same active ingredient found in Viagra. This generic alternative is typically available in blister packs of 10 tablets. Some other generic options of Sildenafil Citrate include Kamagra, Fildena, Suhagra, and Silagra.
What Are the Generic Options of Tadalafil?
Vidalista is recognized as a generic alternative to tadalafil. It is manufactured by Centurion Laboratories. It contains tadalafil, a long-acting phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor that enhances blood flow to help men achieve and maintain erections. Each strip includes 10 tablets, and the effects last up to 36 hours, earning it the nickname “Weekend Pill.” Tadalafil reaches its peak concentration about 2 hours after intake. Other generic options of Tadalafil include brands like Tadacip, Cialis, Tadarise, and Apcalis.
Can Women Take Viagra?
No, Viagra is not approved for women, and its effects on female sexual dysfunction are not well established. While viagra for women has been studied, the results are inconsistent and do not confirm reliable benefits. Some women may experience improved arousal due to increased blood flow, but sexual dysfunction in women often involves multiple factors beyond circulation. Off-label use is possible under medical supervision, but potential side effects such as headaches and flushing remain a concern. Approved alternatives like flibanserin (Addyi) or bremelanotide (Vyleesi) may be more suitable for certain types of female sexual dysfunction.
