Sildenafil citrate, commonly prescribed for erectile dysfunction, is available in doses ranging from 25 mg to 100 mg, with 50 mg typically recommended as the standard starting dose. While some men may benefit from higher doses like 100 mg, taking more than 100 mg per day is not approved by the FDA and increases the risk of side effects such as headache, flushing, dizziness, visual disturbances, and dangerously low blood pressure.
Clinical trials have tested experimental doses as high as 150 mg and 200 mg, but these are considered off-label and have shown limited added benefit with significantly higher adverse effects. Several factors influence how much sildenafil a person should take, including age, liver or kidney function, coexisting health conditions (especially heart-related), and interactions with medications like nitrates or CYP3A4 inhibitors.
In the sections below, we break down everything you need to know about sildenafil citrate dosages, how they work, what the safe limits are, when higher doses may be considered, and the factors that determine the right dosage for you.
What Is Sildenafil Citrate?
Sildenafil citrate is a medication primarily used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). It belongs to a class of drugs known as phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors. Chemically, sildenafil is a synthetic compound that mimics the natural molecule cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and selectively inhibits the PDE5 enzyme, which is predominantly found in the corpus cavernosum of the penis and the lungs. Originally developed for angina, its use in erectile dysfunction was discovered coincidentally and approved by the FDA in 1998 under the brand name Viagra.
Sildenafil is most commonly prescribed for erectile dysfunction, helping men achieve and maintain an erection sufficient for sexual activity. It is also approved for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension, where it works by relaxing the blood vessels in the lungs to reduce blood pressure and improve exercise capacity. A study in PLOS ONE (2013) found that regular use of sildenafil fixed problems in the nitric oxide pathway that cause priapism (long-lasting, painful erections). It reduced stress in blood vessels, restored normal signaling, and brought erection frequency and duration back to normal levels.
Beyond these approved uses, sildenafil is also being researched for off-label benefits. A study in the Journal of Cellular Physiology (2007) found that sildenafil helps new blood vessels grow by boosting endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation. Potential neuroprotective effects have been discussed, although further human studies are needed to validate these findings.
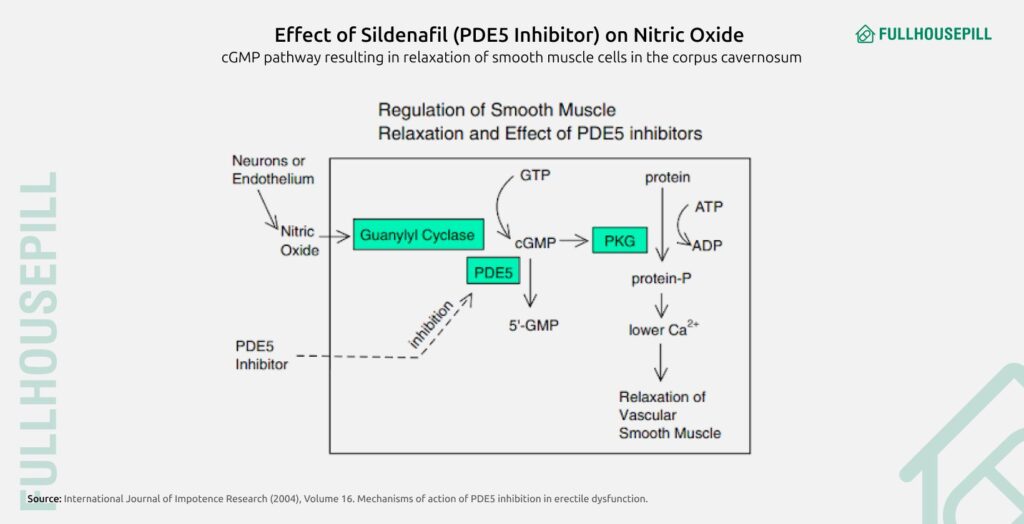
The drug works by enhancing the natural effects of nitric oxide (NO), a chemical released during sexual arousal. NO stimulates the enzyme guanylyl cyclase, leading to a rise in cGMP levels. This leads to the relaxation of smooth muscle in the corpus cavernosum, allowing increased blood flow into the penis. Normally, PDE5 breaks down cGMP, leading to a loss of erection. Sildenafil inhibits PDE5, thereby preserving cGMP levels, prolonging muscle relaxation, and improving erectile function, but only in the presence of sexual stimulation.
What Are the Available Dosage Strengths of Sildenafil?
The sildenafil citrate tablet is available in various strengths to meet different therapeutic needs and individual health conditions. These dosage forms allow healthcare providers to tailor treatment based on age, health status, and how well a person tolerates the medication. The dosage refers to the amount of active ingredient, sildenafil citrate, in each tablet.
Commonly available dosage strengths of a sildenafil citrate tablet:
- 25 mg – It is the lowest dose. It is typically prescribed for older adults or those with liver, kidney, or heart conditions.
- 50 mg – It is the usual starting dosage given to men for treating erectile dysfunction.
- 100 mg – It is the maximum recommended dose, prescribed if lower doses are ineffective and well-tolerated.
While 150 mg and 200 mg sildenafil citrate tablets are available from some sources, they are not medically recommended or officially approved. Using such high doses should only happen under strict medical supervision, if at all. The maximum safe and approved daily dose of sildenafil citrate is 100 mg. Always consult a healthcare provider before exceeding this limit.
Below is a detailed breakdown of each available (and some off-label) sildenafil citrate tablet dosage, including when it’s used, how it compares, and what to consider before taking it.
Sildenafil 25mg
Sildenafil 25 mg is the lowest available tablet strength used to treat erectile dysfunction. It delivers a milder effect than the standard 50 mg dose, making it a suitable option for men who are sensitive to medication or experience side effects at higher doses. While it may not be as potent, it is still effective for men with mild to moderate ED, especially when used under medical guidance.
This dose is typically recommended for men who are over 65, have liver or kidney impairment, or are taking medications that may interact with sildenafil (like CYP3A4 inhibitors like erythromycin or ritonavir). It’s also preferred for those with certain cardiovascular conditions, where lower doses reduce the risk of blood pressure-related side effects. In such cases, 25 mg offers a safer starting point, with the option to increase if needed.
Sildenafil 50mg
Sildenafil 50 mg is the standard recommended starting dose of sildenafil citrate tablet for treating erectile dysfunction in most men. It provides a reliable balance between efficacy and safety, improving the ability to achieve and maintain an erection during sexual activity. Clinical trials show that 50 mg is effective in a majority of patients with varying degrees of ED, regardless of the cause.
Compared to 25 mg, the 50 mg dose offers stronger and more consistent results, while having fewer side effects than the maximum 100 mg dose. It’s often the most prescribed strength because it delivers a high success rate without significantly increasing the risk of adverse events. This dose is typically recommended for adult men under 65 who are otherwise healthy and not on medications that may interact with sildenafil. It may also be prescribed after 25 mg proves insufficient or if the patient has no underlying conditions that would require starting at a lower dose. If needed and tolerated, the dose may be increased to 100 mg or decreased to 25 mg depending on response and side effects.
Sildenafil 100mg
Sildenafil 100 mg is the highest recommended dose of the sildenafil citrate tablet used for treating erectile dysfunction. It contains 100 milligrams of the active ingredient and is typically used when lower doses, like 25 mg or 50 mg, do not produce the desired effect. This strength offers the most potent response in terms of improving erection hardness, duration, and overall sexual satisfaction.
Compared to 50 mg, the 100 mg dose has been shown in clinical trials to offer higher rates of successful intercourse and greater improvements in erectile function scores (eg. IIEF). However, it is also associated with a higher incidence of side effects such as headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and dizziness.
This dose is generally recommended for men who did not respond adequately to 50 mg, provided they are otherwise healthy and do not have contraindications such as severe cardiovascular disease or medications like nitrates. It should always be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare provider to ensure safety, especially since higher doses come with a greater risk of systemic side effects.
Sildenafil 150mg
Sildenafil 150 mg is a non-standard, higher-than-recommended dose of the sildenafil citrate tablet that is not officially approved by regulatory agencies like the FDA. It is sometimes used off-label in men who do not respond adequately to the 100 mg dose but are otherwise healthy and under close medical supervision. While it is not commercially available from most major manufacturers, some pharmacies or online suppliers may offer this strength.
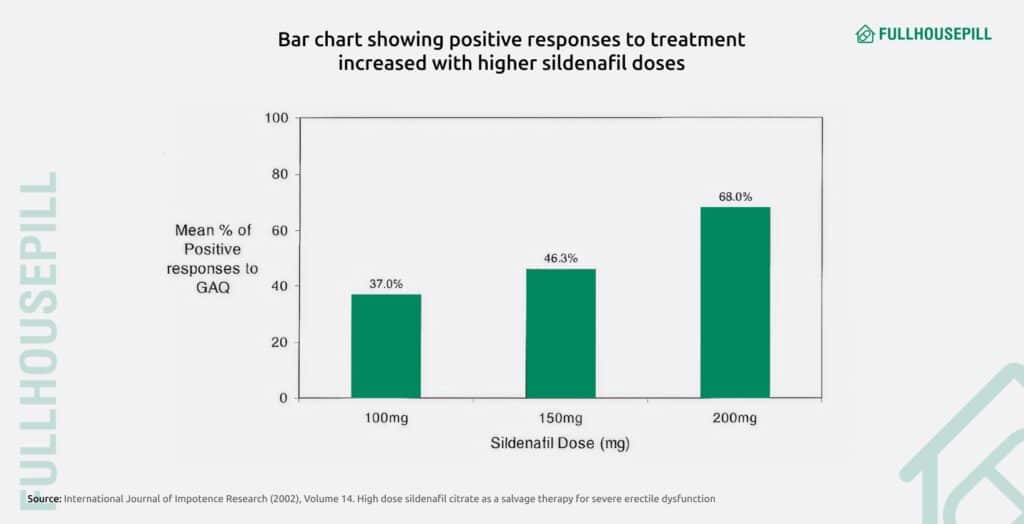
Compared to 100 mg, 150 mg may offer slightly better efficacy in men with severe erectile dysfunction or those who are non-responders to standard doses. As per a study in the International Journal of Impotence Research (2002), men with erectile dysfunction unresponsive to the standard 100 mg dose achieved satisfactory erections with a 150 mg dose of sildenafil. These responders included two men with psychogenic ED and two with arteriogenic ED. Compared to baseline and 100 mg treatment, IIEF scores improved modestly with 150 mg, and 46.3% of users at this dose reported improved erections. The side effect profile was more noticeable than at 100 mg but still tolerable for some patients.
However, the benefits are marginal and often come with a higher risk of side effects, including headaches, flushing, nasal congestion, visual disturbances, and hypotension. Clinical data on this dose are limited. It is not a first-line treatment option and should be used only with caution under medical supervision.
Sildenafil 200mg
Sildenafil 200 mg is an off-label, ultra-high dose of sildenafil citrate tablet that exceeds the maximum FDA-approved limit of 100 mg. It is not routinely prescribed and is typically used only in rare cases under strict medical supervision. Some compounding pharmacies or online suppliers may offer it, but it is not available from most major pharmaceutical manufacturers.
Compared to standard doses (25-100 mg), 200 mg does not significantly improve erectile function in most men but does increase the likelihood of side effects, including severe headache, flushing, nasal congestion, visual changes, and hypotension.
The majority of responders in the same study mentioned above earlier required a 200 mg dose to achieve erections firm enough for intercourse. This group consisted of patients with psychogenic ED, arteriogenic ED, cavernosal veno-occlusive dysfunction, and ED following prostate surgery. The IIEF score improvement was highest at 200 mg, and 68% of users at this dose reported improved erections. However, this benefit came with increased side effects; 63% reported adverse events, and 31% of responders discontinued due to issues like flushing, headache, and dyspepsia. Despite these drawbacks, 200 mg served as a successful salvage option for some severe ED cases unresponsive to lower doses.
What Is the Recommended Dosage of Sildenafil for Erectile Dysfunction?
The recommended dosage of sildenafil for erectile dysfunction is 50 mg taken orally about 30 to 60 minutes before sexual activity, once per day. Depending on effectiveness and tolerability, the dose may be increased to a maximum of 100 mg or decreased to 25 mg. The drug should not be taken more than once in 24 hours, regardless of dose.
According to the FDA-approved prescribing information and guidelines from the American Urological Association, 50 mg is the standard starting dose for most men. However, patients over 65, or those with hepatic or renal impairment, or on medications like CYP3A4 inhibitors, should start with 25 mg to reduce the risk of side effects.
A study in the International Journal of General Medicine (2013) examined men with erectile dysfunction using flexible‑dose sildenafil (starting at 50 mg and increased to 100 mg as needed). Significant improvements in erection hardness and successful intercourse were observed compared to placebo. The benefits emerged within two weeks, and men who tolerated the treatment and continued dosing showed sustained efficacy. The analysis supports sildenafil’s effectiveness in enhancing erectile function in the patient group.
What Factors Influence How Much Sildenafil You Should Take?
The appropriate sildenafil dose depends on factors such as age, overall health, other medications, and the severity of erectile dysfunction. Doctors typically start with 50 mg and adjust up to 100 mg or down to 25 mg based on individual response and tolerability to the prescribed dose.
Age plays a key role; men over 65 often process sildenafil more slowly due to reduced liver and kidney function, so they usually start at 25 mg. Underlying health conditions, like liver disease, kidney impairment, or cardiovascular issues, also require dose adjustments.
Some medicines can affect how sildenafil works in your body. Drugs that block the CYP3A4 enzyme, such as erythromycin, ketoconazole, or certain HIV medicines, can increase sildenafil levels. This means you may need a lower starting dose to avoid side effects. You should never take sildenafil with nitrate medicines like nitroglycerin or isosorbide mononitrate, which are often used for chest pain or heart problems. Mixing them can cause a sudden, dangerous drop in blood pressure because both widen blood vessels. This can be life-threatening. The FDA and medical experts strongly warn against this combination. Always talk to your doctor to find the safest dose for your health needs.
What Is the Sildenafil Dosage for the First Time?
The recommended starting dose of sildenafil for erectile dysfunction is 50 mg, taken about 1 hour before sexual activity, for most men. This initial dose provides a balanced level of effectiveness and tolerability for the average adult. It is taken with or without food, though a high-fat meal may delay its onset.
Depending on your response and side effects, the dose may be adjusted by a healthcare provider to as low as 25 mg or as high as 100 mg. Men over the age of 65 or those with liver or kidney impairment often start at 25 mg to reduce the risk of side effects. It’s important to take the medication only once in 24 hours. A study published in the International Journal of General Medicine (2013) found that 100 mg of sildenafil significantly improved erection hardness and intercourse success from the very first dose, without increasing adverse events in healthy men.
Ultimately, the ideal starting dose depends on factors like age, health status, and current medications. Men over 65, or those with liver or kidney issues, may be prescribed 25 mg initially. Regardless of dose, sildenafil should only be taken once per day and under medical supervision for safe and effective use.
What is the Maximum Safe Dosage of Sildenafil?
The maximum safe dosage of sildenafil is 100 mg once per day, taken orally approximately 30 to 60 minutes before sexual activity. This is the highest FDA-approved dose for treating erectile dysfunction and should not be exceeded under any circumstances. Increasing the dose does not enhance effectiveness but greatly raises the likelihood of side effects.
While larger doses have been tested in controlled environments, they produced more side effects, including headaches, flushing, nasal congestion, hypotension, and visual disturbances, without added benefit in erectile response. The optimal balance between safety and effectiveness was consistently found at 50 mg to 100 mg, depending on individual tolerance and health status.
According to the FDA’s official prescribing information, sildenafil should not be used more than once per day, regardless of dose, and patients with liver or kidney impairment, or those over 65, may require lower doses (eg. 25 mg). Exceeding the 100 mg daily limit increases the risk of complications such as priapism, severe hypotension, and vision or hearing loss. Always follow a doctor’s prescription and never self-adjust your dose.
To understand the boundaries of safe use, let’s explore the maximum recommended dosage of sildenafil, and what qualifies as taking too much.
How Much Sildenafil Is Too Much?
Any dose of sildenafil exceeding 100 mg in 24 hours is considered too much and is not recommended. The maximum approved dosage for erectile dysfunction is 100 mg, taken once daily. Going beyond this limit does not improve sexual performance and significantly increases the risk of serious side effects.
As per a study in Urology (2009) sildenafil (usually 50-100 mg as needed) improved erections, sexual satisfaction, and desire across all age groups, though slightly less in older men. Typical side effects included mild symptoms such as headache, facial flushing, upset stomach, blocked nose, and changes in vision, with similar rates reported in all age groups.
In rare cases, sildenafil overdose has resulted in priapism (painful erection lasting more than 4 hours), vision loss, and cardiovascular events, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions or those combining sildenafil with nitrate medications. Therefore, 100 mg is the ceiling dose, and exceeding it is unsafe and requires immediate medical attention. Always follow your doctor’s prescription to avoid overdose risks.
What Happens If You Overdose or Take Too Much Sildenafil?
Taking too much sildenafil leads to serious and potentially dangerous side effects, especially if the dose exceeds 100 mg or if multiple doses are taken within 24 hours. An overdose increases drug concentration in the bloodstream, intensifying its vasodilatory effects and risking systemic complications.

Potential side effects of a sildenafil overdose are severe headache, dizziness or fainting, flushing and nasal congestion, blurred or blue-tinted vision (cyanopsia), hypotension (low blood pressure), priapism, heart palpitations, nausea, vomiting, sudden hearing loss or tinnitus. In extreme cases, an overdose may lead to cardiovascular collapse, especially in those with pre-existing heart conditions.
If an overdose is suspected, seek immediate medical attention, especially if symptoms like chest pain, vision changes, or a prolonged erection occur. Never exceed prescribed doses, and avoid combining sildenafil with other erectile dysfunction medications or substances that lower blood pressure.
Image.:Sildenafil side-effects in the middle – linked to – severe headache, dizziness or fainting, flushing and nasal congestion, blurred or blue-tinted vision, heart palpitations, nausea, vomiting, sudden hearing loss or tinnitus. (can use the appropriate icons)
Can You Take Sildenafil Every Day?
Yes, sildenafil can be taken every day, but only under medical supervision and typically at a lower daily dose.
Daily use of sildenafil is approved and clinically supported, especially for men with erectile dysfunction who are sexually active more than twice per week. A common daily dose is 5 mg to 25 mg once daily, which is significantly lower than the as-needed dose of 50-100 mg. Daily dosing maintains steady levels of the drug in the bloodstream, potentially improving spontaneity in sexual activity, reducing performance anxiety, and improving erectile function over time.
As per a study published in the Journal of Andrology (2013), daily use of sildenafil (50 mg) for 10 weeks improved blood vessel function in men with type 2 diabetes. It increased nitric oxide availability, reduced vascular inflammation, and enhanced dilation. These findings suggest potential benefits of sildenafil beyond erectile function, including improved vascular health.
However, daily use is not suitable for everyone. It is contraindicated in patients taking nitrates or certain antihypertensives and those with severe liver or kidney impairment. Also, some users may experience persistent side effects like headache, flushing, or nasal congestion. That’s why a healthcare provider must determine if a daily regimen is appropriate based on individual health, medications, and frequency of sexual activity.
Can I Take Multiple Viagra Doses at Once or in a Day?
No, you must not take more than one dose of Viagra at a time or within 24 hours, as it increases the risk of serious side effects.
The standard recommended dose for sildenafil is 50 mg, taken once daily, approximately 30-60 minutes before sexual activity. Depending on tolerability and efficacy, the dose may be adjusted by a doctor to 25 mg or up to a maximum of 100 mg per day, but never exceeded. As per a review in Clinical Interventions in Aging (2009), sildenafil has a half-life of approximately 4 hours and reaches peak plasma levels within 30-120 minutes. While not originally intended for daily use, low daily doses (eg. 25 mg) have been explored for certain vascular or urological benefits.
Additionally, the FDA’s prescribing information for Viagra clearly states that the drug should not be taken more than once a day, regardless of dose. Attempting to take multiple pills in hopes of enhancing performance does not improve efficacy, but rather raises the likelihood of adverse effects like headaches, dizziness, indigestion, blurred vision, or, in extreme cases, priapism that requires emergency medical attention.
Can You Break or Halve Sildenafil Pills?
Yes, you can break or halve sildenafil pills, but only if they are not film-coated or modified-release tablets. Standard sildenafil tablets (like the 50 mg or 100 mg forms) are often scored and can be safely split to adjust dosage, especially when a lower dose like 25 mg is needed. Studies and prescribing guidelines support this practice as a cost-effective and flexible option for dose adjustment. But it’s important to use a proper pill cutter to ensure even division and accurate dosing.
Film-coated or generic tablets without scoring should not be split, as uneven breaking may lead to dosing errors or altered drug release. Splitting may also expose the pill’s interior to moisture, reducing effectiveness over time. Always check the packaging or consult your pharmacist or doctor before splitting any medication, including sildenafil, to ensure it’s safe and effective for your treatment plan.
How to Properly Take Sildenafil for Best Results?
Take sildenafil on an empty stomach, about 30 to 60 minutes before planned sexual activity, and limit fatty meals and alcohol for optimal results. Sexual stimulation is required for the drug to work, as it will not cause an erection on its own. The typical starting dose is 50 mg, but it can be adjusted by your doctor based on your response.
Research shows that high-fat meals delay absorption, reducing both the speed and strength of the drug’s effects. A food-effect study in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2002) gave healthy men a 100 mg oral dose of sildenafil under fasting and high‑fat meal conditions. Compared to fasting, a high‑fat meal delayed the time to peak plasma concentration by about 1 hour and reduced peak concentration by roughly 29%. Therefore, it’s best taken on an empty stomach or after a light meal.
Avoid alcohol or limit it to minimal amounts, as it interferes with blood flow and increases the risk of side effects like dizziness or low blood pressure. For consistent effectiveness, don’t combine sildenafil with nitrate medications or use more than one dose per day. Always follow your doctor’s instructions for safe and tailored dosing.
How does sildenafil compare with other ED medications?
Sildenafil tablet is one of the most commonly prescribed PDE5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction. It works by increasing blood flow to the penis, similar to tadalafil, vardenafil, and avanafil. The main differences are in onset, duration, and patient preference. Sildenafil usually works within 30–60 minutes and lasts about 4–6 hours. Tadalafil lasts up to 36 hours, while vardenafil has a similar duration to sildenafil but may have a slightly quicker onset. Avanafil acts fastest but for a shorter duration. The choice often depends on timing needs, side effect tolerance, and how frequently sexual activity is expected.
What is the dosage difference between tadalafil and sildenafil?
Both drugs treat erectile dysfunction, but they are dosed differently due to their duration. Tadalafil vs sildenafil dosage guidelines show that sildenafil is usually taken in 25 mg, 50 mg, or 100 mg strengths about an hour before sex, while tadalafil is taken as a 10 mg or 20 mg dose before sex or as a lower daily dose of 2.5 mg or 5 mg. Tadalafil’s long half-life allows for more flexibility, while sildenafil is intended for shorter windows of activity. The correct dosage for either drug should be decided by a healthcare provider based on individual needs.
What is the dosage difference between vardenafil and sildenafil?
Vardenafil and sildenafil are both PDE5 inhibitors that improve erectile function, but their dosing differs slightly. Vardenafil vs sildenafil dosage comparisons show that sildenafil comes in 25 mg, 50 mg, and 100 mg strengths, typically taken 30–60 minutes before sexual activity. Vardenafil is available in 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg doses and is usually taken about 30–60 minutes before sex. Both can be taken with or without food, though high-fat meals may delay sildenafil’s effect more noticeably. The choice between them often depends on individual response, side effect tolerance, and how quickly the onset of action is needed.
How long does sildenafil last before it expires?
Unopened sildenafil usually remains effective until the expiration date printed on its packaging, which is often 2–3 years from the manufacturing date. Once opened, storage conditions can influence how long sildenafil expires after the listed date. Exposure to heat, light, or moisture can degrade the active ingredient faster, reducing potency. Even if expired sildenafil is not harmful, it may not provide the intended results. To maintain effectiveness, tablets should be stored in a cool, dry place in their original packaging. For safe use, expired medication should be replaced with a fresh prescription from a healthcare provider.